 |
PDBsum entry 4rcv

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4rcv
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
M. Tuberculosis 1-deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase bound to 1-deoxy-l-erythrulose
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase. Chain: a, b. Fragment: unp residues 1-389. Synonym: dxp reductoisomerase, 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase, 2-c-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate synthase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mycobacterium tuberculosis h37rv. Organism_taxid: 83332. Strain: h37rv. Gene: dxr, p425_02990, rvbd_2870c. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.29Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.176
|
R-free:
|
0.232
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.M.Gulick,C.L.Allen,S.A.Kholodar,A.S.Murkin
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
S.A.Kholodar
et al.
(2015).
The role of phosphate in a multistep enzymatic reaction: reactions of the substrate and intermediate in pieces.
J Am Chem Soc,
137,
2748-2756.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
17-Sep-14
|
Release date:
|
18-Mar-15
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P9WNS1
(DXR_MYCTU) -
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate reductoisomerase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis (strain ATCC 25618 / H37Rv)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
413 a.a.
370 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.267
- 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate + NADP+ = 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 53.85% similarity
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
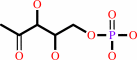 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mg(2+) or cobalt cation or Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Am Chem Soc
137:2748-2756
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The role of phosphate in a multistep enzymatic reaction: reactions of the substrate and intermediate in pieces.
|
|
S.A.Kholodar,
C.L.Allen,
A.M.Gulick,
A.S.Murkin.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Several mechanistically unrelated enzymes utilize the binding energy of their
substrate's nonreacting phosphoryl group to accelerate catalysis. Evidence for
the involvement of the phosphodianion in transition state formation has come
from reactions of the substrate in pieces, in which reaction of a truncated
substrate lacking its phosphorylmethyl group is activated by inorganic
phosphite. What has remained unknown until now is how the phosphodianion group
influences the reaction energetics at different points along the reaction
coordinate. 1-Deoxy-d-xylulose-5-phosphate (DXP) reductoisomerase (DXR), which
catalyzes the isomerization of DXP to 2-C-methyl-d-erythrose 4-phosphate (MEsP)
and subsequent NADPH-dependent reduction, presents a unique opportunity to
address this concern. Previously, we have reported the effect of covalently
linked phosphate on the energetics of DXP turnover. Through the use of
chemically synthesized MEsP and its phosphate-truncated analogue,
2-C-methyl-d-glyceraldehyde, the current study revealed a loss of 6.1 kcal/mol
of kinetic barrier stabilization upon truncation, of which 4.4 kcal/mol was
regained in the presence of phosphite dianion. The activating effect of
phosphite was accompanied by apparent tightening of its interactions within the
active site at the intermediate stage of the reaction, suggesting a role of the
phosphodianion in disfavoring intermediate release and in modulation of the
on-enzyme isomerization equilibrium. The results of kinetic isotope effect and
structural studies indicate rate limitation by physical steps when the covalent
linkage is severed. These striking differences in the energetics of the natural
reaction and the reactions in pieces provide a deeper insight into the
contribution of enzyme-phosphodianion interactions to the reaction coordinate.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

