 |
PDBsum entry 2hzf

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Electron transport, oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2hzf
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.8.5.1
- glutathione dehydrogenase (ascorbate).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-dehydroascorbate + 2 glutathione = glutathione disulfide + L-ascorbate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
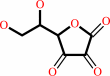 L-dehydroascorbate
L-dehydroascorbate
|
+
|
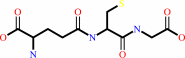 2
×
glutathione
2
×
glutathione
|
=
|
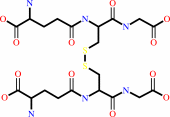 glutathione disulfide
glutathione disulfide
|
+
|
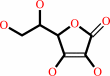 L-ascorbate
L-ascorbate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
365:1545-1558
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of a poxviral glutaredoxin in the oxidized and reduced states show redox-correlated structural changes.
|
|
J.P.Bacik,
B.Hazes.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Glutaredoxins act as reducing agents for the large subunit of ribonucleotide
reductase (R1) in many prokaryotes and eukaryotes, including humans. The same
relationship has been proposed for the glutaredoxin and R1 proteins expressed by
all orthopoxviruses, including vaccinia, variola, and ectromelia virus.
Interestingly, the orthopoxviral proteins share 45% and 78% sequence identity
with human glutaredoxin-1 (Grx-1) and R1, respectively. To study
structure-function relationships of the vertebrate Grx-1 family, and reveal
potential viral adaptations, we have determined crystal structures of the
ectromelia virus glutaredoxin, EVM053, in the oxidized and reduced states. The
structures show a large redox-induced conformational rearrangement of Tyr21 and
Thr22 near the active site. We predict that the movement of Tyr21 is a
viral-specific adaptation that increases the redox potential by stabilizing the
reduced state. The conformational switch of Thr22 appears to be shared by
vertebrate Grx-1 and may affect the strictly conserved Lys20. A crystal
packing-induced structural change in residues 68-70 affects the GSH-binding
loop, and our structures reveal a potential interaction network that connects
the GSH-binding loop and the active site. EVM053 also exhibits a novel
cis-proline (Pro53) in a loop that has been shown to contribute to R1-binding in
Escherichia coli Grx-1. The cis-peptide bond of Pro53 may be required to promote
electrostatic interactions between Lys52 and the C-terminal carboxylate of R1.
Finally, dimethylarsenite was covalently attached to Cys23 in one reduced EVM053
structure and our preliminary data show that EVM053 has dimethylarsenate
reductase activity.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Cartoon representation of EVM053 in the oxidized
conformation. Helices are shown as coils and strands as arrows.
The disulfide bond formed by the active site cysteine residues
is shown in orange and the cis-Pro53 is drawn in ball-and-stick
format. This Figure was generated using MOLSCRIPT^67 and
Raster3D.^68
|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Electron density (2|F[obs]|–|F[calc]|) for the
active site of EVM053 in the (a) oxidized; (b) reduced; (c)
dimethylarsenylated states. The disulfide bond in the oxidized
structure and the proposed hydrogen bond in the reduced
structure are indicated by broken lines. This Figure was
generated using Xfit^65 and Raster3D.^68
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2007,
365,
1545-1558)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
L.Li,
N.Cheng,
K.D.Hirschi,
and
X.Wang
(2010).
Structure of Arabidopsis chloroplastic monothiol glutaredoxin AtGRXcp.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
725-732.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
D.A.Gell,
L.Feng,
S.Zhou,
P.D.Jeffrey,
K.Bendak,
A.Gow,
M.J.Weiss,
Y.Shi,
and
J.P.Mackay
(2009).
A cis-proline in alpha-hemoglobin stabilizing protein directs the structural reorganization of alpha-hemoglobin.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
29462-29469.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Van Vliet,
M.R.Mohamed,
L.Zhang,
N.Y.Villa,
S.J.Werden,
J.Liu,
and
G.McFadden
(2009).
Poxvirus proteomics and virus-host protein interactions.
|
| |
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev,
73,
730-749.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Yu,
N.N.Zhang,
P.D.Yin,
P.X.Cui,
and
C.Z.Zhou
(2008).
Glutathionylation-triggered conformational changes of glutaredoxin Grx1 from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Proteins,
72,
1077-1083.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Mi,
Y.H.Liang,
L.Li,
and
X.D.Su
(2008).
The crystal structure of human chloride intracellular channel protein 2: a disulfide bond with functional implications.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
509-513.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Sheng,
J.Ye,
and
B.P.Rosen
(2007).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of Escherichia coliglutaredoxin 2 in complex with glutathione and of a cysteine-less variant without glutathione.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
280-282.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

