 |
PDBsum entry 4jaw
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.2.1.140
- lacto-N-biosidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-D-Glc + H2O = beta-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine + lactose
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
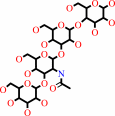 beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-D-Glc
beta-D-Gal-(1->3)-beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->3)-beta-D-Gal-(1->4)-D-Glc
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
beta-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
|
+
|
lactose
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 47.83% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
288:11795-11806
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of a glycoside hydrolase family 20 lacto-N-biosidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum.
|
|
T.Ito,
T.Katayama,
M.Hattie,
H.Sakurama,
J.Wada,
R.Suzuki,
H.Ashida,
T.Wakagi,
K.Yamamoto,
K.A.Stubbs,
S.Fushinobu.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Human milk oligosaccharides contain a large variety of oligosaccharides, of
which lacto-N-biose I (Gal-β1,3-GlcNAc; LNB) predominates as a major core
structure. A unique metabolic pathway specific for LNB has recently been
identified in the human commensal bifidobacteria. Several strains of infant
gut-associated bifidobacteria possess lacto-N-biosidase, a membrane-anchored
extracellular enzyme, that liberates LNB from the nonreducing end of human milk
oligosaccharides and plays a key role in the metabolic pathway of these
compounds. Lacto-N-biosidase belongs to the glycoside hydrolase family 20, and
its reaction proceeds via a substrate-assisted catalytic mechanism. Several
crystal structures of GH20 β-N-acetylhexosaminidases, which release
monosaccharide GlcNAc from its substrate, have been determined, but to date, a
structure of lacto-N-biosidase is unknown. Here, we have determined the first
three-dimensional structures of lacto-N-biosidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum
JCM1254 in complex with LNB and LNB-thiazoline (Gal-β1,3-GlcNAc-thiazoline) at
1.8-Å resolution. Lacto-N-biosidase consists of three domains, and the
C-terminal domain has a unique β-trefoil-like fold. Compared with other
β-N-acetylhexosaminidases, lacto-N-biosidase has a wide substrate-binding
pocket with a -2 subsite specific for β-1,3-linked Gal, and the residues
responsible for Gal recognition were identified. The bound ligands are
recognized by extensive hydrogen bonds at all of their hydroxyls consistent with
the enzyme's strict substrate specificity for the LNB moiety. The GlcNAc sugar
ring of LNB is in a distorted conformation near (4)E, whereas that of
LNB-thiazoline is in a (4)C1 conformation. A possible conformational pathway for
the lacto-N-biosidase reaction is discussed.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

