 |
PDBsum entry 3e8a

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Lyase/lyase inhibitor
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3e8a
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 190 a.a.
190 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 188 a.a.
188 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 328 a.a.
328 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
 |
Obsolete entry |
 |
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase/lyase inhibitor
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Complex of gs-alpha with the catalytic domains of mammalian adenylyl cyclase: complex with adenosine 5-o-(l- thiophosphate) and low ca concentration
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Adenylate cyclase type 5. Chain: a. Fragment: c1a domain. Synonym: adenylate cyclase type v, atp pyrophosphate-lyase 5, adenylyl cyclase 5, ca(2+)-inhibitable adenylyl cyclase. Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Adenylate cyclase type 2. Chain: b.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Canis lupus familiaris. Dogs. Organism_taxid: 9615. Gene: adcy5, adenylyl cyclase type v. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Rattus norvegicus. Brown rat,rat,rats. Organism_taxid: 10116.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.242
|
R-free:
|
0.309
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
T.-C.Mou,S.R.Sprang
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
T.C.Mou
et al.
(2009).
Structural basis for inhibition of mammalian adenylyl cyclase by calcium.
Biochemistry,
48,
3387-3397.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Aug-08
|
Release date:
|
12-May-09
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P30803
(ADCY5_CANLF) -
Adenylate cyclase type 5 from Canis lupus familiaris
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
1265 a.a.
190 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.4.6.1.1
- adenylate cyclase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP = 3',5'-cyclic AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
ATP
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
=
|
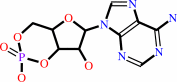 3',5'-cyclic AMP
3',5'-cyclic AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
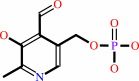 Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
48:3387-3397
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for inhibition of mammalian adenylyl cyclase by calcium.
|
|
T.C.Mou,
N.Masada,
D.M.Cooper,
S.R.Sprang.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Type V and VI mammalian adenylyl cyclases (AC5, AC6) are inhibited by Ca(2+) at
both sub- and supramicromolar concentration. This inhibition may provide
feedback in situations where cAMP promotes opening of Ca(2+) channels, allowing
fine control of cardiac contraction and rhythmicity in cardiac tissue where AC5
and AC6 predominate. Ca(2+) inhibits the soluble AC core composed of the C1
domain of AC5 (VC1) and the C2 domain of AC2 (IIC2). As observed for holo-AC5,
inhibition is biphasic, showing "high-affinity" (K(i) = approximately 0.4
microM) and "low-affinity" (K(i) = approximately 100 microM) modes of
inhibition. At micromolar concentration, Ca(2+) inhibition is nonexclusive with
respect to pyrophosphate (PP(i)), a noncompetitive inhibitor with respect to
ATP, but at >100 microM Ca(2+), inhibition appears to be exclusive with
respect to PP(i). The 3.0 A resolution structure of
Galphas.GTPgammaS/forskolin-activated VC1:IIC2 crystals soaked in the presence
of ATPalphaS and 8 microM free Ca(2+) contains a single, loosely coordinated
metal ion. ATP soaked into VC1:IIC2 crystals in the presence of 1.5 mM Ca(2+) is
not cyclized, and two calcium ions are observed in the 2.9 A resolution
structure of the complex. In both of the latter complexes VC1:IIC2 adopts the
"open", catalytically inactive conformation characteristic of the apoenzyme, in
contrast to the "closed", active conformation seen in the presence of ATP
analogues and Mg(2+) or Mn(2+). Structures of the pyrophosphate (PP(i)) complex
with 10 mM Mg(2+) (2.8 A) or 2 mM Ca(2+) (2.7 A) also adopt the open
conformation, indicating that the closed to open transition occurs after cAMP
release. In the latter complexes, Ca(2+) and Mg(2+) bind only to the
high-affinity "B" metal site associated with substrate/product stabilization.
Ca(2+) thus stabilizes the inactive conformation in both ATP- and PP(i)-bound
states.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Toyoshima,
S.Yonekura,
J.Tsueda,
and
S.Iwasawa
(2011).
Trinitrophenyl derivatives bind differently from parent adenine nucleotides to Ca2+-ATPase in the absence of Ca2+.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
108,
1833-1838.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Hyde,
B.E.Eckenroth,
B.A.Smith,
W.A.Eberley,
N.H.Heintz,
J.E.Jackman,
and
S.Doublié
(2010).
tRNA(His) guanylyltransferase (THG1), a unique 3'-5' nucleotidyl transferase, shares unexpected structural homology with canonical 5'-3' DNA polymerases.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
107,
20305-20310.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |
| |

