 |
PDBsum entry 4zjb

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase/biosynthetic protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zjb
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase/biosynthetic protein
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of (3r)-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase(fabz) in complex with holo-acp from helicobacter pylori
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase fabz. Chain: a, b. Synonym: (3r)-hydroxymyristoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase, beta-hydroxyacyl-acp dehydratase. Engineered: yes. Acyl carrier protein. Chain: g. Synonym: acp. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Helicobacter pylori. Organism_taxid: 210. Gene: fabz. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Gene: acpp, eg63_02640, hpy173_03440, hpy1786_00110, hpy1846_06495, hpy207_02635, hpy228_03880, hpy499_02145, jm68_05695.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.55Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.194
|
R-free:
|
0.231
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
L.Zhang,L.Zhang,X.Shen,H.Jiang
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
L.Zhang
et al.
(2016).
Crystal structure of FabZ-ACP complex reveals a dynamic seesaw-like catalytic mechanism of dehydratase in fatty acid biosynthesis.
Cell Res,
26,
1330-1344.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
29-Apr-15
|
Release date:
|
02-Nov-16
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.4.2.1.59
- 3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] dehydratase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (3R)-hydroxyacyl-[ACP] = a (2E)-enoyl-[ACP] + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
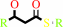 (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier protein]
(3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-[acyl-carrier protein]
|
=
|
trans-2-enoyl-[acyl- carrier protein]
|
+
|
H(2)O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Cell Res
26:1330-1344
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structure of FabZ-ACP complex reveals a dynamic seesaw-like catalytic mechanism of dehydratase in fatty acid biosynthesis.
|
|
L.Zhang,
J.Xiao,
J.Xu,
T.Fu,
Z.Cao,
L.Zhu,
H.Z.Chen,
X.Shen,
H.Jiang,
L.Zhang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Fatty acid biosynthesis (FAS) is a vital process in cells. Fatty acids are
essential for cell assembly and cellular metabolism. Abnormal FAS directly
correlates with cell growth delay and human diseases, such as metabolic
syndromes and various cancers. The FAS system utilizes an acyl carrier protein
(ACP) as a transporter to stabilize and shuttle the growing fatty acid chain
throughout enzymatic modules for stepwise catalysis. Studying the interactions
between enzymatic modules and ACP is, therefore, critical for understanding the
biological function of the FAS system. However, the information remains unclear
due to the high flexibility of ACP and its weak interaction with enzymatic
modules. We present here a 2.55 Å crystal structure of type II FAS dehydratase
FabZ in complex with holo-ACP, which exhibits a highly symmetrical FabZ
hexamer-ACP3 stoichiometry with each ACP binding to a FabZ dimer
subunit. Further structural analysis, together with biophysical and
computational results, reveals a novel dynamic seesaw-like ACP binding and
catalysis mechanism for the dehydratase module in the FAS system, which is
regulated by a critical gatekeeper residue (Tyr100 in FabZ) that manipulates the
movements of the β-sheet layer. These findings improve the general
understanding of the dehydration process in the FAS system and will potentially
facilitate drug and therapeutic design for diseases associated with
abnormalities in FAS.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

