 |
PDBsum entry 5wg4

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Transferase/signaling protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
5wg4
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 621 a.a.
621 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 339 a.a.
339 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 59 a.a.
59 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase/signaling protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Human grk2 in complex with gbetagamma subunits and ccg257284
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1. Chain: a. Synonym: beta-ark-1,g-protein coupled receptor kinase 2. Engineered: yes. Guanine nucleotide-binding protein g(i)/g(s)/g(t) subunit beta-1. Chain: b. Synonym: transducin beta chain 1. Engineered: yes.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: grk2, adrbk1, bark, bark1. Expressed in: trichoplusia. Expression_system_taxid: 7110. Bos taurus. Bovine. Organism_taxid: 9913.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.31Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.235
|
R-free:
|
0.279
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.Bouley,J.J.G.Tesmer
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
R.Bouley
et al.
(2017).
Structural Determinants Influencing the Potency and Selectivity of Indazole-Paroxetine Hybrid G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 Inhibitors.
Mol Pharmacol,
92,
707-717.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-Jul-17
|
Release date:
|
27-Dec-17
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P25098
(ARBK1_HUMAN) -
Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
689 a.a.
621 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain A:
E.C.2.7.11.15
- [beta-adrenergic-receptor] kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[beta-adrenergic receptor] + ATP = [beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate + ADP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
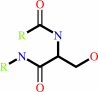 [beta-adrenergic receptor]
[beta-adrenergic receptor]
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
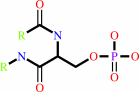 [beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate
[beta-adrenergic receptor]-phosphate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Mol Pharmacol
92:707-717
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural Determinants Influencing the Potency and Selectivity of Indazole-Paroxetine Hybrid G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 Inhibitors.
|
|
R.Bouley,
H.V.Waldschmidt,
M.C.Cato,
A.Cannavo,
J.Song,
J.Y.Cheung,
X.Q.Yao,
W.J.Koch,
S.D.Larsen,
J.J.G.Tesmer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs) phosphorylate activated receptors to
promote arrestin binding, decoupling from heterotrimeric G proteins, and
internalization. GRK2 and GRK5 are overexpressed in the failing heart and thus
have become therapeutic targets. Previously, we discovered two classes of
GRK2-selective inhibitors, one stemming from GSK180736A, a Rho-associated
coiled-coil containing kinase 1 (ROCK1) inhibitor, the other from paroxetine, a
selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor. These two classes of compounds bind to
the GRK2 active site in a similar configuration but contain different
hinge-binding "warheads": indazole and benzodioxole, respectively. We
surmised from our prior studies that an indazole would be the stronger hinge
binder and would impart increased potency when substituted for benzodioxole in
paroxetine derivatives. To test this hypothesis, we synthesized a series of
hybrid compounds that allowed us to compare the effects of inhibitors that
differ only in the identity of the warhead. The indazole-paroxetine analogs were
indeed more potent than their respective benzodioxole derivatives but lost
selectivity. To investigate how these two warheads dictate selectivity, we
determined the crystal structures of three of the indazole hybrid compounds
(CCG224061, CCG257284, and CCG258748) in complex with
GRK2-GβγComparison of these structures with those of analogous
benzodioxole-containing complexes confirmed that the indazole-paroxetine hybrids
form stronger interactions with the hinge of the kinase but also stabilize a
distinct conformation of the kinase domain of GRK2 compared with previous
complexes with paroxetine analogs. This conformation is analogous to one that
can be assumed by GRK5, at least partially explaining the loss in selectivity.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |

