 |
PDBsum entry 3fpc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3fpc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Chimera of alcohol dehydrogenase by exchange of the cofactor binding domain res 153-294 of t. Brockii adh by e. Histolytica adh
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
NADP-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Engineered: yes. Other_details: chimera of alcohol dehydrogenase by exchange of cofactor binding domain res 153-294 of thermoanaerobacter brockii by entamoeba histolytica
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Thermoanaerobacter brockii, entamoeba histolytica. Thermoanaerobium brockii. Organism_taxid: 29323, 5759. Gene: adh1, adh1. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.118
|
R-free:
|
0.155
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
F.Felix,E.Goihberg,L.Shimon,Y.Burstein
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
E.Goihberg
et al.
(2010).
Biochemical and structural properties of chimeras constructed by exchange of cofactor-binding domains in alcohol dehydrogenases from thermophilic and mesophilic microorganisms.
Biochemistry,
49,
1943-1953.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
05-Jan-09
|
Release date:
|
19-Jan-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.1.1.80
- isopropanol dehydrogenase (NADP(+)).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
propan-2-ol + NADP+ = acetone + NADPH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
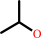 propan-2-ol
propan-2-ol
|
+
|
NADP(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 60.00% similarity
|
=
|
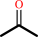 acetone
acetone
|
+
|
 NADPH
NADPH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
49:1943-1953
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Biochemical and structural properties of chimeras constructed by exchange of cofactor-binding domains in alcohol dehydrogenases from thermophilic and mesophilic microorganisms.
|
|
E.Goihberg,
M.Peretz,
S.Tel-Or,
O.Dym,
L.Shimon,
F.Frolow,
Y.Burstein.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The cofactor-binding domains (residues 153-295) of the alcohol dehydrogenases
from the thermophile Thermoanaerobacter brockii (TbADH), the mesophilic
bacterium Clostridium beijerinckii (CbADH), and the protozoan parasite Entamoeba
histolytica (EhADH1) have been exchanged. Three chimeras have been constructed.
In the first chimera, the cofactor-binding domain of thermophilic TbADH was
replaced with the cofactor-binding domain of its mesophilic counterpart CbADH
[chimera Chi21((TCT))]. This domain exchange significantly destabilized the
parent thermophilic enzyme (DeltaT(1/2) = -18 degrees C). The reverse exchange
in CbADH [chimera Chi22((CTC))], however, had little effect on the thermal
stability of the parent mesophilic protein. Furthermore, substituting the
cofactor-binding domain of TbADH with the homologous domain of EhADH1 [chimera
Chi23((TET))] substantially reduced the thermal stability of the thermophilic
ADH (DeltaT(1/2) = -51 degrees C) and impeded the oligomerization of the enzyme.
All three chimeric proteins and one of their site-directed mutants were
crystallized, and their three-dimensional (3D) structures were determined.
Comparison of the 3D structures of the chimeras and the chimeric mutant with the
structures of their parent ADHs showed no significant changes to their Calpha
chains, suggesting that the difference in the thermal stability of the three
parent ADHs and their chimeric mutants could be due to a limited number of
substitutions located at strategic positions, mainly at the oligomerization
interfaces. Indeed, stabilization of the chimeras was achieved, to a significant
extent, either by introduction of a proline residue at a strategic position in
the major horse liver ADH-type dimerization interface (DeltaT(1/2) = 35 degrees
C) or by introduction of intersubunit electrostatic interactions (DeltaT(1/2) =
6 degrees C).

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

