 |
PDBsum entry 2cxn

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of mouse amf / phosphate complex
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase. Chain: a, b. Synonym: cytokine, gpi, phosphoglucose isomerase, pgi, phosphohexose isomerase, phi, neuroleukin, nlk. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Mus musculus. House mouse. Organism_taxid: 10090. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
1.40Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.172
|
R-free:
|
0.188
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
N.Tanaka,A.Haga,N.Naba,K.Shiraiwa,Y.Kusakabe,K.Hashimoto,T.Funasaka, H.Nagase,A.Raz,K.T.Nakamura
|
Key ref:

|
 |
N.Tanaka
et al.
(2006).
Crystal structures of mouse autocrine motility factor in complex with carbohydrate phosphate inhibitors provide insight into structure-activity relationship of the inhibitors.
J Mol Biol,
356,
312-324.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
30-Jun-05
|
Release date:
|
23-May-06
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P06745
(G6PI_MOUSE) -
Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase from Mus musculus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
558 a.a.
557 a.a.*
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|
*
PDB and UniProt seqs differ
at 2 residue positions (black
crosses)
|
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.9
- glucose-6-phosphate isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate = beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
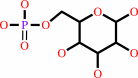 alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
|
=
|
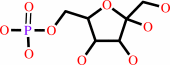 beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
356:312-324
(2006)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of mouse autocrine motility factor in complex with carbohydrate phosphate inhibitors provide insight into structure-activity relationship of the inhibitors.
|
|
N.Tanaka,
A.Haga,
N.Naba,
K.Shiraiwa,
Y.Kusakabe,
K.Hashimoto,
T.Funasaka,
H.Nagase,
A.Raz,
K.T.Nakamura.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Autocrine motility factor (AMF), a tumor-secreted cytokine, stimulates cell
migration in vitro and metastasis in vivo. AMF is identical to the extracellular
cytokines neuroleukin and maturation factor and, interestingly, to the
intracellular enzyme phosphoglucose isomerase. The cytokine activity of AMF is
inhibited by carbohydrate phosphate compounds as they compete for AMF binding
with the carbohydrate moiety of the AMF receptor (AMFR), which is a glycosylated
seven transmembrane helix protein. Here, we report the first comprehensive
high-resolution crystal structure analyses of the inhibitor-free form and the
eight types of inhibitor (phosphate, erythrose 4-phosphate (E4P), arabinose
5-phosphate (A5P), sorbitol 6-phosphate (S6P), 6-phosphogluconic acid (6PGA),
fructose 6-phosphate (F6P), glucose 6-phosphate (G6P), or mannose 6-phosphate
(M6P)) complexes of mouse AMF (mAMF). We assayed the inhibitory activities of
these inhibitors against the cytokine activity of mAMF. The inhibitory
activities of the six-carbon sugars (G6P, F6P, M6P, and 6PGA) were found to be
significantly higher than those of the four or five-carbon sugars (E4P or A5P).
The inhibitory activities clearly depend on the length of the inhibitor
molecules. A structural comparison revealed that a water-mediated hydrogen bond
between one end of the inhibitor and a rigid portion of the protein surface in
the shorter-chain inhibitor (E4P) complex is replaced by a direct hydrogen bond
in the longer-chain inhibitor (6PGA) complex. Thus, to obtain a new compound
with higher inhibitory activities against AMF, water molecules at the inhibitor
binding site of AMF should be replaced by a functional group of inhibitors in
order to introduce direct interactions with the protein surface. The present
structure-activity relationship studies will be valuable not only for designing
more effective AMF inhibitors but also for studying general protein-inhibitor
interactions.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. The inhibitor-binding site in subunit A of mouse
AMF. The carbon and phosphorus atoms of the bound inhibitor
molecule are shown in cyan and green, respectively. The bound
inhibitor molecule is superimposed on the F[o] -F[c] omit
electron density map (contoured at 15.0s (red) and 3.0s (violet)
for (a), (b), (g), and (h), and at 15.0s (red) and 4.0s (violet)
for (c), (d), (e), and (f)). Possible hydrogen bonds are
indicated by broken lines (green). The bound water molecules are
shown as ball models (pink). (a) Acetate (in inhibitor-free
mAMF); (b) phosphate; (c) E4P; (d) A5P; (e) S6P; (f) 6PGA; (g)
F6P; (h) G6P (the bound ligand is modeled as the reaction
product F6P).
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. Inhibitory activities of carbohydrate phosphate
compounds against the cytokine activity of mAMF. (a) The cell
motility-stimulating activity of mAMF toward mouse melanoma
B16-BL6 cells analyzed by phagokinetic track assay in the
presence of various inhibitors at three concentrations
([inhibitor]/[mAMF]=1/5, 1, and 5). (b) Statistical analysis for
the difference of the inhibitory activities of AMF inhibitors
examined by Student's t-test (n>30).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2006,
356,
312-324)
copyright 2006.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.Tanaka
(2007).
[Structural and functional studies on proteins as potential drug discovery targets]
|
| |
Yakugaku Zasshi,
127,
1673-1683.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

