 |
PDBsum entry 2cgo

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2cgo
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.30
- hypoxia-inducible factor-asparagine dioxygenase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-asparaginyl-[hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunit] + 2-oxoglutarate + O2 = (3S)-3-hydroxy-L-asparaginyl-[hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunit] + succinate + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-asparaginyl-[hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunit]
|
+
|
 2-oxoglutarate
2-oxoglutarate
|
+
|
 O2
O2
|
=
|
(3S)-3-hydroxy-L-asparaginyl-[hypoxia-inducible factor alpha subunit]
|
+
|
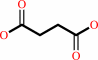 succinate
succinate
|
+
|
CO2
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Fe(2+); L-ascorbate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Fe(2+)
|
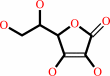 L-ascorbate
L-ascorbate
|
|
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.1.14.11.n4
- ?????
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
282:3293-3301
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural and mechanistic studies on the inhibition of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor hydroxylases by tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates.
|
|
K.S.Hewitson,
B.M.Liénard,
M.A.McDonough,
I.J.Clifton,
D.Butler,
A.S.Soares,
N.J.Oldham,
L.A.McNeill,
C.J.Schofield.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In humans both the levels and activity of the alpha-subunit of the
hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (HIF-alpha) are regulated by its
post-translation hydroxylation as catalyzed by iron- and 2-oxoglutarate
(2OG)-dependent prolyl and asparaginyl hydroxylases (PHD1-3 and
factor-inhibiting HIF (FIH), respectively). One consequence of hypoxia is the
accumulation of tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediates (TCAIs). In vitro assays
were used to assess non-2OG TCAIs as inhibitors of purified PHD2 and FIH. Under
the assay conditions, no significant FIH inhibition was observed by the TCAIs or
pyruvate, but fumarate, succinate, and isocitrate inhibited PHD2. Mass
spectrometric analyses under nondenaturing conditions were used to investigate
the binding of TCAIs to PHD2 and supported the solution studies. X-ray crystal
structures of FIH in complex with Fe(II) and fumarate or succinate revealed
similar binding modes for each in the 2OG co-substrate binding site. The in
vitro results suggest that the cellular inhibition of PHD2, but probably not
FIH, by fumarate and succinate may play a role in the Warburg effect providing
that appropriate relative concentrations of the components are achieved under
physiological conditions.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
FIGURE 1. The reactions catalyzed by the HIF hydroxylases
(PHDs and FIH).
|
 |
Figure 4.
FIGURE 4. Inhibition of t-PHD2 by the TCAIs (at 1 mM final
concentration). No inc refers to the assay without a
preincubation step; 1hrinc refers to a 1-h preincubation of
t-PHD2 with iron, buffer, and compound (where applicable), and
1hrinc + asc refers to a 1-h preincubation of t-PHD2 with iron,
buffer, and ascorbate.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2007,
282,
3293-3301)
copyright 2007.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
A.E.Hansen,
A.T.Kristensen,
I.Law,
J.T.Jørgensen,
and
S.A.Engelholm
(2011).
Hypoxia-inducible factors--regulation, role and comparative aspects in tumourigenesis.
|
| |
Vet Comp Oncol,
9,
16-37.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Frezza,
P.J.Pollard,
and
E.Gottlieb
(2011).
Inborn and acquired metabolic defects in cancer.
|
| |
J Mol Med,
89,
213-220.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Chowdhury,
K.K.Yeoh,
Y.M.Tian,
L.Hillringhaus,
E.A.Bagg,
N.R.Rose,
I.K.Leung,
X.S.Li,
E.C.Woon,
M.Yang,
M.A.McDonough,
O.N.King,
I.J.Clifton,
R.J.Klose,
T.D.Claridge,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
C.J.Schofield,
and
A.Kawamura
(2011).
The oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate inhibits histone lysine demethylases.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
12,
463-469.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Czibik
(2010).
Complex role of the HIF system in cardiovascular biology.
|
| |
J Mol Med,
88,
1101-1111.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.L.Semenza
(2010).
HIF-1: upstream and downstream of cancer metabolism.
|
| |
Curr Opin Genet Dev,
20,
51-56.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Moon,
S.Han,
H.Park,
and
J.Choe
(2010).
Crystal structures of human FIH-1 in complex with quinol family inhibitors.
|
| |
Mol Cells,
29,
471-474.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.M.Phang,
W.Liu,
and
O.Zabirnyk
(2010).
Proline metabolism and microenvironmental stress.
|
| |
Annu Rev Nutr,
30,
441-463.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.O'Flaherty,
J.Adam,
L.C.Heather,
A.V.Zhdanov,
Y.L.Chung,
M.X.Miranda,
J.Croft,
S.Olpin,
K.Clarke,
C.W.Pugh,
J.Griffiths,
D.Papkovsky,
H.Ashrafian,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
and
P.J.Pollard
(2010).
Dysregulation of hypoxia pathways in fumarate hydratase-deficient cells is independent of defective mitochondrial metabolism.
|
| |
Hum Mol Genet,
19,
3844-3851.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Sakurai,
N.R.Rose,
L.Schultz,
A.M.Quinn,
A.Jadhav,
S.S.Ng,
U.Oppermann,
C.J.Schofield,
and
A.Simeonov
(2010).
A miniaturized screen for inhibitors of Jumonji histone demethylases.
|
| |
Mol Biosyst,
6,
357-364.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Nagel,
N.P.Talbot,
J.Mecinović,
T.G.Smith,
A.M.Buchan,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2010).
Therapeutic manipulation of the HIF hydroxylases.
|
| |
Antioxid Redox Signal,
12,
481-501.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Jokilehto,
and
P.M.Jaakkola
(2010).
The role of HIF prolyl hydroxylases in tumour growth.
|
| |
J Cell Mol Med,
14,
758-770.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Schubert,
T.Soucek,
and
B.Blouw
(2009).
The induction of HIF-1 reduces astrocyte activation by amyloid beta peptide.
|
| |
Eur J Neurosci,
29,
1323-1334.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Roudier,
and
A.Perrin
(2009).
Considering the role of pyruvate in tumor cells during hypoxia.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1796,
55-62.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Paddenberg,
N.Howold,
C.Hoger,
H.Janssen,
V.Grau,
and
W.Kummer
(2009).
Organ preservation solutions attenuate accumulation and nuclear translocation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in the hepatoma cell line HepG2.
|
| |
Cell Biochem Funct,
27,
516-525.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Bleijlevens,
T.Shivarattan,
E.Flashman,
Y.Yang,
P.J.Simpson,
P.Koivisto,
B.Sedgwick,
C.J.Schofield,
and
S.J.Matthews
(2008).
Dynamic states of the DNA repair enzyme AlkB regulate product release.
|
| |
EMBO Rep,
9,
872-877.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.M.Lienard,
A.Conejo-García,
I.Stolze,
C.Loenarz,
N.J.Oldham,
P.J.Ratcliffe,
and
C.J.Schofield
(2008).
Evaluation of aspirin metabolites as inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor hydroxylases.
|
| |
Chem Commun (Camb),
(),
6393-6395.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.H.Fong,
and
K.Takeda
(2008).
Role and regulation of prolyl hydroxylase domain proteins.
|
| |
Cell Death Differ,
15,
635-641.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Lisy,
and
D.J.Peet
(2008).
Turn me on: regulating HIF transcriptional activity.
|
| |
Cell Death Differ,
15,
642-649.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Bishop,
D.Gallagher,
A.Pascual,
C.A.Lygate,
J.P.de Bono,
L.G.Nicholls,
P.Ortega-Saenz,
H.Oster,
B.Wijeyekoon,
A.I.Sutherland,
A.Grosfeld,
J.Aragones,
M.Schneider,
K.van Geyte,
D.Teixeira,
A.Diez-Juan,
J.Lopez-Barneo,
K.M.Channon,
P.H.Maxwell,
C.W.Pugh,
A.M.Davies,
P.Carmeliet,
and
P.J.Ratcliffe
(2008).
Abnormal sympathoadrenal development and systemic hypotension in PHD3-/- mice.
|
| |
Mol Cell Biol,
28,
3386-3400.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.McFate,
A.Mohyeldin,
H.Lu,
J.Thakar,
J.Henriques,
N.D.Halim,
H.Wu,
M.J.Schell,
T.M.Tsang,
O.Teahan,
S.Zhou,
J.A.Califano,
N.H.Jeoung,
R.A.Harris,
and
A.Verma
(2008).
Pyruvate dehydrogenase complex activity controls metabolic and malignant phenotype in cancer cells.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
22700-22708.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.G.Kaelin,
and
P.J.Ratcliffe
(2008).
Oxygen sensing by metazoans: the central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway.
|
| |
Mol Cell,
30,
393-402.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

