 |
PDBsum entry 2fue

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.2.8
- phosphomannomutase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
GDP-L-Fucose and GDP-mannose Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate = D-mannose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
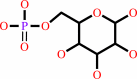 D-mannose 6-phosphate
D-mannose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
281:14918-14926
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The X-ray crystal structures of human alpha-phosphomannomutase 1 reveal the structural basis of congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1a.
|
|
N.R.Silvaggi,
C.Zhang,
Z.Lu,
J.Dai,
D.Dunaway-Mariano,
K.N.Allen.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Congenital disorder of glycosylation type 1a (CDG-1a) is a congenital disease
characterized by severe defects in nervous system development. It is caused by
mutations in alpha-phosphomannomutase (of which there are two isozymes,
alpha-PMM1 and alpha-PPM2). Here we report the x-ray crystal structures of human
alpha-PMM1 in the open conformation, with and without the bound substrate,
alpha-D-mannose 1-phosphate. Alpha-PMM1, like most haloalkanoic acid
dehalogenase superfamily (HADSF) members, consists of two domains, the cap and
core, which open to bind substrate and then close to provide a solvent-exclusive
environment for catalysis. The substrate phosphate group is observed at a
positively charged site of the cap domain, rather than at the core domain
phosphoryl-transfer site defined by the Asp(19) nucleophile and Mg(2+) cofactor.
This suggests that substrate binds first to the cap and then is swept into the
active site upon cap closure. The orientation of the acid/base residue Asp(21)
suggests that alpha-phosphomannomutase (alpha-PMM) uses a different method of
protecting the aspartylphosphate from hydrolysis than the HADSF member
beta-phosphoglucomutase. It is hypothesized that the electrostatic repulsion of
positive charges at the interface of the cap and core domains stabilizes
alpha-PMM1 in the open conformation and that the negatively charged substrate
binds to the cap, thereby facilitating its closure over the core domain. The two
isozymes, alpha-PMM1 and alpha-PMM2, are shown to have a conserved active-site
structure and to display similar kinetic properties. Analysis of the known
mutation sites in the context of the structures reveals the genotype-phenotype
relationship underlying CDG-1a.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
FIGURE 1. Scheme for the reaction catalyzed by human  -phosphomannomutase.
The C-1 and C-6 positions on the hexose ring are labeled in the
first step. -phosphomannomutase.
The C-1 and C-6 positions on the hexose ring are labeled in the
first step.
|
 |
Figure 2.
FIGURE 2. A, structure of human  -phosphomannomutase
complexed with -phosphomannomutase
complexed with  -D-mannose 1-phosphate.
The cap domain is magenta and the core domain cyan. Man-1-P is
shown as ball-and-stick (orange) and the two Mg^2+ ions as
metallic spheres. The image was rendered using MOL-SCRIPT (38)
and POVRAY. B, schematic representation of the arrangement of
secondary structure elements in -D-mannose 1-phosphate.
The cap domain is magenta and the core domain cyan. Man-1-P is
shown as ball-and-stick (orange) and the two Mg^2+ ions as
metallic spheres. The image was rendered using MOL-SCRIPT (38)
and POVRAY. B, schematic representation of the arrangement of
secondary structure elements in  -PMM1 core (cyan) and
cap (magenta). -PMM1 core (cyan) and
cap (magenta).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2006,
281,
14918-14926)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.Y.Chu,
Q.C.Zheng,
X.Li,
Y.S.Zhao,
J.L.Zhang,
and
H.X.Zhang
(2011).
DFT investigation on the reaction mechanism catalyzed by α-phosphomannomutase1 in protonated/deprotonated states.
|
| |
J Mol Model,
17,
577-585.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Yu,
Y.Li,
B.Li,
X.Liu,
L.Hao,
J.Chen,
W.Qian,
S.Li,
G.Wang,
S.Bai,
H.Ye,
H.Qin,
Q.Shen,
L.Chen,
A.Zhang,
and
D.Wang
(2010).
Molecular analysis of phosphomannomutase (PMM) genes reveals a unique PMM duplication event in diverse Triticeae species and the main PMM isozymes in bread wheat tissues.
|
| |
BMC Plant Biol,
10,
214.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Quental,
A.Moleirinho,
L.Azevedo,
and
A.Amorim
(2010).
Evolutionary history and functional diversification of phosphomannomutase genes.
|
| |
J Mol Evol,
71,
119-127.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Suenaga,
M.Hatakeyama,
A.B.Kiyatkin,
R.Radhakrishnan,
M.Taiji,
and
B.N.Kholodenko
(2009).
Molecular dynamics simulations reveal that Tyr-317 phosphorylation reduces Shc binding affinity for phosphotyrosyl residues of epidermal growth factor receptor.
|
| |
Biophys J,
96,
2278-2288.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.H.Freeze
(2009).
Towards a therapy for phosphomannomutase 2 deficiency, the defect in CDG-Ia patients.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1792,
835-840.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Dai,
L.Finci,
C.Zhang,
S.Lahiri,
G.Zhang,
E.Peisach,
K.N.Allen,
and
D.Dunaway-Mariano
(2009).
Analysis of the structural determinants underlying discrimination between substrate and solvent in beta-phosphoglucomutase catalysis.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
1984-1995.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Haeuptle,
and
T.Hennet
(2009).
Congenital disorders of glycosylation: an update on defects affecting the biosynthesis of dolichol-linked oligosaccharides.
|
| |
Hum Mutat,
30,
1628-1641.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Veiga-da-Cunha,
W.Vleugels,
P.Maliekal,
G.Matthijs,
and
E.Van Schaftingen
(2008).
Mammalian phosphomannomutase PMM1 is the brain IMP-sensitive glucose-1,6-bisphosphatase.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
33988-33993.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Quelhas,
R.Quental,
L.Vilarinho,
A.Amorim,
and
L.Azevedo
(2007).
Congenital disorder of glycosylation type Ia: searching for the origin of common mutations in PMM2.
|
| |
Ann Hum Genet,
71,
348-353.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.N.Phillips,
B.G.Fox,
J.L.Markley,
B.F.Volkman,
E.Bae,
E.Bitto,
C.A.Bingman,
R.O.Frederick,
J.G.McCoy,
B.L.Lytle,
B.S.Pierce,
J.Song,
and
S.N.Twigger
(2007).
Structures of proteins of biomedical interest from the Center for Eukaryotic Structural Genomics.
|
| |
J Struct Funct Genomics,
8,
73-84.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

