 |
PDBsum entry 2i7b

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.37
- fucosylgalactoside 3-alpha-galactosyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-galactosyl derivative + UDP-alpha-D- galactose = an alpha-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-[alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)]-beta-D- galactosyl derivative + UDP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-galactosyl derivative
|
+
|
UDP-alpha-D- galactose
|
=
|
alpha-D-galactosyl-(1->3)-[alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)]-beta-D- galactosyl derivative
|
+
|
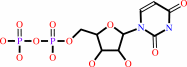 UDP
UDP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.40
- glycoprotein-fucosylgalactoside alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
an alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-galactosyl derivative + UDP-N-acetyl- alpha-D-galactosamine = an N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosaminyl-(1->3)-[alpha- L-fucosyl-(1->2)]-beta-D-galactosyl derivative + UDP + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-L-fucosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-galactosyl derivative
|
+
|
UDP-N-acetyl- alpha-D-galactosamine
|
=
|
N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosaminyl-(1->3)-[alpha- L-fucosyl-(1->2)]-beta-D-galactosyl derivative
|
+
|
 UDP
UDP
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Transfusion
47:864-875
(2007)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural basis for red cell phenotypic changes in newly identified, naturally occurring subgroup mutants of the human blood group B glycosyltransferase.
|
|
B.Hosseini-Maaf,
J.A.Letts,
M.Persson,
E.Smart,
P.Y.LePennec,
H.Hustinx,
Z.Zhao,
M.M.Palcic,
S.V.Evans,
M.A.Chester,
M.L.Olsson.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
BACKGROUND: Four amino-acid-changing polymorphisms differentiate the blood group
A and B alleles. Multiple missense mutations are associated with weak expression
of A and B antigens but the structural changes causing subgroups have not been
studied. STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: Individuals or families having serologically
weak B antigen on their red cells were studied. Alleles were characterized by
sequencing of exons 1 through 7 in the ABO gene. Single crystal X-ray
diffraction, three-dimensional-structure molecular modeling, and enzyme kinetics
showed the effects of the B allele mutations on the glycosyltransferases.
RESULTS: Seven unrelated individuals with weak B phenotypes possessed seven
different B alleles, five of which are new and result in substitution of highly
conserved amino acids: M189V, I192T, F216I, D262N, and A268T. One of these
(F216I) was due to a hybrid allele resulting from recombination between B and
O(1v) alleles. The two other alleles were recently described in other ethnic
groups and result in V175M and L232P. The first crystal-structure determination
(A268T) of a subgroup glycosyltransferase and molecular modeling (F216I, D262N,
L232P) indicated conformational changes in the enzyme that could explain the
diminished enzyme activity. The effect of three mutations could not be
visualized since they occur in a disordered loop. CONCLUSION: The genetic
background for B(w) phenotypes is very heterogeneous but usually arises through
seemingly random missense mutations throughout the last ABO exon. The targeted
amino acid residues, however, are well conserved during evolution. Based on
analysis of the resulting structural changes in the glycosyltransferase, the
mutations are likely to disrupt molecular bonds of importance for enzymatic
function.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
L.L.Lairson,
B.Henrissat,
G.J.Davies,
and
S.G.Withers
(2008).
Glycosyltransferases: structures, functions, and mechanisms.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
77,
521-555.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.H.Yazer,
B.Hosseini-Maaf,
and
M.L.Olsson
(2008).
Blood grouping discrepancies between ABO genotype and phenotype caused by O alleles.
|
| |
Curr Opin Hematol,
15,
618-624.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |

