 |
PDBsum entry 3e9h

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Lysyl-tRNA synthetase from bacillus stearothermophilus complexed with l-lysylsulfamoyl adenosine
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Lysyl-tRNA synthetase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: lysine--tRNA ligase, lysrs. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Bacillus stearothermophilus. Organism_taxid: 1422. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.190
|
R-free:
|
0.241
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
H.Sakurama,T.Takita,B.Mikami,T.Itoh,K.Yasukawa,K.Inouye
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
H.Sakurama
et al.
(2009).
Two crystal structures of lysyl-tRNA synthetase from Bacillus stearothermophilus in complex with lysyladenylate-like compounds: insights into the irreversible formation of the enzyme-bound adenylate of L-lysine hydroxamate.
J Biochem (tokyo),
145,
555-563.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
22-Aug-08
|
Release date:
|
14-Jul-09
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9RHV9
(SYK_GEOSE) -
Lysine--tRNA ligase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
494 a.a.
484 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.1.1.6
- lysine--tRNA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
tRNA(Lys) + L-lysine + ATP = L-lysyl-tRNA(Lys) + AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 tRNA(Lys)
tRNA(Lys)
|
+
|
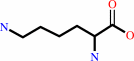 L-lysine
L-lysine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
L-lysyl-tRNA(Lys)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 52.78% similarity
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biochem (tokyo)
145:555-563
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Two crystal structures of lysyl-tRNA synthetase from Bacillus stearothermophilus in complex with lysyladenylate-like compounds: insights into the irreversible formation of the enzyme-bound adenylate of L-lysine hydroxamate.
|
|
H.Sakurama,
T.Takita,
B.Mikami,
T.Itoh,
K.Yasukawa,
K.Inouye.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase forms an enzyme-bound intermediate, aminoacyladenylate
in the amino-acid activation reaction. This reaction is monitored by measuring
the ATP-PPi exchange reason in which [(32)P]PPi is incorporated into ATP. We
previously reported that L-lysine hydroxamate completely inhibited the
L-lysine-dependent ATP-PPi exchange reaction catalysed by lysyl-tRNA synthetase
from Bacillus stearothermophilus (BsLysRS). Several experiments suggested that
BsLysRS can adenylate L-lysine hydroxamate, but the enzyme-bound
lysyladenylate-like compound does not undergo the nucleophilic attack of PPi.
This contrasts with the two reports for seryl-tRNA synthetase (SerRS): (i)
L-serine hydroxamate was utilized by yeast SerRS as a substrate in the ATP-PPi
exchange; and (ii) a seryladenylate-like compound was formed from L-serine
hydroxamate in the crystal structure of Thermus thermophilus SerRS. To gain
clues about the mechanistic difference, we have determined the crystal
structures of two complexes of BsLysRS with the adenylate of L-lysine
hydroxamate and with 5'-O-[N-(L-Lysyl)sulphamoyl] adenosine. The comparisons of
the two BsLysRS structures and the above SerRS structure revealed the specific
side-chain shift of Glu411 of BsLysRS in the complex with the adenylate of
L-lysine hydroxamate. In support of other structural comparisons, the result
suggested that Glu411 plays a key role in the arrangement of PPi for the
nucleophilic attack.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
W.W.Navarre,
S.B.Zou,
H.Roy,
J.L.Xie,
A.Savchenko,
A.Singer,
E.Edvokimova,
L.R.Prost,
R.Kumar,
M.Ibba,
and
F.C.Fang
(2010).
PoxA, yjeK, and elongation factor P coordinately modulate virulence and drug resistance in Salmonella enterica.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
39,
209-221.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

