 |
PDBsum entry 4zki
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.2.7.13.3
- histidine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
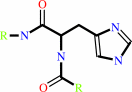 protein L-histidine
protein L-histidine
|
=
|
ADP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol
73:793-803
(2017)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Conformational dynamics of the essential sensor histidine kinase WalK.
|
|
Y.Cai,
M.Su,
A.Ahmad,
X.Hu,
J.Sang,
L.Kong,
X.Chen,
C.Wang,
J.Shuai,
A.Han.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Two-component systems (TCSs) are key elements in bacterial signal transduction
in response to environmental stresses. TCSs generally consist of sensor
histidine kinases (SKs) and their cognate response regulators (RRs). Many SKs
exhibit autokinase, phosphoryltransferase and phosphatase activities, which
regulate RR activity through a phosphorylation and dephosphorylation cycle.
However, how SKs perform different enzymatic activities is poorly understood.
Here, several crystal structures of the minimal catalytic region of WalK, an
essential SK from Lactobacillus plantarum that shares 60% sequence identity with
its homologue VicK from Streptococcus mutans, are presented. WalK adopts an
asymmetrical closed structure in the presence of ATP or ADP, in which one of the
CA domains is positioned close to the DHp domain, thus leading both the β- and
γ-phosphates of ATP/ADP to form hydrogen bonds to the ℇ- but not the
δ-nitrogen of the phosphorylatable histidine in the DHp domain. In addition,
the DHp domain in the ATP/ADP-bound state has a 25.7° asymmetrical helical
bending coordinated with the repositioning of the CA domain; these processes are
mutually exclusive and alternate in response to helicity changes that are
possibly regulated by upstream signals. In the absence of ATP or ADP, however,
WalK adopts a completely symmetric open structure with its DHp domain centred
between two outward-reaching CA domains. In summary, these structures of WalK
reveal the intrinsic dynamic properties of an SK structure as a molecular basis
for multifunctionality.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

