
|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 215 a.a.
215 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 160 a.a.
160 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 288 a.a.
288 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 168 a.a.
168 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 32 a.a.
32 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 32 a.a.
32 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 37 a.a.
37 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 29 a.a.
29 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Photosynthesis
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of the cytochrome b6f complex with tridecyl- stigmatellin (tds) from m.Laminosus
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Cytochrome b6. Chain: a. Cytochrome b6-f complex subunit 4. Chain: b. Synonym: 17 kda polypeptide. Apocytochrome f. Chain: c. Cytochrome b6-f complex iron-sulfur subunit. Chain: d.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mastigocladus laminosus. Organism_taxid: 83541. Organism_taxid: 83541
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.41Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.188
|
R-free:
|
0.256
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
W.A.Cramer,E.Yamashita,H.Zhang
|
Key ref:

|
 |
E.Yamashita
et al.
(2007).
Structure of the Cytochrome b(6)f Complex: Quinone Analogue Inhibitors as Ligands of Heme c(n).
J Mol Biol,
370,
39-52.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
05-Jan-07
|
Release date:
|
12-Jun-07
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P83791
(CYB6_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6 from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
215 a.a.
215 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83792
(PETD_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6-f complex subunit 4 from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
160 a.a.
160 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83793
(CYF_MASLA) -
Cytochrome f from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
333 a.a.
288 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83794
(UCRI_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6-f complex iron-sulfur subunit from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
179 a.a.
168 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83795
(PETL_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6-f complex subunit 6 from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
32 a.a.
32 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83796
(PETM_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6-f complex subunit 7 from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
35 a.a.
32 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chain D:
E.C.7.1.1.6
- plastoquinol--plastocyanin reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 oxidized [plastocyanin] + a plastoquinol + 2 H+(in) = 2 reduced [plastocyanin] + a plastoquinone + 4 H+(out)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2
×
oxidized [plastocyanin]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 40.62% similarity
|
+
|
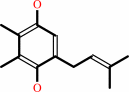 plastoquinol
plastoquinol
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)(in)
|
=
|
2
×
reduced [plastocyanin]
|
+
|
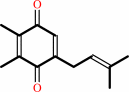 plastoquinone
plastoquinone
|
+
|
4
×
H(+)(out)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
370:39-52
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure of the Cytochrome b(6)f Complex: Quinone Analogue Inhibitors as Ligands of Heme c(n).
|
|
E.Yamashita,
H.Zhang,
W.A.Cramer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A native structure of the cytochrome b(6)f complex with improved resolution was
obtained from crystals of the complex grown in the presence of divalent cadmium.
Two Cd(2+) binding sites with different occupancy were determined: (i) a higher
affinity site, Cd1, which bridges His143 of cytochrome f and the acidic residue,
Glu75, of cyt b(6); in addition, Cd1 is coordinated by 1-2 H(2)O or 1-2 Cl(-);
(ii) a second site, Cd2, of lower affinity for which three identified ligands
are Asp58 (subunit IV), Glu3 (PetG subunit) and Glu4 (PetM subunit). Binding
sites of quinone analogue inhibitors were sought to map the pathway of transfer
of the lipophilic quinone across the b(6)f complex and to define the function of
the novel heme c(n). Two sites were found for the chromone ring of the
tridecyl-stigmatellin (TDS) quinone analogue inhibitor, one near the p-side
[2Fe-2S] cluster. A second TDS site was found on the n-side of the complex
facing the quinone exchange cavity as an axial ligand of heme c(n). A similar
binding site proximal to heme c(n) was found for the n-side inhibitor, NQNO.
Binding of these inhibitors required their addition to the complex before lipid
used to facilitate crystallization. The similar binding of NQNO and TDS as axial
ligands to heme c(n) implies that this heme utilizes plastoquinone as a natural
ligand, thus defining an electron transfer complex consisting of hemes b(n),
c(n), and PQ, and the pathway of n-side reduction of the PQ pool. The NQNO
binding site explains several effects associated with its inhibitory action: the
negative shift in heme c(n) midpoint potential, the increased amplitude of
light-induced heme b(n) reduction, and an altered EPR spectrum attributed to
interaction between hemes c(n) and b(n). A decreased extent of heme c(n)
reduction by reduced ferredoxin in the presence of NQNO allows observation of
the heme c(n) Soret band in a chemical difference spectrum.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Two cadmium (Cd^2+) binding sites on the p-side of
the M. laminosus b[6]f complex. (a) Position of higher occupancy
site (Cd1) is close to the inter-monomer interface, and that of
lower occupancy (Cd2) site is near the small subunits and the
exterior of the complex. View is parallel to the plane of the
membrane. Distances: (i) from Cd1 site, and (ii) from Cd2, to
the [2Fe-2S] cluster on the same and opposite side monomer, (i)
38.9 Å and 40.1 Å, and (ii) 57.1 and 28.0 Å.
Color code: cytochrome b[6] (cyan), subunit IV (purple),
cytochrome f (red), ISP (yellow), PetG, PetL, PetM, and PetN
(green). (b, stereo) Environment of Cd1 and Cd2 sites shown in
more detail. Lower occupancy of the Cd2 site is shown by the
smaller cage of electron density. A lipid molecule (possibly
galactolipid) described in the coordinates of the C. reinhardtii
b[6]f complex (pdb; 1Q90), but not previously discussed, is
closer to Cd2. Distances: higher (Cd1) to lower occupancy (Cd2)
Cd^2+ site, 23.2 Å; higher occupancy Cd1 site to heme
b[p], 24.0 Å; Cd2 to residues Glu78, Trp79 and Y80 of the
PEWY loop on the same monomer, 13, 12, and 16 Å. The seven
peaks of largest amplitude in the anomalous difference map are:
Cd1 site (18.5 σ), heme b[p] (18.1 σ), heme c[n] (17.6 σ),
heme b[n] (17.0 σ), heme f (13.3 σ), [2Fe-2S] site (11.1 σ),
Cd2 site (6.3 σ). The anomalous scattering factors (f  letter
double prime ) for Fe and Cd at 0.98 Å are 1.50 and 2.13,
respectively. The B factors of the Cd1 and Cd2 sites are 80
Å^2 and 178 Å^2. letter
double prime ) for Fe and Cd at 0.98 Å are 1.50 and 2.13,
respectively. The B factors of the Cd1 and Cd2 sites are 80
Å^2 and 178 Å^2.
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. F[o]–F[c] difference map of (a) p- and (b) n-side
binding site of TDS in the b[6]f complex. (a) p-side. The extra
density within H-bond distance of the His129 ligand of the
[2Fe-2S] cluster and between the ef and cd1 loops is attributed
to the chromone ring of TDS. As in Figure 2(a), the
origin of the electron density under the cd2 loop, presumably
lipid and/or detergent, is not known. (b) n-side. The position
of TDS is shown relative to heme c[n], which is exposed to the
quinone-exchange cavity. TDS is on the side of heme c[n] distal
to heme b[n]. TM helices and surface helices within loops
labeled as in Figure 2. F[o]–F[c] maps contoured at 4 σ.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2007,
370,
39-52)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
E.C.Hobbs,
F.Fontaine,
X.Yin,
and
G.Storz
(2011).
An expanding universe of small proteins.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
14,
167-173.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Szymańska,
J.Dłużewska,
I.Slesak,
and
J.Kruk
(2011).
Ferredoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase bound to cytochrome b₆f complex is active in plastoquinone reduction: implications for cyclic electron transport.
|
| |
Physiol Plant,
141,
289-298.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Dreher,
R.Hielscher,
A.Prodöhl,
P.Hellwig,
and
D.Schneider
(2010).
Characterization of two cytochrome b6 proteins from the cyanobacterium Gloeobacter violaceus PCC 7421.
|
| |
J Bioenerg Biomembr,
42,
517-526.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Baymann,
and
W.Nitschke
(2010).
Heliobacterial Rieske/cytb complex.
|
| |
Photosynth Res,
104,
177-187.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.McLuskey,
A.W.Roszak,
Y.Zhu,
and
N.W.Isaacs
(2010).
Crystal structures of all-alpha type membrane proteins.
|
| |
Eur Biophys J,
39,
723-755.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Guskov,
J.Kern,
A.Gabdulkhakov,
M.Broser,
A.Zouni,
and
W.Saenger
(2009).
Cyanobacterial photosystem II at 2.9-A resolution and the role of quinones, lipids, channels and chloride.
|
| |
Nat Struct Mol Biol,
16,
334-342.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.I.Twigg,
D.Baniulis,
W.A.Cramer,
and
M.P.Hendrich
(2009).
EPR detection of an O(2) surrogate bound to heme c(n) of the cytochrome b(6)f complex.
|
| |
J Am Chem Soc,
131,
12536-12537.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.de Lacroix de Lavalette,
L.Barucq,
J.Alric,
F.Rappaport,
and
F.Zito
(2009).
Is the redox state of the ci heme of the cytochrome b6f complex dependent on the occupation and structure of the Qi site and vice versa?
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
20822-20829.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Baniulis,
E.Yamashita,
J.P.Whitelegge,
A.I.Zatsman,
M.P.Hendrich,
S.S.Hasan,
C.M.Ryan,
and
W.A.Cramer
(2009).
Structure-Function, Stability, and Chemical Modification of the Cyanobacterial Cytochrome b6f Complex from Nostoc sp. PCC 7120.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
9861-9869.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Caffarri,
R.Kouril,
S.Kereïche,
E.J.Boekema,
and
R.Croce
(2009).
Functional architecture of higher plant photosystem II supercomplexes.
|
| |
EMBO J,
28,
3052-3063.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Esser,
M.Elberry,
F.Zhou,
C.A.Yu,
L.Yu,
and
D.Xia
(2008).
Inhibitor-complexed Structures of the Cytochrome bc1 from the Photosynthetic Bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
2846-2857.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.Lezhneva,
R.Kuras,
G.Ephritikhine,
and
C.de Vitry
(2008).
A Novel Pathway of Cytochrome c Biogenesis Is Involved in the Assembly of the Cytochrome b6f Complex in Arabidopsis Chloroplasts.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
24608-24616.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Lyska,
S.Paradies,
K.Meierhoff,
and
P.Westhoff
(2007).
HCF208, a homolog of Chlamydomonas CCB2, is required for accumulation of native cytochrome b6 in Arabidopsis thaliana.
|
| |
Plant Cell Physiol,
48,
1737-1746.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|

| |

