 |
PDBsum entry 3v1p

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase/lyase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3v1p
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase/lyase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the mutant q185a of orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase from methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum complexed with the inhibitor bmp
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: omp decarboxylase, ompdcase, ompdecase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus. Organism_taxid: 187420. Strain: delta h. Gene: pyrf, mth_129. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.37Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.166
|
R-free:
|
0.178
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.A.Fedorov,E.V.Fedorov,B.Desai,J.A.Gerlt,S.C.Almo
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
B.J.Desai
et al.
(2012).
Conformational changes in orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase: a structure-based explanation for how the 5'-phosphate group activates the enzyme.
Biochemistry,
51,
8665-8678.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
09-Dec-11
|
Release date:
|
21-Nov-12
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O26232
(PYRF_METTH) -
Orotidine 5'-phosphate decarboxylase from Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (strain ATCC 29096 / DSM 1053 / JCM 10044 / NBRC 100330 / Delta H)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
228 a.a.
220 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.1.23
- orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Pyrimidine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
orotidine 5'-phosphate + H+ = UMP + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 orotidine 5'-phosphate
orotidine 5'-phosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
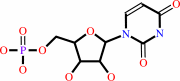 UMP
UMP
|
+
|
CO2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 95.45% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
51:8665-8678
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Conformational changes in orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase: a structure-based explanation for how the 5'-phosphate group activates the enzyme.
|
|
B.J.Desai,
B.M.Wood,
A.A.Fedorov,
E.V.Fedorov,
B.Goryanova,
T.L.Amyes,
J.P.Richard,
S.C.Almo,
J.A.Gerlt.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The binding of a ligand to orotidine 5'-monophosphate decarboxylase (OMPDC) is
accompanied by a conformational change from an open, inactive conformation
(E(o)) to a closed, active conformation (E(c)). As the substrate traverses the
reaction coordinate to form the stabilized vinyl carbanion/carbene intermediate,
interactions that destabilize the carboxylate group of the substrate and
stabilize the intermediate (in the E(c)·S(⧧) complex) are enforced. Focusing
on the OMPDC from Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus, we find the
"remote" 5'-phosphate group of the substrate activates the enzyme 2.4
× 10(8)-fold; the activation is equivalently described by an intrinsic binding
energy (IBE) of 11.4 kcal/mol. We studied residues in the activation that (1)
directly contact the 5'-phosphate group, (2) participate in a hydrophobic
cluster near the base of the active site loop that sequesters the bound
substrate from the solvent, and (3) form hydrogen bonding interactions across
the interface between the "mobile" and "fixed" half-barrel
domains of the (β/α)(8)-barrel structure. Our data support a model in which
the IBE provided by the 5'-phosphate group is used to allow interactions both
near the N-terminus of the active site loop and across the domain interface that
stabilize both the E(c)·S and E(c)·S(⧧) complexes relative to the E(o)·S
complex. The conclusion that the IBE of the 5'-phosphate group provides
stabilization to both the E(c)·S and E(c)·S(⧧) complexes, not just the
E(c)·S(⧧) complex, is central to understanding the structural origins of
enzymatic catalysis as well as the requirements for the de novo design of
enzymes that catalyze novel reactions.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

