 |
PDBsum entry 2zc5

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Biosynthetic protein
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
2zc5
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.2.4.99.28
- peptidoglycan glycosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
[GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)](n)- di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate + beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)- Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)-di-trans,octa- cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate = [GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D- Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)](n+1)-di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate + di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
[GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)](n)- di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)- Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)-di-trans,octa- cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
=
|
[GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D- Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)](n+1)-di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
 di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 3:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D:
E.C.3.4.16.4
- serine-type D-Ala-D-Ala carboxypeptidase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
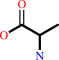
D-alanyl-D-alanine + H2O = 2 D-alanine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
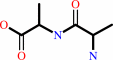 [GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)](n)- di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
[GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)](n)- di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
+
|
beta-D-GlcNAc-(1->4)- Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D-Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)-di-trans,octa- cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
=
|
 2
×
[GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D- Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)](n+1)-di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
2
×
[GlcNAc-(1->4)-Mur2Ac(oyl-L-Ala-gamma-D- Glu-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala)](n+1)-di-trans,octa-cis-undecaprenyl diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Antimicrob Agents Chemother
52:2053-2060
(2008)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Crystal structures of biapenem and tebipenem complexed with penicillin-binding proteins 2X and 1A from Streptococcus pneumoniae.
|
|
M.Yamada,
T.Watanabe,
N.Baba,
Y.Takeuchi,
F.Ohsawa,
S.Gomi.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Biapenem is a parenteral carbapenem antibiotic that exhibits wide-ranging
antibacterial activity, remarkable chemical stability, and extensive stability
against human renal dehydropeptidase-I. Tebipenem is the active form of
tebipenem pivoxil, a novel oral carbapenem antibiotic that has a high level of
bioavailability in humans, in addition to the above-mentioned features.
beta-lactam antibiotics, including carbapenems, target penicillin-binding
proteins (PBPs), which are membrane-associated enzymes that play essential roles
in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. To envisage the binding of carbapenems to PBPs,
we determined the crystal structures of the trypsin-digested forms of both PBP
2X and PBP 1A from Streptococcus pneumoniae strain R6, each complexed with
biapenem or tebipenem. The structures of the complexes revealed that the
carbapenem C-2 side chains form hydrophobic interactions with Trp374 and Thr526
of PBP 2X and with Trp411 and Thr543 of PBP 1A. The Trp and Thr residues are
conserved in PBP 2B. These results suggest that interactions between the C-2
side chains of carbapenems and the conserved Trp and Thr residues in PBPs play
important roles in the binding of carbapenems to PBPs.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
S.Sainsbury,
L.Bird,
V.Rao,
S.M.Shepherd,
D.I.Stuart,
W.N.Hunter,
R.J.Owens,
and
J.Ren
(2011).
Crystal structures of penicillin-binding protein 3 from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: comparison of native and antibiotic-bound forms.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
405,
173-184.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Powell,
J.Tomberg,
A.M.Deacon,
R.A.Nicholas,
and
C.Davies
(2009).
Crystal structures of penicillin-binding protein 2 from penicillin-susceptible and -resistant strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae reveal an unexpectedly subtle mechanism for antibiotic resistance.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
1202-1212.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |
|

