 |
PDBsum entry 3a0x

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.13.3
- histidine kinase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
ATP + protein L-histidine = ADP + protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
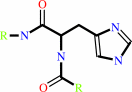 protein L-histidine
protein L-histidine
|
=
|
 ADP
ADP
|
+
|
protein N-phospho-L-histidine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
17:1333-1344
(2009)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of PAS-linked histidine kinase and the response regulator complex.
|
|
S.Yamada,
H.Sugimoto,
M.Kobayashi,
A.Ohno,
H.Nakamura,
Y.Shiro.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
We determined the structure of the complex of the sensory histidine kinase (HK)
and its cognate response regulator (RR) in the two-component signal transduction
system of Thermotoga maritima. This was accomplished by fitting the
high-resolution structures of the isolated HK domains and the RR onto the
electron density map (3.8 A resolution) of the HK/RR complex crystal. Based on
the structural information, we evaluated the roles of both interdomain and
intermolecular interactions in the signal transduction of the cytosolic
PAS-linked HK and RR system, in particular the O(2)-sensor FixL/FixJ system. The
PAS-sensor domain of HK interacts with the catalytic domain of the same
polypeptide chain by creating an interdomain beta sheet. The interaction site
between HK and RR, which was confirmed by NMR, is suitable for the
intermolecular transfer reaction of the phosphoryl group, indicating that the
observed interaction is important for the phosphatase activity of HK that
dephosphorylates phospho-RR.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Structural Comparison of the PAS Domain of ThkA and
the PAS-Sensor Domain of FixL
(A) Structure of the PAS
domain of ThkA.
(B) In the FixL PAS domain, the structures
of the oxy (red) and deoxy (gray) forms are superimposed. The
heme in FixL is shown as a stick model.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Construction of the Structure of the ThkA/TrrA
Complex
(A) Electron density (final 2F[o] − F[c] map) of
the 2:2 complex at 3.8 Å resolution. Red spheres are the
anomalous differences Fourier maps (3.5 σ) of either Hg or Se
atoms obtained from the crystal of Hg-SeMet-ThkA
(F486M,F489M,H546M)/SeMet-TrrA(D52M,L89M) (see Table S5).
(B) The map (A) is viewed along a two-fold axis and the map is
represented as a grid.
(C) The overall ThkA/TrrA complex in
the 2:2 dimer. The view is the same as in (A).
(D) The
structure viewed along a two-fold axis.
(E–H) Qualities
of the fitting into the map (2F[o] − F[c] map contoured at 1
σ) for the PAS domain of ThkA (E), DHp of ThkA (F), CA of ThkA
(G), and TrrA (H).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2009,
17,
1333-1344)
copyright 2009.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.D.Gutu,
K.J.Wayne,
L.T.Sham,
and
M.E.Winkler
(2010).
Kinetic characterization of the WalRKSpn (VicRK) two-component system of Streptococcus pneumoniae: dependence of WalKSpn (VicK) phosphatase activity on its PAS domain.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
192,
2346-2358.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Möglich,
and
K.Moffat
(2010).
Engineered photoreceptors as novel optogenetic tools.
|
| |
Photochem Photobiol Sci,
9,
1286-1300.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Szurmant,
and
J.A.Hoch
(2010).
Interaction fidelity in two-component signaling.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
13,
190-197.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.L.López-Redondo,
F.Moronta,
P.Salinas,
J.Espinosa,
R.Cantos,
R.Dixon,
A.Marina,
and
A.Contreras
(2010).
Environmental control of phosphorylation pathways in a branched two-component system.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
78,
475-489.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.C.Stewart
(2010).
Protein histidine kinases: assembly of active sites and their regulation in signaling pathways.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
13,
133-141.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Krell,
J.Lacal,
A.Busch,
H.Silva-Jiménez,
M.E.Guazzaroni,
and
J.L.Ramos
(2010).
Bacterial sensor kinases: diversity in the recognition of environmental signals.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
64,
539-559.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Yamashita
(2010).
[Recent studies on gas sensors, CooA, FixL, and Dos].
|
| |
Yakugaku Zasshi,
130,
1181-1187.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

