 |
PDBsum entry 4zvx

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zvx
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.3
- aldehyde dehydrogenase (NAD(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an aldehyde + NAD+ + H2O = a carboxylate + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
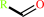 aldehyde
aldehyde
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
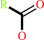 carboxylate
carboxylate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.31
- L-aminoadipate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
(S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate + NADP+ + H2O = L-2-aminoadipate + NADPH + 2 H+
|
|
2.
|
(S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate + NAD+ + H2O = L-2-aminoadipate + NADH + 2 H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
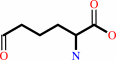 (S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
(S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
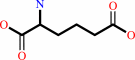 L-2-aminoadipate
L-2-aminoadipate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 (S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
(S)-2-amino-6-oxohexanoate
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
 L-2-aminoadipate
L-2-aminoadipate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.8
- betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
betaine aldehyde + NAD+ + H2O = glycine betaine + NADH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
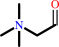 betaine aldehyde
betaine aldehyde
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
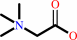 glycine betaine
glycine betaine
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
54:5513-5522
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural Basis of Substrate Recognition by Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 7A1.
|
|
M.Luo,
J.J.Tanner.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 7A1 (ALDH7A1) is part of lysine catabolism and catalyzes
the NAD(+)-dependent oxidation of α-aminoadipate semialdehyde to
α-aminoadipate. Herein, we describe a structural study of human ALDH7A1 focused
on substrate recognition. Five crystal structures and small-angle X-ray
scattering data are reported, including the first crystal structure of any ALDH7
family member complexed with α-aminoadipate. The product binds with the
ε-carboxylate in the oxyanion hole, the aliphatic chain packed into an aromatic
box, and the distal end of the product anchored by electrostatic interactions
with five conserved residues. This binding mode resembles that of glutamate
bound to the proline catabolic enzyme ALDH4A1. Analysis of ALDH7A1 and ALDH4A1
structures suggests key interactions that underlie substrate discrimination.
Structures of apo ALDH7A1 reveal dramatic conformational differences from the
product complex. Product binding is associated with a 16 Å movement of the
C-terminus into the active site, which stabilizes the active conformation of the
aldehyde substrate anchor loop. The fact that the C-terminus is part of the
active site was hitherto unknown. Interestingly, the C-terminus and aldehyde
anchor loop are disordered in a new tetragonal crystal form of the apoenzyme,
implying that these parts of the enzyme are highly flexible. Our results suggest
that the active site of ALDH7A1 is disassembled when the aldehyde site is
vacant, and the C-terminus is a mobile element that forms quaternary structural
interactions that aid aldehyde binding. These results are relevant to the
c.1512delG genetic deletion associated with pyridoxine-dependent epilepsy, which
alters the C-terminus of ALDH7A1.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

