 |
PDBsum entry 3cd0

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
3cd0
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.1.1.1.34
- hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Mevalonate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(R)-mevalonate + 2 NADP+ + CoA = (3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA + 2 NADPH + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
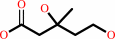 (R)-mevalonate
(R)-mevalonate
|
+
|
 2
×
NADP(+)
2
×
NADP(+)
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
=
|
(3S)-3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA
|
+
|
 2
×
NADPH
2
×
NADPH
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
J Med Chem
51:3804-3813
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Thermodynamic and structure guided design of statin based inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase.
|
|
R.W.Sarver,
E.Bills,
G.Bolton,
L.D.Bratton,
N.L.Caspers,
J.B.Dunbar,
M.S.Harris,
R.H.Hutchings,
R.M.Kennedy,
S.D.Larsen,
A.Pavlovsky,
J.A.Pfefferkorn,
G.Bainbridge.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Clinical studies have demonstrated that statins, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl
coenzyme A reductase (HMGR) inhibitors, are effective at lowering mortality
levels associated with cardiovascular disease; however, 2-7% of patients may
experience statin-induced myalgia that limits compliance with a treatment
regimen. High resolution crystal structures, thermodynamic binding parameters,
and biochemical data were used to design statin inhibitors with improved HMGR
affinity and therapeutic index relative to statin-induced myalgia. These studies
facilitated the identification of imidazole 1 as a potent (IC 50 = 7.9 nM)
inhibitor with excellent hepatoselectivity (>1000-fold) and good in vivo
efficacy. The binding of 1 to HMGR was found to be enthalpically driven with a
Delta H of -17.7 kcal/M. Additionally, a second novel series of bicyclic
pyrrole-based inhibitors was identified that induced order in a protein flap of
HMGR. Similar ordering was detected in a substrate complex, but has not been
reported in previous statin inhibitor complexes with HMGR.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Schön,
N.Madani,
A.B.Smith,
J.M.Lalonde,
and
E.Freire
(2011).
Some binding-related drug properties are dependent on thermodynamic signature.
|
| |
Chem Biol Drug Des,
77,
161-165.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Arnaboldi,
and
A.Corsini
(2010).
Do structural differences in statins correlate with clinical efficacy?
|
| |
Curr Opin Lipidol,
21,
298-304.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.A.Edwards,
J.M.Mason,
K.Clinch,
P.C.Tyler,
G.B.Evans,
and
V.L.Schramm
(2009).
Altered enthalpy-entropy compensation in picomolar transition state analogues of human purine nucleoside phosphorylase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
5226-5238.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Freire
(2009).
A thermodynamic approach to the affinity optimization of drug candidates.
|
| |
Chem Biol Drug Des,
74,
468-472.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.P.Perchellet,
E.M.Perchellet,
K.R.Crow,
K.R.Buszek,
N.Brown,
S.Ellappan,
G.Gao,
D.Luo,
M.Minatoya,
and
G.H.Lushington
(2009).
Novel synthetic inhibitors of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase activity that inhibit tumor cell proliferation and are structurally unrelated to existing statins.
|
| |
Int J Mol Med,
24,
633-643.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

