 |
PDBsum entry 3s1c

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3s1c
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.5.99.12
- cytokinin dehydrogenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-dimethylallyladenine + A + H2O = 3-methyl-2-butenal + adenine + AH2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
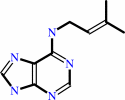 N(6)-dimethylallyladenine
N(6)-dimethylallyladenine
|
+
|
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 62.50% similarity
|
=
|
3-methyl-2-butenal
|
+
|
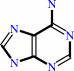 adenine
adenine
|
+
|
AH2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Febs J
283:361-377
(2016)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Kinetic and structural investigation of the cytokinin oxidase/dehydrogenase active site.
|
|
D.Kopečný,
R.Končitíková,
H.Popelka,
P.Briozzo,
A.Vigouroux,
M.Kopečná,
D.Zalabák,
M.Šebela,
J.Skopalová,
I.Frébort,
S.Moréra.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cytokinins are hormones that regulate plant development and their environmental
responses. Their levels are mainly controlled by the cytokinin
oxidase/dehydrogenase (CKO), which oxidatively cleaves cytokinins using
redox-active electron acceptors. CKO belongs to the group of flavoproteins with
an 8α-N1-histidyl FAD covalent linkage. Here, we investigated the role of seven
active site residues, H105, D169, E288, V378, E381, P427 and L492, in substrate
binding and catalysis of the CKO1 from maize (Zea mays, ZmCKO1) combining
site-directed mutagenesis with kinetics and X-ray crystallography. We identify
E381 as a key residue for enzyme specificity that restricts substrate binding as
well as quinone electron acceptor binding. We show that D169 is important for
catalysis and that H105 covalently linked to FAD maintains the enzyme's
structural integrity, stability and high rates with electron acceptors. The
L492A mutation significantly modulates the cleavage of aromatic cytokinins and
zeatin isomers. The high resolution X-ray structures of ZmCKO1 and the E381S
variant in complex with N6-(2-isopentenyl)adenosine reveal the binding mode of
cytokinin ribosides. Those of ZmCKO2 and ZmCKO4a contain a mobile domain, which
might contribute to binding of the N9 substituted cytokinins.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

