 |
PDBsum entry 2bc1

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2bc1
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.7.1.1.2
- NADH:ubiquinone reductase (H(+)-translocating).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
a ubiquinone + NADH + 5 H+(in) = a ubiquinol + NAD+ + 4 H+(out)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 ubiquinone
ubiquinone
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
5
×
H(+)(in)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 76.36% similarity
|
=
|
 ubiquinol
ubiquinol
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
+
|
4
×
H(+)(out)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
FMN; Iron-sulfur
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
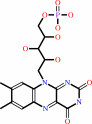 FMN
FMN
|
 Iron-sulfur
Iron-sulfur
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
54:6815-6829
(2015)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural Analysis of Streptococcus pyogenes NADH Oxidase: Conformational Dynamics Involved in Formation of the C(4a)-Peroxyflavin Intermediate.
|
|
J.R.Wallen,
T.C.Mallett,
T.Okuno,
D.Parsonage,
H.Sakai,
T.Tsukihara,
A.Claiborne.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
In probing the oxygen reactivity of an Enterococcus faecalis NADH oxidase (Nox;
O2 → 2H2O) C42S mutant lacking the Cys42-sulfenic acid (Cys42-SOH) redox
center, we provided direct evidence of a C(4a)-peroxyflavin intermediate in the
oxidative half-reaction and also described a conformational or chemical change
that is rate-limiting for full reoxidation of the homodimer. In this work, the
Nox from Streptococcus pyogenes (SpyNox) has been expressed and crystallized,
and the overoxidized wild-type [Cys44-SOH → Cys44-sulfinic acid (Cys44-SO2H)]
and C44S mutant enzyme structures have been refined at 2.0 and 2.15 Å,
respectively. We show that azide binds to the two-electron reduced wild-type
(EH2) enzyme and to the mutant enzyme in solution, but with a significantly
higher affinity for the mutant protein. The spectral course of the titration
with the SpyNox EH2 form clearly indicates progressive displacement of the
Cys44-S(-) → FAD charge-transfer interaction. An azide soak with C44S Nox
crystals led to the structure of the complex, as refined at 2.10 Å. The
active-site N3(-) ligand is proximal to the Ser44 and His11 side chains, and a
significant shift in the Ser44 side chain also appears. This provides an
attractive explanation for the azide-induced loss of charge-transfer absorbance
seen with the wild-type EH2 form and also permits accommodation of a
C(4a)-peroxyflavin structural model. The conformation of Ser44 and the
associated helical element, and the resulting steric accommodation, appear to be
linked to the conformational change described in the E. faecalis C42S Nox
oxidative half-reaction.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

