 |
PDBsum entry 2jg2

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
High resolution structure of spt with plp internal aldimine
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Serine palmitoyltransferase. Chain: a. Engineered: yes. Other_details: plp forming internal aldimine with lys265
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Pseudomonas paucimobilis. Organism_taxid: 13689. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.30Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.155
|
R-free:
|
0.185
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
B.A.Yard,L.G.Carter,K.A.Johnson,I.M.Overton,S.A.Mcmahon,M.Dorward, H.Liu,D.Puech,M.Oke,G.J.Barton,J.H.Naismith,D.J.Campopiano
|
Key ref:

|
 |
B.A.Yard
et al.
(2007).
The structure of serine palmitoyltransferase; gateway to sphingolipid biosynthesis.
J Mol Biol,
370,
870-886.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
07-Feb-07
|
Release date:
|
01-May-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q93UV0
(SPT_SPHPI) -
Serine palmitoyltransferase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
420 a.a.
399 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.50
- serine C-palmitoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-serine + hexadecanoyl-CoA + H+ = 3-oxosphinganine + CO2 + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
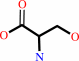 L-serine
L-serine
|
+
|
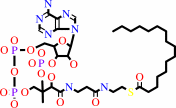 hexadecanoyl-CoA
hexadecanoyl-CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
3-oxosphinganine
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 93.75% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
370:870-886
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structure of serine palmitoyltransferase; gateway to sphingolipid biosynthesis.
|
|
B.A.Yard,
L.G.Carter,
K.A.Johnson,
I.M.Overton,
M.Dorward,
H.Liu,
S.A.McMahon,
M.Oke,
D.Puech,
G.J.Barton,
J.H.Naismith,
D.J.Campopiano.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Sphingolipid biosynthesis commences with the condensation of L-serine and
palmitoyl-CoA to produce 3-ketodihydrosphingosine (KDS). This reaction is
catalysed by the PLP-dependent enzyme serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT; EC
2.3.1.50), which is a membrane-bound heterodimer (SPT1/SPT2) in eukaryotes such
as humans and yeast and a cytoplasmic homodimer in the Gram-negative bacterium
Sphingomonas paucimobilis. Unusually, the outer membrane of S. paucimobilis
contains glycosphingolipid (GSL) instead of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and SPT
catalyses the first step of the GSL biosynthetic pathway in this organism. We
report here the crystal structure of the holo-form of S. paucimobilis SPT at 1.3
A resolution. The enzyme is a symmetrical homodimer with two active sites and a
monomeric tertiary structure consisting of three domains. The PLP cofactor is
bound covalently to a lysine residue (Lys265) as an internal aldimine/Schiff
base and the active site is composed of residues from both subunits, located at
the bottom of a deep cleft. Models of the human SPT1/SPT2 heterodimer were
generated from the bacterial structure by bioinformatics analysis. Mutations in
the human SPT1-encoding subunit have been shown to cause a neuropathological
disease known as hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type I (HSAN1). Our
models provide an understanding of how these mutations may affect the activity
of the enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Proposed reaction mechanism of SPT. (a)
Transaldimination of internal aldimine (holo-SPT), I with
L-serine to form external aldimine, II; (b) deprotonation of
C^α by base to form quinonoid, III; (c) Claisen condensation to
form putative β-ketoacid-aldimine complex, IV; (d)
decarboxylation to form product quinonoid, V; (e) reprotonation
of quinonoid to form product external aldimine, VI (f) release
of product 3-ketodihydrosphingosine (KDS) and regeneration of I.
|
 |
Figure 7.
Figure 7. Stereo view showing the proximity of the Asn100
residue of monomer B to the PLP cofactor of monomer A in the S.
paucimobilis SPT homodimer. Monomer A is drawn in green and
monomer B is drawn in blue. Asn100 of monomer B is shown in CPK.
Using the sequence alignment in Figure 9, the S. paucimobilis
SPT Asn100 residue maps to residue Cys133 on the SPT1 subunit of
human SPT. Mutations at this residue C133W and C133Y are known
to cause the autosomal disease hereditary sensory and autonomic
neuropathy type I (HSAN1). The conserved residues His159 and
His234 which interact directly with the PLP cofactor are also
highlighted.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2007,
370,
870-886)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.Rotthier,
M.Auer-Grumbach,
K.Janssens,
J.Baets,
A.Penno,
L.Almeida-Souza,
K.Van Hoof,
A.Jacobs,
E.De Vriendt,
B.Schlotter-Weigel,
W.Löscher,
P.Vondráček,
P.Seeman,
P.De Jonghe,
P.Van Dijck,
A.Jordanova,
T.Hornemann,
and
V.Timmerman
(2010).
Mutations in the SPTLC2 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase cause hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type I.
|
| |
Am J Hum Genet,
87,
513-522.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Bourquin,
H.Riezman,
G.Capitani,
and
M.G.Grütter
(2010).
Structure and function of sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism.
|
| |
Structure,
18,
1054-1065.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Lowther,
B.A.Yard,
K.A.Johnson,
L.G.Carter,
V.T.Bhat,
M.C.Raman,
D.J.Clarke,
B.Ramakers,
S.A.McMahon,
J.H.Naismith,
and
D.J.Campopiano
(2010).
Inhibition of the PLP-dependent enzyme serine palmitoyltransferase by cycloserine: evidence for a novel decarboxylative mechanism of inactivation.
|
| |
Mol Biosyst,
6,
1682-1693.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.C.Raman,
K.A.Johnson,
D.J.Clarke,
J.H.Naismith,
and
D.J.Campopiano
(2010).
The serine palmitoyltransferase from Sphingomonas wittichii RW1: An interesting link to an unusual acyl carrier protein.
|
| |
Biopolymers,
93,
811-822.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Oke,
L.G.Carter,
K.A.Johnson,
H.Liu,
S.A.McMahon,
X.Yan,
M.Kerou,
N.D.Weikart,
N.Kadi,
M.A.Sheikh,
S.Schmelz,
M.Dorward,
M.Zawadzki,
C.Cozens,
H.Falconer,
H.Powers,
I.M.Overton,
C.A.van Niekerk,
X.Peng,
P.Patel,
R.A.Garrett,
D.Prangishvili,
C.H.Botting,
P.J.Coote,
D.T.Dryden,
G.J.Barton,
U.Schwarz-Linek,
G.L.Challis,
G.L.Taylor,
M.F.White,
and
J.H.Naismith
(2010).
The Scottish Structural Proteomics Facility: targets, methods and outputs.
|
| |
J Struct Funct Genomics,
11,
167-180.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.A.Momin,
H.Park,
J.C.Allegood,
M.Leipelt,
S.L.Kelly,
A.H.Merrill,
and
K.Hanada
(2009).
Characterization of mutant serine palmitoyltransferase 1 in LY-B cells.
|
| |
Lipids,
44,
725-732.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Han,
S.D.Gupta,
K.Gable,
S.Niranjanakumari,
P.Moitra,
F.Eichler,
R.H.Brown,
J.M.Harmon,
and
T.M.Dunn
(2009).
Identification of small subunits of mammalian serine palmitoyltransferase that confer distinct acyl-CoA substrate specificities.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
8186-8191.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.C.Raman,
K.A.Johnson,
B.A.Yard,
J.Lowther,
L.G.Carter,
J.H.Naismith,
and
D.J.Campopiano
(2009).
The External Aldimine Form of Serine Palmitoyltransferase: STRUCTURAL, KINETIC, AND SPECTROSCOPIC ANALYSIS OF THE WILD-TYPE ENZYME AND HSAN1 MUTANT MIMICS.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
17328-17339.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.W.Ring,
G.Schwär,
and
H.B.Bode
(2009).
Biosynthesis of 2-hydroxy and iso-even fatty acids is connected to sphingolipid formation in myxobacteria.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
10,
2003-2010.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hornemann,
A.Penno,
S.Richard,
G.Nicholson,
F.S.van Dijk,
A.Rotthier,
V.Timmerman,
and
A.von Eckardstein
(2009).
A systematic comparison of all mutations in hereditary sensory neuropathy type I (HSAN I) reveals that the G387A mutation is not disease associated.
|
| |
Neurogenetics,
10,
135-143.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Lendrihas,
J.Zhang,
G.A.Hunter,
and
G.C.Ferreira
(2009).
Arg-85 and Thr-430 in murine 5-aminolevulinate synthase coordinate acyl-CoA-binding and contribute to substrate specificity.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
18,
1847-1859.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Shiraiwa,
H.Ikushiro,
and
H.Hayashi
(2009).
Multifunctional role of his159in the catalytic reaction of serine palmitoyltransferase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
15487-15495.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Bieberich
(2008).
Ceramide signaling in cancer and stem cells.
|
| |
Future Lipidol,
3,
273-300.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Ikushiro,
S.Fujii,
Y.Shiraiwa,
and
H.Hayashi
(2008).
Acceleration of the substrate Calpha deprotonation by an analogue of the second substrate palmitoyl-CoA in Serine Palmitoyltransferase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
7542-7553.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.M.Overton,
G.Padovani,
M.A.Girolami,
and
G.J.Barton
(2008).
ParCrys: a Parzen window density estimation approach to protein crystallization propensity prediction.
|
| |
Bioinformatics,
24,
901-907.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.T.Pruett,
A.Bushnev,
K.Hagedorn,
M.Adiga,
C.A.Haynes,
M.C.Sullards,
D.C.Liotta,
and
A.H.Merrill
(2008).
Biodiversity of sphingoid bases ("sphingosines") and related amino alcohols.
|
| |
J Lipid Res,
49,
1621-1639.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

