 |
PDBsum entry 3d2d

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3d2d
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.21.3.3
- reticuline oxidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Stylopine biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(S)-reticuline + O2 = (S)-scoulerine + H2O2 + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
(S)-reticuline
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
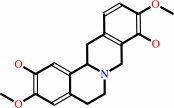 (S)-scoulerine
(S)-scoulerine
|
+
|
 H2O2
H2O2
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FAD
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
FAD
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
FAD)
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Nat Chem Biol
4:739-741
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A concerted mechanism for berberine bridge enzyme.
|
|
A.Winkler,
A.Lyskowski,
S.Riedl,
M.Puhl,
T.M.Kutchan,
P.Macheroux,
K.Gruber.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Berberine bridge enzyme catalyzes the conversion of (S)-reticuline to
(S)-scoulerine by formation of a carbon-carbon bond between the N-methyl group
and the phenolic ring. We elucidated the structure of berberine bridge enzyme
from Eschscholzia californica and determined the kinetic rates for three active
site protein variants. Here we propose a catalytic mechanism combining
base-catalyzed proton abstraction with concerted carbon-carbon coupling
accompanied by hydride transfer from the N-methyl group to the N5 atom of the
FAD cofactor.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
(a) Overall reaction catalyzed by BBE^1 (Enzyme Commission
number 1.21.3.3). (b) Schematic representation of the protein
structure. The N-terminal FAD-binding subdomains are shown in
blue and green (including the C-terminal  -helical
stretch in light green), and the central substrate binding
domain is shown in magenta. N-linked sugar residues (blue) and
the FAD cofactor (orange) are represented as stick models. The
amino acids involved in the bicovalent linkage of FAD are shown
in green. (c) Active site environments of the structures from
the monoclinic crystals showing polar amino acids as dark green
stick models. Alternate conformations were observed for Glu417.
The flavin cofactor is shown in orange with its dual mode of
attachment to the protein backbone via His104 and Cys166
represented in green. (d) Interactions between the substrate and
active site amino acids (green). The substrate is shown in
yellow, and FAD is shown in orange. Distances are indicated in
Å. -helical
stretch in light green), and the central substrate binding
domain is shown in magenta. N-linked sugar residues (blue) and
the FAD cofactor (orange) are represented as stick models. The
amino acids involved in the bicovalent linkage of FAD are shown
in green. (c) Active site environments of the structures from
the monoclinic crystals showing polar amino acids as dark green
stick models. Alternate conformations were observed for Glu417.
The flavin cofactor is shown in orange with its dual mode of
attachment to the protein backbone via His104 and Cys166
represented in green. (d) Interactions between the substrate and
active site amino acids (green). The substrate is shown in
yellow, and FAD is shown in orange. Distances are indicated in
Å.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Macmillan Publishers Ltd:
Nat Chem Biol
(2008,
4,
739-741)
copyright 2008.
|
|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.K.Sydor,
S.M.Barry,
O.M.Odulate,
F.Barona-Gomez,
S.W.Haynes,
C.Corre,
L.Song,
and
G.L.Challis
(2011).
Regio- and stereodivergent antibiotic oxidative carbocyclizations catalysed by Rieske oxygenase-like enzymes.
|
| |
Nat Chem,
3,
388-392.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.C.Liu,
Y.S.Li,
S.Y.Lyu,
L.J.Hsu,
Y.H.Chen,
Y.T.Huang,
H.C.Chan,
C.J.Huang,
G.H.Chen,
C.C.Chou,
M.D.Tsai,
and
T.L.Li
(2011).
Interception of teicoplanin oxidation intermediates yields new antimicrobial scaffolds.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
7,
304-309.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Winkler,
K.Motz,
S.Riedl,
M.Puhl,
P.Macheroux,
and
K.Gruber
(2009).
Structural and mechanistic studies reveal the functional role of bicovalent flavinylation in berberine bridge enzyme.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
19993-20001.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.P.Heuts,
N.S.Scrutton,
W.S.McIntire,
and
M.W.Fraaije
(2009).
What's in a covalent bond? On the role and formation of covalently bound flavin cofactors.
|
| |
FEBS J,
276,
3405-3427.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.W.Fraaije,
and
A.Mattevi
(2008).
Cyclization in concert.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
4,
719-721.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

