 |
PDBsum entry 2r5c

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.63
- kynurenine--glyoxylate transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
L-kynurenine + glyoxylate = kynurenate + glycine + H2O
|
|
2.
|
3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine + glyoxylate = xanthurenate + glycine + H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
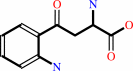 L-kynurenine
L-kynurenine
|
+
|
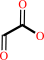 glyoxylate
glyoxylate
|
=
|
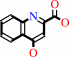 kynurenate
kynurenate
|
+
|
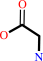 glycine
glycine
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 44.00% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
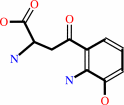 3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine
3-hydroxy-L-kynurenine
|
+
|
 glyoxylate
glyoxylate
|
=
|
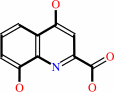 xanthurenate
xanthurenate
|
+
|
 glycine
glycine
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 42.31% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.7
- kynurenine--oxoglutarate transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-kynurenine + 2-oxoglutarate = kynurenate + L-glutamate + H2O
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 L-kynurenine
L-kynurenine
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
=
|
 kynurenate
kynurenate
|
+
|
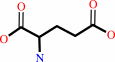 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
H2O
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
C6P)
matches with 65.22% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Biochemistry
47:1622-1630
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural insight into the mechanism of substrate specificity of aedes kynurenine aminotransferase.
|
|
Q.Han,
Y.G.Gao,
H.Robinson,
J.Li.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Aedes aegypti kynurenine aminotransferase (AeKAT) is a multifunctional
aminotransferase. It catalyzes the transamination of a number of amino acids and
uses many biologically relevant alpha-keto acids as amino group acceptors. AeKAT
also is a cysteine S-conjugate beta-lyase. The most important function of AeKAT
is the biosynthesis of kynurenic acid, a natural antagonist of NMDA and
alpha7-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Here, we report the crystal structures
of AeKAT in complex with its best amino acid substrates, glutamine and cysteine.
Glutamine is found in both subunits of the biological dimer, and cysteine is
found in one of the two subunits. Both substrates form external aldemines with
pyridoxal 5-phosphate in the structures. This is the first instance in which one
pyridoxal 5-phosphate enzyme has been crystallized with cysteine or glutamine
forming external aldimine complexes, cysteinyl aldimine and glutaminyl aldimine.
All the units with substrate are in the closed conformation form, and the unit
without substrate is in the open form, which suggests that the binding of
substrate induces the conformation change of AeKAT. By comparing the active site
residues of the AeKAT-cysteine structure with those of the human KAT
I-phenylalanine structure, we determined that Tyr286 in AeKAT is changed to
Phe278 in human KAT I, which may explain why AeKAT transaminates hydrophilic
amino acids more efficiently than human KAT I does.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
Q.Han,
H.Robinson,
T.Cai,
D.A.Tagle,
and
J.Li
(2011).
Biochemical and structural characterization of mouse mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase, a newly identified kynurenine aminotransferase-IV.
|
| |
Biosci Rep,
31,
323-332.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Han,
T.Cai,
D.A.Tagle,
and
J.Li
(2010).
Structure, expression, and function of kynurenine aminotransferases in human and rodent brains.
|
| |
Cell Mol Life Sci,
67,
353-368.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Han,
H.Robinson,
T.Cai,
D.A.Tagle,
and
J.Li
(2009).
Biochemical and structural properties of mouse kynurenine aminotransferase III.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
29,
784-793.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Han,
H.Robinson,
T.Cai,
D.A.Tagle,
and
J.Li
(2009).
Structural insight into the inhibition of human kynurenine aminotransferase I/glutamine transaminase K.
|
| |
J Med Chem,
52,
2786-2793.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Rossi,
R.Schwarcz,
and
M.Rizzi
(2008).
Curiosity to kill the KAT (kynurenine aminotransferase): structural insights into brain kynurenic acid synthesis.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
18,
748-755.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Q.Han,
T.Cai,
D.A.Tagle,
H.Robinson,
and
J.Li
(2008).
Substrate specificity and structure of human aminoadipate aminotransferase/kynurenine aminotransferase II.
|
| |
Biosci Rep,
28,
205-215.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Pellicciari,
F.Venturoni,
D.Bellocchi,
A.Carotti,
M.Marinozzi,
A.Macchiarulo,
L.Amori,
and
R.Schwarcz
(2008).
Sequence variants in kynurenine aminotransferase II (KAT II) orthologs determine different potencies of the inhibitor S-ESBA.
|
| |
ChemMedChem,
3,
1199-1202.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

