 |
PDBsum entry 2put

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.16
- glutamine--fructose-6-phosphate transaminase (isomerizing).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-fructose 6-phosphate + L-glutamine = D-glucosamine 6-phosphate + L-glutamate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
D-fructose 6-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
L-glutamine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 40.00% similarity
|
=
|
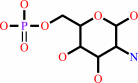 D-glucosamine 6-phosphate
D-glucosamine 6-phosphate
|
+
|
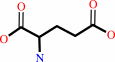 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
372:672-688
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The Crystal and Solution Studies of Glucosamine-6-phosphate Synthase from Candida albicans.
|
|
J.Raczynska,
J.Olchowy,
P.V.Konariev,
D.I.Svergun,
S.Milewski,
W.Rypniewski.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Glucosamine 6-phosphate (GlcN-6-P) synthase is an ubiquitous enzyme that
catalyses the first committed step in the reaction pathway that leads to
formation of uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc), a
precursor of macromolecules that contain amino sugars. Despite sequence
similarities, the enzyme in eukaryotes is tetrameric, whereas in prokaryotes it
is a dimer. The activity of eukaryotic GlcN-6-P synthase (known as Gfa1p) is
regulated by feedback inhibition by UDP-GlcNAc, the end product of the reaction
pathway, whereas in prokaryotes the GlcN-6-P synthase (known as GlmS) is not
regulated at the post-translational level. In bacteria and fungi the enzyme is
essential for cell wall synthesis. In human the enzyme is a mediator of insulin
resistance. For these reasons, Gfa1p is a target in anti-fungal chemotherapy and
in therapeutics for type-2 diabetes. The crystal structure of the Gfa1p
isomerase domain from Candida albicans has been analysed in complex with the
allosteric inhibitor UDP-GlcNAc and in the presence of glucose 6-phosphate,
fructose 6-phosphate and an analogue of the reaction intermediate,
2-amino-2-deoxy-d-mannitol 6-phosphate (ADMP). A solution structure of the
native Gfa1p has been deduced using small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). The
tetrameric Gfa1p can be described as a dimer of dimers, with each half similar
to the related enzyme from Escherichia coli. The core of the protein consists of
the isomerase domains. UDP-GlcNAc binds, together with a metal cation, in a
well-defined pocket on the surface of the isomerase domain. The residues
responsible for tetramerisation and for binding UDP-GlcNAc are conserved only
among eukaryotic sequences. Comparison with the previously studied GlmS from E.
coli reveals differences as well as similarities in the isomerase active site.
This study of Gfa1p focuses on the features that distinguish it from the
prokaryotic homologue in terms of quaternary structure, control of the enzymatic
activity and details of the isomerase active site.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 8.
Figure 8. Schematic representation of ligands interactions
with: (a) Glc-6-P closed form, (b) Glc-6-P/Fru-6-P open form,
(c) ADMP. Contacts present in all chains are depicted as black
broken lines and those present only in some of the chains are
shown as light grey lines. For comparison with the
protein–ligand interactions in E.
|
 |
Figure 9.
Figure 9. (a) The UDP-GlcNAc and the metal cation (blue)
bound to ISOM. A pocket in the protein surface is visible and it
accommodates the uracil ring. The ribose moiety and the
phosphate groups also interact with the protein whereas the
glucosamine moiety extends to the solvent. The 2F[o]-F[c]
electron density map is contoured at 1σ level. (b) Details of
the UDP-GlcNAc binding to ISOM. Hydrogen bonds between
UDP-GlcNAc and the protein are shown as black broken lines and
the interactions of the metal ion (blue sphere) are shown in
grey. (c) Superposition of ISOM with bound UDP-GlcNAc (protein
in red, ligand in green), ISOM without the inhibitor (yellow)
and GlmS ISOM (blue). The largest conformational change
associated with UDP-GlcNAc binding is in the position of the
Trp388 residue.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2007,
372,
672-688)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Chevreux,
C.Atmanene,
P.Lopez,
J.Ouazzani,
A.Van Dorsselaer,
B.Badet,
M.A.Badet-Denisot,
and
S.Sanglier-Cianférani
(2011).
Monitoring the dynamics of monomer exchange using electrospray mass spectrometry: the case of the dimeric glucosamine-6-phosphate synthase.
|
| |
J Am Soc Mass Spectrom,
22,
431-439.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Barreteau,
A.Kovac,
A.Boniface,
M.Sova,
S.Gobec,
and
D.Blanot
(2008).
Cytoplasmic steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Rev,
32,
168-207.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

