 |
PDBsum entry 4qlb

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|



 650 a.a.
650 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 34 a.a.
34 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 33 a.a.
33 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 35 a.a.
35 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structural basis for the recruitment of glycogen synthase by glycogenin
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Probable glycogen [starch] synthase. Chain: a, c, d, b. Fragment: glycogen synthase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Protein gyg-1, isoform b. Chain: g, e, h, f. Fragment: glycogenin (residues 268-302). Engineered: yes.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Caenorhabditis elegans. Roundworm. Organism_taxid: 6239. Gene: gsy-1, y46g5a.31. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Synthetic: yes. Other_details: this sequence of gyg-1 (amino acids 268-302) occurs naturally in c. Elegans
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.180
|
R-free:
|
0.224
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
E.Zeqiraj,A.Judd,F.Sicheri
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
E.Zeqiraj
et al.
(2014).
Structural basis for the recruitment of glycogen synthase by glycogenin.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
111,
E2831.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
11-Jun-14
|
Release date:
|
09-Jul-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9U2D9
(GYS_CAEEL) -
Glycogen [starch] synthase from Caenorhabditis elegans
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
672 a.a.
650 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
H2KYQ5
(GYG1_CAEEL) -
Glycogenin-1 from Caenorhabditis elegans
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
429 a.a.
34 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
Chains A, C, D, B:
E.C.2.4.1.11
- glycogen(starch) synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Glycogen
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n) + UDP-alpha-D-glucose = [(1->4)-alpha-D- glucosyl](n+1) + UDP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[(1->4)-alpha-D-glucosyl](n)
|
+
|
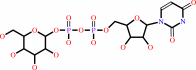 UDP-alpha-D-glucose
UDP-alpha-D-glucose
|
=
|
[(1->4)-alpha-D- glucosyl](n+1)
|
+
|
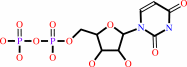 UDP
UDP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains G, E, H, F:
E.C.2.4.1.186
- glycogenin glucosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-tyrosyl-[glycogenin] + UDP-alpha-D-glucose = alpha-D-glucosyl-L- tyrosyl-[glycogenin] + UDP + H+
|
|
2.
|
[1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl](n)-L-tyrosyl-[glycogenin] + UDP-alpha-D- glucose = [1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl](n+1)-L-tyrosyl-[glycogenin] + UDP + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-tyrosyl-[glycogenin]
|
+
|
 UDP-alpha-D-glucose
UDP-alpha-D-glucose
|
=
|
alpha-D-glucosyl-L- tyrosyl-[glycogenin]
|
+
|
 UDP
UDP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl](n)-L-tyrosyl-[glycogenin]
|
+
|
 UDP-alpha-D- glucose
UDP-alpha-D- glucose
|
=
|
[1,4-alpha-D-glucosyl](n+1)-L-tyrosyl-[glycogenin]
|
+
|
 UDP
UDP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Mn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
111:E2831
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for the recruitment of glycogen synthase by glycogenin.
|
|
E.Zeqiraj,
X.Tang,
R.W.Hunter,
M.García-Rocha,
A.Judd,
M.Deak,
A.von Wilamowitz-Moellendorff,
I.Kurinov,
J.J.Guinovart,
M.Tyers,
K.Sakamoto,
F.Sicheri.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Glycogen is a primary form of energy storage in eukaryotes that is essential for
glucose homeostasis. The glycogen polymer is synthesized from glucose through
the cooperative action of glycogen synthase (GS), glycogenin (GN), and glycogen
branching enzyme and forms particles that range in size from 10 to 290 nm. GS is
regulated by allosteric activation upon glucose-6-phosphate binding and
inactivation by phosphorylation on its N- and C-terminal regulatory tails. GS
alone is incapable of starting synthesis of a glycogen particle de novo, but
instead it extends preexisting chains initiated by glycogenin. The molecular
determinants by which GS recognizes self-glucosylated GN, the first step in
glycogenesis, are unknown. We describe the crystal structure of Caenorhabditis
elegans GS in complex with a minimal GS targeting sequence in GN and show that a
34-residue region of GN binds to a conserved surface on GS that is distinct from
previously characterized allosteric and binding surfaces on the enzyme. The
interaction identified in the GS-GN costructure is required for GS-GN
interaction and for glycogen synthesis in a cell-free system and in intact
cells. The interaction of full-length GS-GN proteins is enhanced by an avidity
effect imparted by a dimeric state of GN and a tetrameric state of GS. Finally,
the structure of the N- and C-terminal regulatory tails of GS provide a basis
for understanding phosphoregulation of glycogen synthesis. These results uncover
a central molecular mechanism that governs glycogen metabolism.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| | |

