 |
PDBsum entry 3vth
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.3.6.1.7
- acylphosphatase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an acyl phosphate + H2O = a carboxylate + phosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
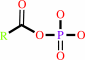 acyl phosphate
acyl phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
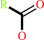 carboxylate
carboxylate
|
+
|
phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B:
E.C.6.2.-.-
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Biol Chem
287:28409-28419
(2012)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for the reaction mechanism of S-carbamoylation of HypE by HypF in the maturation of [NiFe]-hydrogenases.
|
|
Y.Shomura,
Y.Higuchi.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
As a remarkable structural feature of hydrogenase active sites,
[NiFe]-hydrogenases harbor one carbonyl and two cyano ligands, where HypE and
HypF are involved in the biosynthesis of the nitrile group as a precursor of the
cyano groups. HypF catalyzes S-carbamoylation of the C-terminal cysteine of HypE
via three steps using carbamoylphosphate and ATP, producing two unstable
intermediates: carbamate and carbamoyladenylate. Although the crystal structures
of intact HypE homodimers and partial HypF have been reported, it remains
unclear how the consecutive reactions occur without the loss of unstable
intermediates during the proposed reaction scheme. Here we report the crystal
structures of full-length HypF both alone and in complex with HypE at
resolutions of 2.0 and 2.6 Å, respectively. Three catalytic sites of the
structures of the HypF nucleotide- and phosphate-bound forms have been
identified, with each site connected via channels inside the protein. This
finding suggests that the first two consecutive reactions occur without the
release of carbamate or carbamoyladenylate from the enzyme. The structure of
HypF in complex with HypE revealed that HypF can associate with HypE without
disturbing its homodimeric interaction and that the binding manner allows the
C-terminal Cys-351 of HypE to access the S-carbamoylation active site in HypF,
suggesting that the third step can also proceed without the release of
carbamoyladenylate. A comparison of the structure of HypF with the recently
reported structures of O-carbamoyltransferase revealed different reaction
mechanisms for carbamoyladenylate synthesis and a similar reaction mechanism for
carbamoyltransfer to produce the carbamoyl-HypE molecule.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

