 |
PDBsum entry 2od2

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.286
- protein acetyllysine N-acetyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N6-acetyl-L-lysyl-[protein] + NAD+ + H2O = 2''-O-acetyl-ADP-D-ribose + nicotinamide + L-lysyl-[protein]
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
N(6)-acetyl-L-lysyl-[protein]
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 95.56% similarity
|
=
|
2''-O-acetyl-ADP-D-ribose
|
+
|
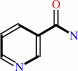 nicotinamide
nicotinamide
|
+
|
L-lysyl-[protein]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 61.54% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Mol Cell
25:463-472
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for nicotinamide inhibition and base exchange in Sir2 enzymes.
|
|
B.D.Sanders,
K.Zhao,
J.T.Slama,
R.Marmorstein.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The Sir2 family of proteins consists of broadly conserved NAD(+)-dependent
deacetylases that are implicated in diverse biological processes, including DNA
regulation, metabolism, and longevity. Sir2 proteins are regulated in part by
the cellular concentrations of a noncompetitive inhibitor, nicotinamide, that
reacts with a Sir2 reaction intermediate via a base-exchange reaction to reform
NAD(+) at the expense of deacetylation. To gain a mechanistic understanding of
nicotinamide inhibition in Sir2 enzymes, we captured the structure of
nicotinamide bound to a Sir2 homolog, yeast Hst2, in complex with its
acetyl-lysine 16 histone H4 substrate and a reaction intermediate analog,
ADP-HPD. Together with related biochemical studies and structures, we identify a
nicotinamide inhibition and base-exchange site that is distinct from the
so-called "C pocket" binding site for the nicotinamide group of NAD(+). These
results provide insights into the Sir2 mechanism of nicotinamide inhibition and
have important implications for the development of Sir2-specific effectors.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Structures of the Free yHst2/ADP-HPD/Histone H4
Complex
(A) Ternary yHst2 (gray) complex, highlighting
strictly conserved (red) and conserved (pink) residues; the
binding sites of acetyl-lysine (green), carba-NAD^+ (cyan), and
ADP-ribose (yellow); and the conserved C and D pockets.
Hydrogen bonds between the acetyl-lysine and carba-NAD^+ are
shown as yellow dotted lines. Residues 43–48 of the flexible
loop and residue 64 were omitted for clarity.
(B)
Superimposition of the yHst2/ADP-ribose/H4 complex (magenta)
with the yHst2/ADP-HPD/H4 complex (cyan) and the
yHst2/ADP-HPD/H4 complex bound to nicotinamide (blue). The
intermediate analog, acetylated histone H4 ligands, and
nicotinamide are shown in green for the ADP-ribose complex,
yellow for the free ADP-HPD complex, and orange for the
nicotinamide-bound ADP-HDP complex.
(C) Simulated annealing
omit density contoured at 1.0 σ showing density for the protein
(blue) and ADP-HPD (atoms individually colored). Water molecules
are shown as blue spheres.
(D) yHst2 bound to ADP-HPD
(atoms individually colored) and highlighting residues that make
hydrogen bonds (red dashed lines) or van der Waals contacts with
ADP-HPD. Hydrogen bonding residues are colored pink, residues
that make van der Waals interactions are colored cyan, and
residues that make both interactions are colored purple.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. The Overall Structure of yHst2 I117F Bound to
Carba-NAD^+ and Acetyl-Lysine
(A) Simulated annealing omit
density contoured at 1.0 σ showing density for the protein
(gray), carba-NAD^+ (cyan), acetyl-lysine (magenta), and the
mutated I117F residue (yellow).
(B) The superposition of
the nicotinamide-bound yHst2/ADP-HPD/H4 and the yHst2
I117F/carba-NAD^+/H4 structures. The yHst2 protein is shown in
blue, and the mutated I117F side chain (yellow) and the
nicotinamide molecule (red) are shown both in stick and modeled
in terms of the van der Waals radius of each atom of the
molecules.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Mol Cell
(2007,
25,
463-472)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Schemies,
U.Uciechowska,
W.Sippl,
and
M.Jung
(2010).
NAD(+) -dependent histone deacetylases (sirtuins) as novel therapeutic targets.
|
| |
Med Res Rev,
30,
861-889.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.McLaughlin,
C.M.Strain-Damerell,
K.Xie,
D.Brekasis,
A.S.Soares,
M.S.Paget,
and
C.L.Kielkopf
(2010).
Structural basis for NADH/NAD+ redox sensing by a Rex family repressor.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
38,
563-575.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Kaur,
A.V.Shivange,
and
N.Roy
(2010).
Structural analysis of trypanosomal sirtuin: an insight for selective drug design.
|
| |
Mol Divers,
14,
169-178.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Van Gool,
M.Gallí,
C.Gueydan,
V.Kruys,
P.P.Prevot,
A.Bedalov,
R.Mostoslavsky,
F.W.Alt,
T.De Smedt,
and
O.Leo
(2009).
Intracellular NAD levels regulate tumor necrosis factor protein synthesis in a sirtuin-dependent manner.
|
| |
Nat Med,
15,
206-210.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ito,
N.Yoshimura,
M.Kurosawa,
S.Ishii,
N.Nukina,
and
H.Okazawa
(2009).
Knock-down of PQBP1 impairs anxiety-related cognition in mouse.
|
| |
Hum Mol Genet,
18,
4239-4254.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Jin,
W.Wei,
Y.Jiang,
H.Peng,
J.Cai,
C.Mao,
H.Dai,
W.Choy,
J.E.Bemis,
M.R.Jirousek,
J.C.Milne,
C.H.Westphal,
and
R.B.Perni
(2009).
Crystal structures of human SIRT3 displaying substrate-induced conformational changes.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
24394-24405.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.M.Giammona,
S.Panuganti,
J.M.Kemper,
P.A.Apostolidis,
S.Lindsey,
E.T.Papoutsakis,
and
W.M.Miller
(2009).
Mechanistic studies on the effects of nicotinamide on megakaryocytic polyploidization and the roles of NAD+ levels and SIRT inhibition.
|
| |
Exp Hematol,
37,
1340.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Pfister,
C.Ma,
B.E.Morrison,
and
S.R.D'Mello
(2008).
Opposing effects of sirtuins on neuronal survival: SIRT1-mediated neuroprotection is independent of its deacetylase activity.
|
| |
PLoS ONE,
3,
e4090.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Hu,
S.Wang,
and
Y.Zhang
(2008).
Highly dissociative and concerted mechanism for the nicotinamide cleavage reaction in Sir2Tm enzyme suggested by ab initio QM/MM molecular dynamics simulations.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
130,
16721-16728.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.U.Kadam,
J.Tavares,
V.M.Kiran,
A.Cordeiro,
A.Ouaissi,
and
N.Roy
(2008).
Structure function analysis of Leishmania sirtuin: an ensemble of in silico and biochemical studies.
|
| |
Chem Biol Drug Des,
71,
501-506.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.J.Merrick,
and
M.T.Duraisingh
(2007).
Plasmodium falciparum Sir2: an unusual sirtuin with dual histone deacetylase and ADP-ribosyltransferase activity.
|
| |
Eukaryot Cell,
6,
2081-2091.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Wolberger
(2007).
Identification of a new nicotinamide binding site in a sirtuin: a reassessment.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
28,
1102-1103.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Lin
(2007).
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide: beyond a redox coenzyme.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
5,
2541-2554.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Hodawadekar,
and
R.Marmorstein
(2007).
Chemistry of acetyl transfer by histone modifying enzymes: structure, mechanism and implications for effector design.
|
| |
Oncogene,
26,
5528-5540.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lall
(2007).
Primers on chromatin.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
14,
1110-1115.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

