 |
PDBsum entry 2ezc

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Phosphotransferase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2ezc
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.7.3.9
- phosphoenolpyruvate--protein phosphotransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-histidyl-[protein] + phosphoenolpyruvate = N(pros)-phospho-L-histidyl- [protein] + pyruvate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-histidyl-[protein]
|
+
|
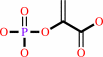 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
=
|
N(pros)-phospho-L-histidyl- [protein]
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Nat Struct Biol
4:443-449
(1997)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Defining long range order in NMR structure determination from the dependence of heteronuclear relaxation times on rotational diffusion anisotropy.
|
|
N.Tjandra,
D.S.Garrett,
A.M.Gronenborn,
A.Bax,
G.M.Clore.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Structure determination by NMR presently relies on short range restraints
between atoms in close spatial proximity, principally in the form of short (<
5 A) interproton distances. In the case of modular or multidomain proteins and
linear nucleic acids, the density of short interproton distance contacts between
structural elements far apart in the sequence may be insufficient to define
their relative orientations. In this paper we show how the dependence of
heteronuclear longitudinal and transverse relaxation times on the rotational
diffusion anisotropy of non-spherical molecules can be readily used to directly
provide restraints for simulated annealing structure refinement that
characterize long range order a priori. The method is demonstrated using the
N-terminal domain of Enzyme I,a protein of 259 residues comprising two distinct
domains with a diffusion anisotropy(Dparallel/Dperpendicular)of approximately 2.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.J.de Vries,
M.van Dijk,
and
A.M.Bonvin
(2010).
The HADDOCK web server for data-driven biomolecular docking.
|
| |
Nat Protoc,
5,
883-897.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ryabov,
G.M.Clore,
and
C.D.Schwieters
(2010).
Direct use of 15N relaxation rates as experimental restraints on molecular shape and orientation for docking of protein-protein complexes.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
132,
5987-5989.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Xiao,
and
J.Baum
(2009).
Structural insights from (15)N relaxation data for an anisotropic collagen peptide.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
18194-18195.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.A.Mooney,
K.Schweimer,
P.Rösch,
M.Gottesman,
and
R.Landick
(2009).
Two structurally independent domains of E. coli NusG create regulatory plasticity via distinct interactions with RNA polymerase and regulators.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
391,
341-358.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.A.Ramelot,
S.Raman,
A.P.Kuzin,
R.Xiao,
L.C.Ma,
T.B.Acton,
J.F.Hunt,
G.T.Montelione,
D.Baker,
and
M.A.Kennedy
(2009).
Improving NMR protein structure quality by Rosetta refinement: a molecular replacement study.
|
| |
Proteins,
75,
147-167.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ryabov,
J.Y.Suh,
A.Grishaev,
G.M.Clore,
and
C.D.Schwieters
(2009).
Using the experimentally determined components of the overall rotational diffusion tensor to restrain molecular shape and size in NMR structure determination of globular proteins and protein-protein complexes.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
9522-9531.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.S.Maltsev,
A.H.Ahmed,
M.K.Fenwick,
D.E.Jane,
and
R.E.Oswald
(2008).
Mechanism of partial agonism at the GluR2 AMPA receptor: Measurements of lobe orientation in solution.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
10600-10610.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Van Melckebeke,
M.Devany,
C.Di Primo,
F.Beaurain,
J.J.Toulmé,
D.L.Bryce,
and
J.Boisbouvier
(2008).
Liquid-crystal NMR structure of HIV TAR RNA bound to its SELEX RNA aptamer reveals the origins of the high stability of the complex.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
9210-9215.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Kuszewski,
R.A.Thottungal,
G.M.Clore,
and
C.D.Schwieters
(2008).
Automated error-tolerant macromolecular structure determination from multidimensional nuclear Overhauser enhancement spectra and chemical shift assignments: improved robustness and performance of the PASD algorithm.
|
| |
J Biomol NMR,
41,
221-239.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Tjandra,
M.Suzuki,
and
S.L.Chang
(2007).
Refinement of protein structure against non-redundant carbonyl 13C NMR relaxation.
|
| |
J Biomol NMR,
38,
243-253.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Ryabov,
and
D.Fushman
(2007).
Structural assembly of multidomain proteins and protein complexes guided by the overall rotational diffusion tensor.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
129,
7894-7902.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Gabel,
B.Simon,
and
M.Sattler
(2006).
A target function for quaternary structural refinement from small angle scattering and NMR orientational restraints.
|
| |
Eur Biophys J,
35,
313-327.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Chen,
W.Im,
and
C.L.Brooks
(2006).
Balancing solvation and intramolecular interactions: toward a consistent generalized Born force field.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
128,
3728-3736.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.D.van Dijk,
D.Fushman,
and
A.M.Bonvin
(2005).
Various strategies of using residual dipolar couplings in NMR-driven protein docking: application to Lys48-linked di-ubiquitin and validation against 15N-relaxation data.
|
| |
Proteins,
60,
367-381.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.G.Cook,
L.N.Johnson,
and
J.M.McDonnell
(2005).
Structural characterization of Ca2+/CaM in complex with the phosphorylase kinase PhK5 peptide.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
1511-1522.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Lingel,
B.Simon,
E.Izaurralde,
and
M.Sattler
(2005).
The structure of the flock house virus B2 protein, a viral suppressor of RNA interference, shows a novel mode of double-stranded RNA recognition.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
6,
1149-1155.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Dancea,
and
U.Günther
(2005).
Automated protein NMR structure determination using wavelet de-noised NOESY spectra.
|
| |
J Biomol NMR,
33,
139-152.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Fossi,
J.Linge,
D.Labudde,
D.Leitner,
M.Nilges,
and
H.Oschkinat
(2005).
Influence of chemical shift tolerances on NMR structure calculations using ARIA protocols for assigning NOE data.
|
| |
J Biomol NMR,
31,
21-34.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.B.Nabuurs,
E.Krieger,
C.A.Spronk,
A.J.Nederveen,
G.Vriend,
and
G.W.Vuister
(2005).
Definition of a new information-based per-residue quality parameter.
|
| |
J Biomol NMR,
33,
123-134.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.M.Clore,
and
C.D.Schwieters
(2002).
Theoretical and computational advances in biomolecular NMR spectroscopy.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
12,
146-153.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Iwahara,
M.Iwahara,
G.W.Daughdrill,
J.Ford,
and
R.T.Clubb
(2002).
The structure of the Dead ringer-DNA complex reveals how AT-rich interaction domains (ARIDs) recognize DNA.
|
| |
EMBO J,
21,
1197-1209.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.S.Ulmer,
J.M.Werner,
and
I.D.Campbell
(2002).
SH3-SH2 domain orientation in Src kinases: NMR studies of Fyn.
|
| |
Structure,
10,
901-911.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Kaji,
M.C.Kiel,
G.Hirokawa,
A.R.Muto,
Y.Inokuchi,
and
H.Kaji
(2001).
The fourth step of protein synthesis: disassembly of the posttermination complex is catalyzed by elongation factor G and ribosome recycling factor, a near-perfect mimic of tRNA.
|
| |
Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol,
66,
515-529.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Desvaux,
J.C.Gabriel,
P.Berthault,
and
F.Camerel
(2001).
First Use of a Mineral Liquid Crystal for Measurement of Residual Dipolar Couplings of a Nonlabeled Biomolecule We would like to thank Dr. Patrick Davidson for helpful discussions, Stéphane Grolleau for TGA (thermogravimetric analysis) measurements, and Prof. Pierre Sinaÿ and Dr. Yongmin Zhang for the gift of the pentasaccharide. Financial support from the CNRS, the Ministry of Education (PhD fellowship for F.C.), the Région Pays de Loire, and the GDR-CNRS 690 FORMES (D(2)O) is gratefully acknowledged.
|
| |
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,
40,
373-376.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.J.Chou,
S.Li,
C.B.Klee,
and
A.Bax
(2001).
Solution structure of Ca(2+)-calmodulin reveals flexible hand-like properties of its domains.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
8,
990-997.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Yoshida,
S.Uchiyama,
H.Nakano,
H.Kashimori,
H.Kijima,
T.Ohshima,
Y.Saihara,
T.Ishino,
H.Shimahara,
T.Yoshida,
K.Yokose,
T.Ohkubo,
A.Kaji,
and
Y.Kobayashi
(2001).
Solution structure of the ribosome recycling factor from Aquifex aeolicus.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
40,
2387-2396.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Baber,
D.Levens,
D.Libutti,
and
N.Tjandra
(2000).
Chemical shift mapped DNA-binding sites and 15N relaxation analysis of the C-terminal KH domain of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
6022-6032.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Sahu,
A.K.Bhuyan,
A.Majumdar,
and
J.B.Udgaonkar
(2000).
Backbone dynamics of barstar: a (15)N NMR relaxation study.
|
| |
Proteins,
41,
460-474.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.P.Smith,
Y.Hashimoto,
A.R.Pickford,
I.D.Campbell,
and
J.M.Werner
(2000).
Interface characterization of the type II module pair from fibronectin.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
39,
8374-8381.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.C.LiWang,
J.J.Cao,
H.Zheng,
Z.Lu,
S.C.Peiper,
and
P.J.LiWang
(1999).
Dynamics study on the anti-human immunodeficiency virus chemokine viral macrophage-inflammatory protein-II (VMIP-II) reveals a fully monomeric protein.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
38,
442-453.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.B.Bertelsen,
H.Zhou,
D.F.Lowry,
G.C.Flynn,
and
F.W.Dahlquist
(1999).
Topology and dynamics of the 10 kDa C-terminal domain of DnaK in solution.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
8,
343-354.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.McDonnell,
D.Fushman,
C.L.Milliman,
S.J.Korsmeyer,
and
D.Cowburn
(1999).
Solution structure of the proapoptotic molecule BID: a structural basis for apoptotic agonists and antagonists.
|
| |
Cell,
96,
625-634.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.X.Wang,
N.Neamati,
J.Jacob,
I.Palmer,
S.J.Stahl,
J.D.Kaufman,
P.L.Huang,
P.L.Huang,
H.E.Winslow,
Y.Pommier,
P.T.Wingfield,
S.Lee-Huang,
A.Bax,
and
D.A.Torchia
(1999).
Solution structure of anti-HIV-1 and anti-tumor protein MAP30: structural insights into its multiple functions.
|
| |
Cell,
99,
433-442.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.M.Clore,
and
A.M.Gronenborn
(1998).
New methods of structure refinement for macromolecular structure determination by NMR.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
95,
5891-5898.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.M.Clore,
and
A.M.Gronenborn
(1998).
NMR structure determination of proteins and protein complexes larger than 20 kDa.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
2,
564-570.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.A.Baden,
S.P.Sarma,
R.B.Kapust,
R.A.Byrd,
and
D.S.Waugh
(1998).
The amino-terminal domain of human STAT4. Overproduction, purification, and biophysical characterization.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
273,
17109-17114.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.H.Gardner,
and
L.E.Kay
(1998).
The use of 2H, 13C, 15N multidimensional NMR to study the structure and dynamics of proteins.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct,
27,
357-406.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Z.Bu,
S.Koide,
and
D.M.Engelman
(1998).
A solution SAXS study of Borrelia burgdorferi OspA, a protein containing a single-layer beta-sheet.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
7,
2681-2683.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.G.Palmer
(1997).
Probing molecular motion by NMR.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
7,
732-737.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.E.Kay,
and
K.H.Gardner
(1997).
Solution NMR spectroscopy beyond 25 kDa.
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
7,
722-731.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Tjandra,
and
A.Bax
(1997).
Direct measurement of distances and angles in biomolecules by NMR in a dilute liquid crystalline medium.
|
| |
Science,
278,
1111-1114.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Tjandra,
J.G.Omichinski,
A.M.Gronenborn,
G.M.Clore,
and
A.Bax
(1997).
Use of dipolar 1H-15N and 1H-13C couplings in the structure determination of magnetically oriented macromolecules in solution.
|
| |
Nat Struct Biol,
4,
732-738.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

