 |
PDBsum entry 2xbn

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Inhibition of the plp-dependent enzyme serine palmitoyltransferase by cycloserine: evidence for a novel decarboxylative mechanism of inactivation
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Serine palmitoyltransferase. Chain: a. Fragment: residues 2-420. Synonym: spt, spt1. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sphingomonas paucimobilis. Organism_taxid: 13689. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.157
|
R-free:
|
0.181
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Lowther,B.A.Yard,K.A.Johnson,L.G.Carter,V.T.Bhat,M.C.C.Raman, D.J.Clarke,B.Ramakers,S.A.Mcmahon,J.H.Naismith,D.J.Campopiano
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Lowther
et al.
(2010).
Inhibition of the PLP-dependent enzyme serine palmitoyltransferase by cycloserine: evidence for a novel decarboxylative mechanism of inactivation.
Mol Biosyst,
6,
1682-1693.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
13-Apr-10
|
Release date:
|
19-May-10
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q93UV0
(SPT_SPHPI) -
Serine palmitoyltransferase from Sphingomonas paucimobilis
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
420 a.a.
398 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.3.1.50
- serine C-palmitoyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-serine + hexadecanoyl-CoA + H+ = 3-oxosphinganine + CO2 + CoA
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
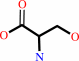 L-serine
L-serine
|
+
|
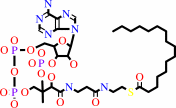 hexadecanoyl-CoA
hexadecanoyl-CoA
|
+
|
H(+)
|
=
|
3-oxosphinganine
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
+
|
 CoA
CoA
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PMP)
matches with 88.24% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Mol Biosyst
6:1682-1693
(2010)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Inhibition of the PLP-dependent enzyme serine palmitoyltransferase by cycloserine: evidence for a novel decarboxylative mechanism of inactivation.
|
|
J.Lowther,
B.A.Yard,
K.A.Johnson,
L.G.Carter,
V.T.Bhat,
M.C.Raman,
D.J.Clarke,
B.Ramakers,
S.A.McMahon,
J.H.Naismith,
D.J.Campopiano.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Cycloserine (CS, 4-amino-3-isoxazolidone) is a cyclic amino acid mimic that is
known to inhibit many essential pyridoxal 5'-phosphate (PLP)-dependent enzymes.
Two CS enantiomers are known; d-cycloserine (DCS, also known as Seromycin) is a
natural product that is used to treat resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis
infections as well as neurological disorders since it is a potent NMDA receptor
agonist, and l-cycloserine (LCS) is a synthetic enantiomer whose usefulness as a
drug has been hampered by its inherent toxicity arising through inhibition of
sphingolipid metabolism. Previous studies on various PLP-dependent enzymes
revealed a common mechanism of inhibition by both enantiomers of CS; the PLP
cofactor is disabled by forming a stable 3-hydroxyisoxazole/pyridoxamine
5'-phosphate (PMP) adduct at the active site where the cycloserine ring remains
intact. Here we describe a novel mechanism of CS inactivation of the
PLP-dependent enzyme serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT) from Sphingomonas
paucimobilis. SPT catalyses the condensation of l-serine and palmitoyl-CoA, the
first step in the de novo sphingolipid biosynthetic pathway. We have used a
range of kinetic, spectroscopic and structural techniques to postulate that both
LCS and DCS inactivate SPT by transamination to form a free pyridoxamine
5'-phosphate (PMP) and beta-aminooxyacetaldehyde that remain bound at the active
site. We suggest this occurs by ring opening of the cycloserine ring followed by
decarboxylation. Enzyme kinetics show that inhibition is reversed by incubation
with excess PLP and that LCS is a more effective SPT inhibitor than DCS.
UV-visible spectroscopic data, combined with site-directed mutagenesis, suggest
that a mobile Arg(378) residue is involved in cycloserine inactivation of SPT.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

