 |
PDBsum entry 4mim
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.4.1.1
- pyruvate carboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
hydrogencarbonate + pyruvate + ATP = oxaloacetate + ADP + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 hydrogencarbonate
hydrogencarbonate
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
+
|
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 85.71% similarity
|
=
|
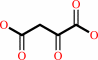 oxaloacetate
oxaloacetate
|
+
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Biotin; Mn(2+) or Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
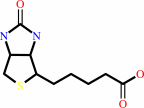 Biotin
Biotin
|
Mn(2+)
|
or
|
Zn(2+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochem Biophys Res Commun
441:377-382
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Insights into the carboxyltransferase reaction of pyruvate carboxylase from the structures of bound product and intermediate analogs.
|
|
A.D.Lietzan,
M.St Maurice.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Pyruvate carboxylase (PC) is a biotin-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the MgATP-
and bicarbonate-dependent carboxylation of pyruvate to oxaloacetate, an
important anaplerotic reaction in central metabolism. The carboxyltransferase
(CT) domain of PC catalyzes the transfer of a carboxyl group from carboxybiotin
to the accepting substrate, pyruvate. It has been hypothesized that the reactive
enolpyruvate intermediate is stabilized through a bidentate interaction with the
metal ion in the CT domain active site. Whereas bidentate ligands are commonly
observed in enzymes catalyzing reactions proceeding through an enolpyruvate
intermediate, no bidentate interaction has yet been observed in the CT domain of
PC. Here, we report three X-ray crystal structures of the Rhizobium etli PC CT
domain with the bound inhibitors oxalate, 3-hydroxypyruvate, and
3-bromopyruvate. Oxalate, a stereoelectronic mimic of the enolpyruvate
intermediate, does not interact directly with the metal ion. Instead, oxalate is
buried in a pocket formed by several positively charged amino acid residues and
the metal ion. Furthermore, both 3-hydroxypyruvate and 3-bromopyruvate, analogs
of the reaction product oxaloacetate, bind in an identical manner to oxalate
suggesting that the substrate maintains its orientation in the active site
throughout catalysis. Together, these structures indicate that the substrates,
products and intermediates in the PC-catalyzed reaction are not oriented in the
active site as previously assumed. The absence of a bidentate interaction with
the active site metal appears to be a unique mechanistic feature among the small
group of biotin-dependent enzymes that act on α-keto acid substrates.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

