 |
PDBsum entry 3b5b

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.1.1.45
- thymidylate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Folate Coenzymes
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
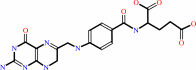
dUMP + (6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate = 7,8-dihydrofolate + dTMP
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
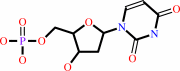 dUMP
dUMP
|
+
|
(6R)-5,10-methylene-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 86.96% similarity
|
=
|
 7,8-dihydrofolate
7,8-dihydrofolate
|
+
|
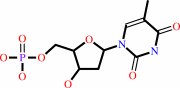 dTMP
dTMP
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Int J Biochem Cell Biol
40:2206-2217
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Role of an invariant lysine residue in folate binding on Escherichia coli thymidylate synthase: calorimetric and crystallographic analysis of the K48Q mutant.
|
|
A.A.Arvizu-Flores,
R.Sugich-Miranda,
R.Arreola,
K.D.Garcia-Orozco,
E.F.Velazquez-Contreras,
W.R.Montfort,
F.Maley,
R.R.Sotelo-Mundo.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Thymidylate synthase (TS) catalyzes the reductive methylation of deoxyuridine
monophosphate (dUMP) using methylene tetrahydrofolate (CH(2)THF) as cofactor,
the glutamate tail of which forms a water-mediated hydrogen bond with an
invariant lysine residue of this enzyme. To understand the role of this
interaction, we studied the K48Q mutant of Escherichia coli TS using structural
and biophysical methods. The k(cat) of the K48Q mutant was 430-fold lower than
wild-type TS in activity, while the K(m) for the (R)-stereoisomer of CH(2)THF
was 300 microM, about 30-fold larger than K(m) from the wild-type TS. Affinity
constants were determined using isothermal titration calorimetry, which showed
that binding was reduced by one order of magnitude for folate-like TS
inhibitors, such as propargyl-dideazafolate (PDDF) or compounds that distort the
TS active site like BW1843U89 (U89). The crystal structure of the K48Q-dUMP
complex revealed that dUMP binding is not impaired in the mutant, and that U89
in a ternary complex of K48Q-nucleotide-U89 was bound in the active site with
subtle differences relative to comparable wild-type complexes. PDDF failed to
form ternary complexes with K48Q and dUMP. Thermodynamic data correlated with
the structural determinations, since PDDF binding was dominated by enthalpic
effects while U89 had an important entropic component. In conclusion, K48 is
critical for catalysis since it leads to a productive CH(2)THF binding, while
mutation at this residue does not affect much the binding of inhibitors that do
not make contact with this group.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
R.J.Falconer,
A.Penkova,
I.Jelesarov,
and
B.M.Collins
(2010).
Survey of the year 2008: applications of isothermal titration calorimetry.
|
| |
J Mol Recognit,
23,
395-413.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

