 |
PDBsum entry 4bbz
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Hydrolase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of human butyrylcholinesterase inhibited by cbdp (2-min soak): cresyl-phosphoserine adduct
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Cholinesterase. Chain: a. Fragment: catalytic domain, residues 29-557. Synonym: acylcholine acylhydrolase, butyrylcholine esterase, choline esterase ii, pseudocholinesterase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Other_details: cresyl-phosphate adduct on s198
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: cricetulus griseus. Expression_system_taxid: 10029. Expression_system_cell_line: cho-k1.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.70Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.169
|
R-free:
|
0.225
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
E.Carletti,J.-P.Colletier,L.M.Schopfer,G.Santoni,P.Masson, O.Lockridge,F.Nachon,M.Weik
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
E.Carletti
et al.
(2013).
Inhibition pathways of the potent organophosphate CBDP with cholinesterases revealed by X-ray crystallographic snapshots and mass spectrometry.
Chem Res Toxicol,
26,
280-289.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
30-Sep-12
|
Release date:
|
06-Feb-13
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P06276
(CHLE_HUMAN) -
Cholinesterase from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
602 a.a.
527 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 3 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.1.1.8
- cholinesterase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an acylcholine + H2O = a carboxylate + choline + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 acylcholine
acylcholine
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
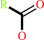 carboxylate
carboxylate
|
+
|
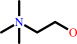 choline
choline
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Chem Res Toxicol
26:280-289
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Inhibition pathways of the potent organophosphate CBDP with cholinesterases revealed by X-ray crystallographic snapshots and mass spectrometry.
|
|
E.Carletti,
J.P.Colletier,
L.M.Schopfer,
G.Santoni,
P.Masson,
O.Lockridge,
F.Nachon,
M.Weik.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Tri-o-cresyl-phosphate (TOCP) is a common additive in jet engine lubricants and
hydraulic fluids suspected to have a role in aerotoxic syndrome in humans. TOCP
is metabolized to cresyl saligenin phosphate (CBDP), a potent irreversible
inhibitor of butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), a natural bioscavenger present in the
bloodstream, and acetylcholinesterase (AChE), the off-switch at cholinergic
synapses. Mechanistic details of cholinesterase (ChE) inhibition have, however,
remained elusive. Also, the inhibition of AChE by CBDP is unexpected, from a
structural standpoint, i.e., considering the narrowness of AChE active site and
the bulkiness of CBDP. In the following, we report on kinetic X-ray
crystallography experiments that provided 2.7-3.3 Å snapshots of the reaction
of CBDP with mouse AChE and human BChE. The series of crystallographic snapshots
reveals that AChE and BChE react with the opposite enantiomers and that an
induced-fit rearrangement of Phe297 enlarges the active site of AChE upon CBDP
binding. Mass spectrometry analysis of aging in either H(2)(16)O or H(2)(18)O
furthermore allowed us to identify the inhibition steps, in which water
molecules are involved, thus providing insights into the mechanistic details of
inhibition. X-ray crystallography and mass spectrometry show the formation of an
aged end product formed in both AChE and BChE that cannot be reactivated by
current oxime-based therapeutics. Our study thus shows that only prophylactic
and symptomatic treatments are viable to counter the inhibition of AChE and BChE
by CBDP.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

