 |
PDBsum entry 2d2c

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Photosynthesis
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2d2c
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 202 a.a.
202 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 137 a.a.
137 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 286 a.a.
286 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 168 a.a.
168 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 32 a.a.
32 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 35 a.a.
35 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 27 a.a.
27 a.a.
|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

 27 a.a.
27 a.a.
|
 |

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Photosynthesis
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of cytochrome b6f complex with dbmib from m. Laminosus
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Cytochrome b6. Chain: a, n. Cytochrome b6-f complex subunit 4. Chain: b, o. Synonym: 17 kda polypeptide. Apocytochrome f. Chain: c, p. Cytochrome b6-f complex iron-sulfur subunit. Chain: d, q.
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mastigocladus laminosus. Organism_taxid: 83541. Organism_taxid: 83541
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 60mer (from
)
60mer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
3.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.276
|
R-free:
|
0.378
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
J.Yan,G.Kurisu,W.A.Cramer
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
J.Yan
et al.
(2006).
Intraprotein transfer of the quinone analogue inhibitor 2,5-dibromo-3-methyl-6-isopropyl-p-benzoquinone in the cytochrome b6f complex.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
69-74.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
07-Sep-05
|
Release date:
|
13-Dec-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P83791
(CYB6_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6 from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
215 a.a.
202 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83792
(PETD_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6-f complex subunit 4 from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
160 a.a.
137 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83793
(CYF_MASLA) -
Cytochrome f from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
333 a.a.
286 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83794
(UCRI_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6-f complex iron-sulfur subunit from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
179 a.a.
168 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83795
(PETL_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6-f complex subunit 6 from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
32 a.a.
32 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|

|

|
|
P83796
(PETM_MASLA) -
Cytochrome b6-f complex subunit 7 from Mastigocladus laminosus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
35 a.a.
35 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains D, Q:
E.C.7.1.1.6
- plastoquinol--plastocyanin reductase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
2 oxidized [plastocyanin] + a plastoquinol + 2 H+(in) = 2 reduced [plastocyanin] + a plastoquinone + 4 H+(out)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2
×
oxidized [plastocyanin]
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 61.11% similarity
|
+
|
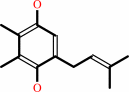 plastoquinol
plastoquinol
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)(in)
|
=
|
2
×
reduced [plastocyanin]
|
+
|
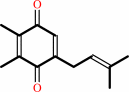 plastoquinone
plastoquinone
|
+
|
4
×
H(+)(out)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
103:69-74
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Intraprotein transfer of the quinone analogue inhibitor 2,5-dibromo-3-methyl-6-isopropyl-p-benzoquinone in the cytochrome b6f complex.
|
|
J.Yan,
G.Kurisu,
W.A.Cramer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Details are presented of the structural analysis of the cytochrome b(6)f complex
from the thermophilic cyanobacterium, Mastigocladus laminosus, in the presence
of the electrochemically positive (p)-side quinone analogue inhibitor,
2,5-dibromo-3-methyl-6-isopropylbenzoquinone (DBMIB). One DBMIB binding site was
found. This site is peripheral to the quinone binding space defined by the
binding sites of other p-side inhibitors previously resolved in cytochrome
bc(1)/b(6)f complexes. This high-affinity site resides in a p-side interfacial
niche bounded by cytochrome f, subunit IV, and cytochrome b(6), is close (8 A)
to the p-side heme b, but distant (19 A) from the [2Fe-2S] cluster. No
significant electron density associated with the DBMIB was found elsewhere in
the structure. However, the site at which DBMIB can inhibit light-induced redox
turnover is within a few A of the [2Fe-2S] cluster, as shown by the absence of
inhibition in mutants of Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 at iron sulfur
protein-Leu-111 near the cluster. The ability of a minimum amount of initially
oxidized DBMIB to inhibit turnover of WT complex after a second light flash
implies that there is a light-activated movement of DBMIB from the distal
peripheral site to an inhibitory site proximal to the [2Fe-2S] cluster. Together
with the necessary passage of quinone/quinol through the small Q(p) portal in
the complex, it is seen that transmembrane traffic of quinone-like molecules
through the core of cytochrome bc complexes can be labyrinthine.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

| | |

