 |
PDBsum entry 2a5h

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
2.1 angstrom x-ray crystal structure of lysine-2,3-aminomutase from clostridium subterminale sb4, with michaelis analog (l-alpha-lysine external aldimine form of pyridoxal-5'-phosphate).
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
L-lysine 2,3-aminomutase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Clostridium subterminale. Organism_taxid: 1550. Gene: kama. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.187
|
R-free:
|
0.225
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
B.W.Lepore,F.J.Ruzicka,P.A.Frey,D.Ringe
|
Key ref:

|
 |
B.W.Lepore
et al.
(2005).
The x-ray crystal structure of lysine-2,3-aminomutase from Clostridium subterminale.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
13819-13824.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
30-Jun-05
|
Release date:
|
04-Oct-05
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q9XBQ8
(KAMA_CLOSU) -
L-lysine 2,3-aminomutase from Clostridium subterminale
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
416 a.a.
409 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.5.4.3.2
- lysine 2,3-aminomutase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Lysine 2,3-Aminomutase
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-lysine = (3S)-3,6-diaminohexanoate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
L-lysine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
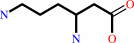 (3S)-3,6-diaminohexanoate
(3S)-3,6-diaminohexanoate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Iron-sulfur
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
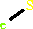 Iron-sulfur
Iron-sulfur
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
102:13819-13824
(2005)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The x-ray crystal structure of lysine-2,3-aminomutase from Clostridium subterminale.
|
|
B.W.Lepore,
F.J.Ruzicka,
P.A.Frey,
D.Ringe.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The x-ray crystal structure of the pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (PLP),
S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM), and [4Fe-4S]-dependent lysine-2,3-aminomutase
(LAM) of Clostridium subterminale has been solved to 2.1-A resolution by
single-wavelength anomalous dispersion methods on a
L-selenomethionine-substituted complex of LAM with [4Fe-4S]2+, PLP, SAM, and
L-alpha-lysine, a very close analog of the active Michaelis complex. The unit
cell contains a dimer of hydrogen-bonded, domain-swapped dimers, the subunits of
which adopt a fold that contains all three cofactors in a central channel
defined by six beta/alpha structural units. Zinc coordination links the
domain-swapped dimers. In each subunit, the solvent face of the channel is
occluded by an N-terminal helical domain, with the opposite end of the channel
packed against the domain-swapped subunit. Hydrogen-bonded ionic contacts hold
the external aldimine of PLP and L-alpha-lysine in position for abstraction of
the 3-pro-R hydrogen of lysine by C5' of SAM. The structure of the SAM/[4Fe-4S]
complex confirms and extends conclusions from spectroscopic studies of LAM and
shows selenium in Se-adenosyl-L-selenomethionine poised to ligate the unique
iron in the [4Fe-4S] cluster upon electron transfer and radical formation. The
chain fold in the central domain is in part analogous to other radical-SAM
enzymes.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 4.
Fig. 4. Ball-and-stick, wall-eyed stereodiagram figure of
the active site. This wall-eyed stereodiagram emphasizes the
stereochemical relationships of the three cofactors, one as
lysyl-PLP external aldimine. The C5' carbon of SeSAM where
radical initiation will occur is 3.8 Å from C3 of the
lysyl side chain. The conserved Arg-134 denies rotation around
the C1-C2 bond of lysyl moiety. Asp-293 interacts with both the
 -amino group of lysine
and N1 of the purine ring of SeSAM, and Asp-330 is in
hydrogen-bonded contact with the -amino group of lysine
and N1 of the purine ring of SeSAM, and Asp-330 is in
hydrogen-bonded contact with the  -amino group. SeSAM is
ligated to the unique iron in the [4Fe-4S] cluster through the
selenomethionyl -amino group. SeSAM is
ligated to the unique iron in the [4Fe-4S] cluster through the
selenomethionyl  -amino and carboxylate
groups. See Fig. 8 for detailed interactions within the active
site. Hydrogen atom positions are provided for reference based
on theoretical constraints only and are not determined by the
diffraction data. -amino and carboxylate
groups. See Fig. 8 for detailed interactions within the active
site. Hydrogen atom positions are provided for reference based
on theoretical constraints only and are not determined by the
diffraction data.
|
 |
Figure 5.
Fig. 5. Close-up of the interaction between N1 of PLP and a
fixed water molecule. This water molecule is held precisely in
place in all four subunits by three main-chain hydrogen bonds
from residues in the loop (R[112]YPDR[116]). The nature of the
hydrogen bonding partners would uniquely position this water
such that a water proton is hydrogen bonded with N1 of the
pyridine nitrogen, implying that the pyridoxal ring is
unprotonated.
|
 |
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
P.L.Roach
(2011).
Radicals from S-adenosylmethionine and their application to biosynthesis.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
15,
267-275.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Kamachi,
T.Kouno,
K.Doitomi,
and
K.Yoshizawa
(2011).
Generation of adenosyl radical from S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) in biotin synthase.
|
| |
J Inorg Biochem,
105,
850-857.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.N.Marsh,
D.P.Patterson,
and
L.Li
(2010).
Adenosyl radical: reagent and catalyst in enzyme reactions.
|
| |
Chembiochem,
11,
604-621.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.B.Broderick
(2010).
Biochemistry: A radically different enzyme.
|
| |
Nature,
465,
877-878.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Silver,
T.Chandra,
E.Zilinskas,
S.Ghose,
W.E.Broderick,
and
J.B.Broderick
(2010).
Complete stereospecific repair of a synthetic dinucleotide spore photoproduct by spore photoproduct lyase.
|
| |
J Biol Inorg Chem,
15,
943-955.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Zhang,
X.Zhu,
A.T.Torelli,
M.Lee,
B.Dzikovski,
R.M.Koralewski,
E.Wang,
J.Freed,
C.Krebs,
S.E.Ealick,
and
H.Lin
(2010).
Diphthamide biosynthesis requires an organic radical generated by an iron-sulphur enzyme.
|
| |
Nature,
465,
891-896.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.H.Tang,
S.O.Mansoorabadi,
G.H.Reed,
and
P.A.Frey
(2009).
Radical triplets and suicide inhibition in reactions of 4-thia-D- and 4-thia-L-lysine with lysine 5,6-aminomutase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
48,
8151-8160.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.S.Duschene,
S.E.Veneziano,
S.C.Silver,
and
J.B.Broderick
(2009).
Control of radical chemistry in the AdoMet radical enzymes.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
13,
74-83.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Percudani,
and
A.Peracchi
(2009).
The B6 database: a tool for the description and classification of vitamin B6-dependent enzymatic activities and of the corresponding protein families.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
10,
273.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Nicolet,
P.Amara,
J.M.Mouesca,
and
J.C.Fontecilla-Camps
(2009).
Unexpected electron transfer mechanism upon AdoMet cleavage in radical SAM proteins.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
14867-14871.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Chatterjee,
Y.Li,
Y.Zhang,
T.L.Grove,
M.Lee,
C.Krebs,
S.J.Booker,
T.P.Begley,
and
S.E.Ealick
(2008).
Reconstitution of ThiC in thiamine pyrimidine biosynthesis expands the radical SAM superfamily.
|
| |
Nat Chem Biol,
4,
758-765.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Vey,
J.Yang,
M.Li,
W.E.Broderick,
J.B.Broderick,
and
C.L.Drennan
(2008).
Structural basis for glycyl radical formation by pyruvate formate-lyase activating enzyme.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
105,
16137-16141.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.L.Grove,
K.H.Lee,
J.St Clair,
C.Krebs,
and
S.J.Booker
(2008).
In vitro characterization of AtsB, a radical SAM formylglycine-generating enzyme that contains three [4Fe-4S] clusters.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
47,
7523-7538.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Marquet,
B.T.Bui,
A.G.Smith,
and
M.J.Warren
(2007).
Iron-sulfur proteins as initiators of radical chemistry.
|
| |
Nat Prod Rep,
24,
1027-1040.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.J.Ruzicka,
and
P.A.Frey
(2007).
Glutamate 2,3-aminomutase: a new member of the radical SAM superfamily of enzymes.
|
| |
Biochim Biophys Acta,
1774,
286-296.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Wang,
and
P.A.Frey
(2007).
Binding energy in the one-electron reductive cleavage of S-adenosylmethionine in lysine 2,3-aminomutase, a radical SAM enzyme.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
12889-12895.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.C.Wang,
and
P.A.Frey
(2007).
S-adenosylmethionine as an oxidant: the radical SAM superfamily.
|
| |
Trends Biochem Sci,
32,
101-110.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Dai,
R.Friemann,
D.A.Glauser,
F.Bourquin,
W.Manieri,
P.Schürmann,
and
H.Eklund
(2007).
Structural snapshots along the reaction pathway of ferredoxin-thioredoxin reductase.
|
| |
Nature,
448,
92-96.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Goto-Ito,
R.Ishii,
T.Ito,
R.Shibata,
E.Fusatomi,
S.I.Sekine,
Y.Bessho,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2007).
Structure of an archaeal TYW1, the enzyme catalyzing the second step of wye-base biosynthesis.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
63,
1059-1068.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Booker,
R.M.Cicchillo,
and
T.L.Grove
(2007).
Self-sacrifice in radical S-adenosylmethionine proteins.
|
| |
Curr Opin Chem Biol,
11,
543-552.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Behshad,
F.J.Ruzicka,
S.O.Mansoorabadi,
D.Chen,
G.H.Reed,
and
P.A.Frey
(2006).
Enantiomeric free radicals and enzymatic control of stereochemistry in a radical mechanism: the case of lysine 2,3-aminomutases.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
45,
12639-12646.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Chartron,
K.S.Carroll,
C.Shiau,
H.Gao,
J.A.Leary,
C.R.Bertozzi,
and
C.D.Stout
(2006).
Substrate recognition, protein dynamics, and iron-sulfur cluster in Pseudomonas aeruginosa adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate reductase.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
364,
152-169.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.H.Naismith
(2006).
Inferring the chemical mechanism from structures of enzymes.
|
| |
Chem Soc Rev,
35,
763-770.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Hänzelmann,
and
H.Schindelin
(2006).
Binding of 5'-GTP to the C-terminal FeS cluster of the radical S-adenosylmethionine enzyme MoaA provides insights into its mechanism.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
6829-6834.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.Buckel,
and
B.T.Golding
(2006).
Radical enzymes in anaerobes.
|
| |
Annu Rev Microbiol,
60,
27-49.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

