 |
PDBsum entry 4zs3

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Fluorescent protein/inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4zs3
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.-
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.53
- mRNA N(6)-methyladenine demethylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an N6-methyladenosine in mRNA + 2-oxoglutarate + O2 = an adenosine in mRNA + formaldehyde + succinate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-methyladenosine in mRNA
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
adenosine in mRNA
|
+
|
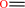 formaldehyde
formaldehyde
|
+
|
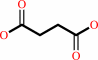 succinate
succinate
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(3+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
137:13736-13739
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Fluorescein Derivatives as Bifunctional Molecules for the Simultaneous Inhibiting and Labeling of FTO Protein.
|
|
T.Wang,
T.Hong,
Y.Huang,
H.Su,
F.Wu,
Y.Chen,
L.Wei,
W.Huang,
X.Hua,
Y.Xia,
J.Xu,
J.Gan,
B.Yuan,
Y.Feng,
X.Zhang,
C.G.Yang,
X.Zhou.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The FTO protein is unequivocally reported to play a critical role in human
obesity and in the regulation of cellular levels of m(6)A modification, which
makes FTO a significant and worthy subject of study. Here, we identified that
fluorescein derivatives can selectively inhibit FTO demethylation, and the
mechanisms behind these activities were elucidated after we determined the X-ray
crystal structures of FTO/fluorescein and FTO/5-aminofluorescein. Furthermore,
these inhibitors can also be applied to the direct labeling and enrichment of
FTO protein combined with photoaffinity labeling assay.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

