 |
PDBsum entry 2vxo

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Ligase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Human gmp synthetase in complex with xmp
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Gmp synthase [glutamine-hydrolyzing]. Chain: a, b. Fragment: residues 20-693. Synonym: glutamine amidotransferase, gmp synthetase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Homo sapiens. Human. Organism_taxid: 9606. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 469008. Expression_system_variant: r3 prare.
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.206
|
R-free:
|
0.256
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Welin,L.Lehtio,J.Andersson,C.H.Arrowsmith,H.Berglund,R.Collins, L.G.Dahlgren,A.M.Edwards,S.Flodin,A.Flores,S.Graslund,M.Hammarstrom, A.Johansson,I.Johansson,T.Karlberg,T.Kotenyova,M.Moche,M.E.Nilsson, T.Nyman,K.Olesen,C.Persson,J.Sagemark,H.Schueler,A.G.Thorsell, L.Tresaugues,S.Van Den Berg,M.Wisniewska,M.Wikstrom,P.Nordlund
|
|
Key ref:
|
 |
M.Welin
et al.
(2013).
Substrate specificity and oligomerization of human GMP synthetase.
J Mol Biol,
425,
4323-4333.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
08-Jul-08
|
Release date:
|
12-Aug-08
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P49915
(GUAA_HUMAN) -
GMP synthase [glutamine-hydrolyzing] from Homo sapiens
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
693 a.a.
643 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.3.5.2
- Gmp synthase (glutamine-hydrolyzing).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
AMP and GMP Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
XMP + L-glutamine + ATP + H2O = GMP + L-glutamate + AMP + diphosphate + 2 H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
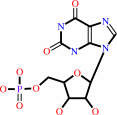 XMP
XMP
|
+
|
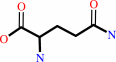 L-glutamine
L-glutamine
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
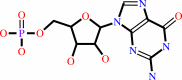 GMP
GMP
|
+
|
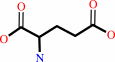 L-glutamate
L-glutamate
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
+
|
2
×
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
425:4323-4333
(2013)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Substrate specificity and oligomerization of human GMP synthetase.
|
|
M.Welin,
L.Lehtiö,
A.Johansson,
S.Flodin,
T.Nyman,
L.Trésaugues,
M.Hammarström,
S.Gräslund,
P.Nordlund.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Guanine monophosphate (GMP) synthetase is a bifunctional two-domain enzyme. The
N-terminal glutaminase domain generates ammonia from glutamine and the
C-terminal synthetase domain aminates xanthine monophosphate (XMP) to form GMP.
Mammalian GMP synthetases (GMPSs) contain a 130-residue-long insert in the
synthetase domain in comparison to bacterial proteins. We report here the
structure of a eukaryotic GMPS. Substrate XMP was bound in the crystal structure
of the human GMPS enzyme. XMP is bound to the synthetase domain and covered by a
LID motif. The enzyme forms a dimer in the crystal structure with subunit
orientations entirely different from the bacterial counterparts. The inserted
sub-domain is shown to be involved in substrate binding and dimerization.
Furthermore, the structural basis for XMP recognition is revealed as well as a
potential allosteric site. Enzymes in the nucleotide metabolism typically
display an increased activity in proliferating cells due to the increased need
for nucleotides. Many drugs used as immunosuppressants and for treatment of
cancer and viral diseases are indeed nucleobase- and nucleoside-based compounds,
which are acting on or are activated by enzymes in this pathway. The information
obtained from the crystal structure of human GMPS might therefore aid in
understanding interactions of nucleoside-based drugs with GMPS and in
structure-based design of GMPS-specific inhibitors.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

