 |
PDBsum entry 3ezh

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.13.3
- histidine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
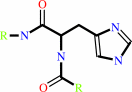 protein L-histidine
protein L-histidine
|
=
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
17:190-201
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural analysis of ligand stimulation of the histidine kinase NarX.
|
|
J.Cheung,
W.A.Hendrickson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Histidine kinase receptors are a large family of membrane-spanning proteins
found in many prokaryotes and some eukaryotes. They are a part of two-component
signal transduction systems, which each comprise a sensor kinase and a response
regulator and are involved with the regulation of many cellular processes. NarX
is a histidine kinase receptor that responds to nitrate and nitrite to effect
regulation of anaerobic respiration in various bacteria. We present
high-resolution X-ray crystal structures of the periplasmic sensor domain from
Escherichia coli NarX in a complex with nitrate and in the apo state. Our
analysis reveals that nitrate-binding induces conformation changes that result
in a piston-type displacement between the N- and C-terminal helices of the
periplasmic domain. Such conformational changes might represent a conserved
mechanism of signaling in histidine kinases by which ligand binding is
communicated across the lipid bilayer.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Comparison of NarX[S] and Tar Dimers
(A) Worm
representation of the dimeric aspartate receptor Tar, drawn in
stereo. Subunits A and B of Tar (Yeh et al., 1996) are colored
yellow and blue, respectively.
(B) Worm representation of
NarX[s1] dimers in stereo. A “Tar-like” NarX[s] dimer is
formed when subunits A (yellow) and B (blue) from
NarX[s1](NO[3]) are independently superimposed upon subunits A
and B of Tar, respectively. Subunit B from the natural NarX[s]
dimer of Figure 1 is shown in gray. The black vertical line
represents the quasi two-fold rotation axis of the observed
dimer. The red line shows the resulting axis of 9.3°
rotation that relates B subunits from the natural, observed
NarX[S]dimer and the constructed Tar-like NarX[s] dimer. In the
orientation of the molecules shown, the red rotation axis
intersects the black rotation axis and is angled approximately
30 degrees above the plane of the figure.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Figure 5. Structure of NarX[S](apo)
The overall
structure of NarX[S2] in a nitrate-free state is shown as a
ribbon diagram. Each monomer is colored individually and labeled
with the PDB chain identifier (PDB code 3EZI).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2009,
17,
190-201)
copyright 2009.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Perry,
K.Koteva,
and
G.Wright
(2011).
Receptor domains of two-component signal transduction systems.
|
| |
Mol Biosyst,
7,
1388-1398.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.D.Manson
(2011).
Not too loose, not too tight--just right. Biphasic control of the Tsr HAMP domain.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
80,
573-576.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.L.Hazelbauer,
and
W.C.Lai
(2010).
Bacterial chemoreceptors: providing enhanced features to two-component signaling.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
13,
124-132.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Maslennikov,
C.Klammt,
E.Hwang,
G.Kefala,
M.Okamura,
L.Esquivies,
K.Mörs,
C.Glaubitz,
W.Kwiatkowski,
Y.H.Jeon,
and
S.Choe
(2010).
Membrane domain structures of three classes of histidine kinase receptors by cell-free expression and rapid NMR analysis.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
10902-10907.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Cheung,
and
W.A.Hendrickson
(2010).
Sensor domains of two-component regulatory systems.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
13,
116-123.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.S.Parkinson
(2010).
Signaling mechanisms of HAMP domains in chemoreceptors and sensor kinases.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
64,
101-122.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.V.Airola,
K.J.Watts,
A.M.Bilwes,
and
B.R.Crane
(2010).
Structure of concatenated HAMP domains provides a mechanism for signal transduction.
|
| |
Structure,
18,
436-448.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.E.Carlyon,
J.L.Ryther,
R.D.VanYperen,
and
J.S.Griffitts
(2010).
FeuN, a novel modulator of two-component signalling identified in Sinorhizobium meliloti.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
77,
170-182.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Krell,
J.Lacal,
A.Busch,
H.Silva-Jiménez,
M.E.Guazzaroni,
and
J.L.Ramos
(2010).
Bacterial sensor kinases: diversity in the recognition of environmental signals.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
64,
539-559.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
V.Stewart,
and
L.L.Chen
(2010).
The S helix mediates signal transmission as a HAMP domain coiled-coil extension in the NarX nitrate sensor from Escherichia coli K-12.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
192,
734-745.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.L.Ng,
Y.Wei,
L.J.Perez,
J.Cong,
T.Long,
M.Koch,
M.F.Semmelhack,
N.S.Wingreen,
and
B.L.Bassler
(2010).
Probing bacterial transmembrane histidine kinase receptor-ligand interactions with natural and synthetic molecules.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
5575-5580.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Cheung,
M.Le-Khac,
and
W.A.Hendrickson
(2009).
Crystal structure of a histidine kinase sensor domain with similarity to periplasmic binding proteins.
|
| |
Proteins,
77,
235-241.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Falke,
and
A.H.Erbse
(2009).
The piston rises again.
|
| |
Structure,
17,
1149-1151.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Gao,
and
A.M.Stock
(2009).
Biological insights from structures of two-component proteins.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
63,
133-154.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

