 |
PDBsum entry 4pyo
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.1.6
- catechol O-methyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a catechol + S-adenosyl-L-methionine = a guaiacol + S-adenosyl-L- homocysteine + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
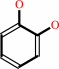 catechol
catechol
|
+
|
 S-adenosyl-L-methionine
S-adenosyl-L-methionine
|
=
|
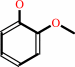 guaiacol
guaiacol
|
+
|
 S-adenosyl-L- homocysteine
S-adenosyl-L- homocysteine
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
70:2163-2174
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Mapping the conformational space accessible to catechol-O-methyltransferase.
|
|
A.Ehler,
J.Benz,
D.Schlatter,
M.G.Rudolph.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Methylation catalysed by catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) is the main pathway
of catechol neurotransmitter deactivation in the prefrontal cortex. Low levels
of this class of neurotransmitters are held to be causative of diseases such as
schizophrenia, depression and Parkinson's disease. Inhibition of COMT may
increase neurotransmitter levels, thus offering a route for treatment.
Structure-based drug design hitherto seems to be based on the closed enzyme
conformation. Here, a set of apo, semi-holo, holo and Michaelis form crystal
structures are described that define the conformational space available to COMT
and that include likely intermediates along the catalytic pathway. Domain swaps
and sizeable loop movements around the active site testify to the flexibility of
this enzyme, rendering COMT a difficult drug target. The low affinity of the
co-substrate S-adenosylmethionine and the large conformational changes involved
during catalysis highlight significant energetic investment to achieve the
closed conformation. Since each conformation of COMT is a bona fide target for
inhibitors, other states than the closed conformation may be promising to
address. Crystallographic data for an alternative avenue of COMT inhibition,
i.e. locking of the apo state by an inhibitor, are presented. The set of COMT
structures may prove to be useful for the development of novel classes of
inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

