 |
PDBsum entry 4f0x
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of human malonyl-coa decarboxylase (peroxisomal isoform)
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Malonyl-coa decarboxylase, mitochondrial. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Synonym: mcd. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Gene: dcylm, mlycd. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.29Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.246
|
R-free:
|
0.267
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
D.Aparicio,R.Perez,I.Fita
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
D.Aparicio
et al.
(2013).
Structural asymmetry and disulfide bridges among subunits modulate the activity of human malonyl-CoA decarboxylase.
J Biol Chem,
288,
11907-11919.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
05-May-12
|
Release date:
|
20-Mar-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O95822
(DCMC_HUMAN) -
Malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, mitochondrial from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
493 a.a.
456 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 1 residue position (black
cross)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.9
- malonyl-CoA decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
malonyl-CoA + H+ = acetyl-CoA + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
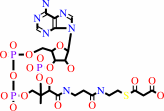 malonyl-CoA
malonyl-CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
acetyl-CoA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 45.10% similarity
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
288:11907-11919
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural asymmetry and disulfide bridges among subunits modulate the activity of human malonyl-CoA decarboxylase.
|
|
D.Aparicio,
R.Pérez-Luque,
X.Carpena,
M.Díaz,
J.C.Ferrer,
P.C.Loewen,
I.Fita.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA by malonyl-CoA decarboxylase (MCD;
EC 4.1.1.9) is an essential facet in the regulation of fatty acid metabolism.
The structure of human peroxisomal MCD reveals a molecular tetramer that is best
described as a dimer of structural heterodimers, in which the two subunits
present markedly different conformations. This molecular organization is
consistent with half-of-the-sites reactivity. Each subunit has an all-helix
N-terminal domain and a catalytic C-terminal domain with an acetyltransferase
fold (GNAT superfamily). Intersubunit disulfide bridges, Cys-206-Cys-206 and
Cys-243-Cys-243, can link the four subunits of the tetramer, imparting positive
cooperativity to the catalytic process. The combination of a half-of-the-sites
mechanism within each structural heterodimer and positive cooperativity in the
tetramer produces a complex regulatory picture that is further complicated by
the multiple intracellular locations of the enzyme. Transport into the
peroxisome has been investigated by docking human MCD onto the peroxisomal
import protein peroxin 5, which revealed interactions that extend beyond the
C-terminal targeting motif.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

