 |
PDBsum entry 4cqm

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
4cqm
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|





 (+ 2 more)
248 a.a.
(+ 2 more)
248 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|





 (+ 2 more)
232 a.a.
(+ 2 more)
232 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of heterotetrameric human ketoacyl reductase complexed with NAD and NADP
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Estradiol 17-beta-dehydrogenase 8. Chain: a, e, h, i, l, m, p. Synonym: 17-beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 8,17-beta-hsd 8,3- oxoacyl-acyl-carrier-protein reductase, protein ke6,ke-6,really interesting new gene 2 protein, testosterone 17-beta-dehydrogenase 8, 3-ketoacyl reductase alpha subunit. Ec: 1.1.1.62, 1.1.1.239, 1.1.1.100. Engineered: yes. Carbonyl reductase family member 4.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 511693. Expression_system_variant: plyss rare.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.34Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.205
|
R-free:
|
0.236
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
R.Venkatesan,S.K.Sahteli,L.O.Awoniyi,G.Jiang,P.Prus,A.J.Kastoniotis, J.K.Hiltunen,R.K.Wierenga,Z.Chen
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
R.Venkatesan
et al.
(2014).
Insights into mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis from the structure of heterotetrameric 3-ketoacyl-ACP reductase/3R-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase.
Nat Commun,
5,
4805.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Feb-14
|
Release date:
|
10-Sep-14
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, D, E, H, I, L, M, P:
E.C.1.1.1.239
- 3alpha-(17beta)-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (NAD(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
testosterone + NAD+ = androst-4-ene-3,17-dione + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 testosterone
testosterone
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
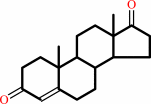 androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
androst-4-ene-3,17-dione
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, D, E, H, I, L, M, P:
E.C.1.1.1.62
- 17beta-estradiol 17-dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
17beta-estradiol + NAD+ = estrone + NADH + H+
|
|
2.
|
17beta-estradiol + NADP+ = estrone + NADPH + H+
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
NAD(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
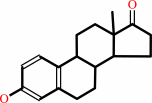 estrone
estrone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
17beta-estradiol
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
 estrone
estrone
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 4:
|
 |
Chains A, D, E, H, I, L, M, P:
E.C.1.1.1.n12
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 5:
|
 |
Chains B, C, F, G, J, K, N, O:
E.C.1.1.1.100
- 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a (3R)-hydroxyacyl-[ACP] + NADP+ = a 3-oxoacyl-[ACP] + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(3R)-hydroxyacyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
=
|
3-oxoacyl-[ACP]
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 6:
|
 |
Chains B, C, F, G, J, K, N, O:
E.C.1.6.5.10
- Nadph dehydrogenase (quinone).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a quinone + NADPH + H+ = a quinol + NADP+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
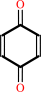 quinone
quinone
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
quinol
|
+
|
 NADP(+)
NADP(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Flavoprotein
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Commun
5:4805
(2014)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Insights into mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis from the structure of heterotetrameric 3-ketoacyl-ACP reductase/3R-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase.
|
|
R.Venkatesan,
S.K.Sah-Teli,
L.O.Awoniyi,
G.Jiang,
P.Prus,
A.J.Kastaniotis,
J.K.Hiltunen,
R.K.Wierenga,
Z.Chen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis (mtFAS) is essential for respiratory growth
in yeast and mammalian embryonic survival. The human 3-ketoacyl-acyl carrier
protein (ACP) reductase (KAR) of mtFAS is a heterotetrameric α2β2-assembly
composed of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type-8 (HSD17B8, α-subunit) and
carbonyl reductase type-4 (CBR4, β-subunit). Here we provide a structural
explanation for the stability of the heterotetramer from the crystal structure
with NAD(+) and NADP(+) bound to the HSD17B8 and CBR4 subunits, respectively,
and show that the catalytic activity of the NADPH- and ACP-dependent CBR4
subunit is crucial for a functional HsKAR. Therefore, mtFAS is NADPH- and ACP
dependent, employing the 3R-hydroxyacyl-ACP intermediate. HSD17B8 assists in the
formation of the competent HsKAR assembly. The intrinsic NAD(+)- and
CoA-dependent activity of the HSD17B8 subunit on the 3R-hydroxyacyl-CoA
intermediates may indicate a role for this subunit in routing 3R-hydroxyacyl-CoA
esters, potentially arising from the metabolism of unsaturated fatty acids, into
the mitochondrial β-oxidation pathway.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

