 |
PDBsum entry 1w3t

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Sulfolobus solfataricus 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate (kdg) aldolase complex with d-kdgal, d-glyceraldehyde and pyruvate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2-keto-3-deoxy gluconate aldolase. Chain: a, b, c, d. Synonym: eda. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Sulfolobus solfataricus. Organism_taxid: 2287. Expressed in: escherichia coli bl21(de3). Expression_system_taxid: 469008.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
Tetramer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.10Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.155
|
R-free:
|
0.204
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
A.Theodossis,H.Walden,E.J.Westwick,H.Connaris,H.J.Lamble,D.W.Hough, M.J.Danson,G.L.Taylor
|
Key ref:

|
 |
A.Theodossis
et al.
(2004).
The structural basis for substrate promiscuity in 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate aldolase from the Entner-Doudoroff pathway in Sulfolobus solfataricus.
J Biol Chem,
279,
43886-43892.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
19-Jul-04
|
Release date:
|
02-Sep-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
O54288
(KDGA_SACSO) -
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-phosphogluconate/2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phosphogalactonate aldolase from Saccharolobus solfataricus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
294 a.a.
293 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.4.1.2.55
- 2-dehydro-3-deoxy-phosphogluconate/2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phosphogalactonate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
|
1.
|
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phospho-D-gluconate = D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + pyruvate
|
|
2.
|
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phospho-D-galactonate = D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + pyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phospho-D-gluconate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 68.75% similarity
|
=
|
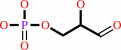 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
2-dehydro-3-deoxy-6-phospho-D-galactonate
|
=
|
 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
pyruvate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 41.67% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
279:43886-43892
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
The structural basis for substrate promiscuity in 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate aldolase from the Entner-Doudoroff pathway in Sulfolobus solfataricus.
|
|
A.Theodossis,
H.Walden,
E.J.Westwick,
H.Connaris,
H.J.Lamble,
D.W.Hough,
M.J.Danson,
G.L.Taylor.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The hyperthermophilic Archaea Sulfolobus solfataricus grows optimally above 80
degrees C and metabolizes glucose by a non-phosphorylative variant of the
Entner-Doudoroff pathway. In this pathway glucose dehydrogenase and gluconate
dehydratase catalyze the oxidation of glucose to gluconate and the subsequent
dehydration of gluconate to D-2-keto-3-deoxygluconate (KDG). KDG aldolase (KDGA)
then catalyzes the cleavage of KDG to D-glyceraldehyde and pyruvate. It has
recently been shown that all the enzymes of this pathway exhibit a catalytic
promiscuity that also enables them to be used for the metabolism of galactose.
This phenomenon, known as metabolic pathway promiscuity, depends crucially on
the ability of KDGA to cleave KDG and D-2-keto-3-deoxygalactonate (KDGal), in
both cases producing pyruvate and D-glyceraldehyde. In turn, the aldolase
exhibits a remarkable lack of stereoselectivity in the condensation reaction of
pyruvate and D-glyceraldehyde, forming a mixture of KDG and KDGal. We now report
the structure of KDGA, determined by multiwavelength anomalous diffraction
phasing, and confirm that it is a member of the tetrameric N-acetylneuraminate
lyase superfamily of Schiff base-forming aldolases. Furthermore, by soaking
crystals of the aldolase at more than 80 degrees C below its temperature
activity optimum, we have been able to trap Schiff base complexes of the natural
substrates pyruvate, KDG, KDGal, and pyruvate plus D-glyceraldehyde, which have
allowed rationalization of the structural basis of promiscuous substrate
recognition and catalysis. It is proposed that the active site of the enzyme is
rigid to keep its thermostability but incorporates extra functionality to be
promiscuous.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 3.
FIG. 3. S. solfataricus KGDA catalytic mechanism. Suggested
mechanism of KDGA based on that proposed for NAL, indicating the
ability of the enzyme to accept substrates that vary at both
stereocenters C-4 and C-5. Complexes trapped in this study are
shown in bold.
|
 |
Figure 4.
FIG. 4. Substrate-enzyme interactions. Schematic summary of
interactions made with the diastereomers KDG and KDGal.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2004,
279,
43886-43892)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
I.Campeotto,
A.H.Bolt,
T.A.Harman,
C.Dennis,
C.H.Trinh,
S.E.Phillips,
A.Nelson,
A.R.Pearson,
and
A.Berry
(2010).
Structural insights into substrate specificity in variants of N-acetylneuraminic Acid lyase produced by directed evolution.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
404,
56-69.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Reher,
T.Fuhrer,
M.Bott,
and
P.Schönheit
(2010).
The nonphosphorylative Entner-Doudoroff pathway in the thermoacidophilic euryarchaeon Picrophilus torridus involves a novel 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate- specific aldolase.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
192,
964-974.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
O.Khersonsky,
and
D.S.Tawfik
(2010).
Enzyme promiscuity: a mechanistic and evolutionary perspective.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
79,
471-505.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
I.Campeotto,
S.B.Carr,
C.H.Trinh,
A.S.Nelson,
A.Berry,
S.E.Phillips,
and
A.R.Pearson
(2009).
Structure of an Escherichia coli N-acetyl-D-neuraminic acid lyase mutant, E192N, in complex with pyruvate at 1.45 angstrom resolution.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
65,
1088-1090.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Wolterink-van Loo,
M.A.Siemerink,
G.Perrakis,
T.Kaper,
S.W.Kengen,
and
J.van der Oost
(2009).
Improving low-temperature activity of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate aldolase.
|
| |
Archaea,
2,
233-239.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Bolt,
A.Berry,
and
A.Nelson
(2008).
Directed evolution of aldolases for exploitation in synthetic organic chemistry.
|
| |
Arch Biochem Biophys,
474,
318-330.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Pauluhn,
H.Ahmed,
E.Lorentzen,
S.Buchinger,
D.Schomburg,
B.Siebers,
and
E.Pohl
(2008).
Crystal structure and stereochemical studies of KD(P)G aldolase from Thermoproteus tenax.
|
| |
Proteins,
72,
35-43.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.A.Potter,
M.Kerou,
H.J.Lamble,
S.D.Bull,
D.W.Hough,
M.J.Danson,
and
G.L.Taylor
(2008).
The structure of Sulfolobus solfataricus 2-keto-3-deoxygluconate kinase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
64,
1283-1287.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Manicka,
Y.Peleg,
T.Unger,
S.Albeck,
O.Dym,
H.M.Greenblatt,
G.Bourenkov,
V.Lamzin,
S.Krishnaswamy,
and
J.L.Sussman
(2008).
Crystal structure of YagE, a putative DHDPS-like protein from Escherichia coli K12.
|
| |
Proteins,
71,
2102-2108.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
T.J.Ettema,
H.Ahmed,
A.C.Geerling,
J.van der Oost,
and
B.Siebers
(2008).
The non-phosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPN) of Sulfolobus solfataricus: a key-enzyme of the semi-phosphorylative branch of the Entner-Doudoroff pathway.
|
| |
Extremophiles,
12,
75-88.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Kehrer,
H.Ahmed,
H.Brinkmann,
and
B.Siebers
(2007).
Glycerate kinase of the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermoproteus tenax: new insights into the phylogenetic distribution and physiological role of members of the three different glycerate kinase classes.
|
| |
BMC Genomics,
8,
301.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Shimada,
B.Mikami,
S.Watanabe,
and
K.Makino
(2007).
Preliminary crystallographic analysis of L-2-keto-3-deoxyarabonate dehydratase, an enzyme involved in an alternative bacterial pathway of L-arabinose metabolism.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
393-395.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.P.Kanaujia,
C.V.Ranjani,
J.Jeyakanthan,
M.Nishida,
Y.Kitamura,
S.Baba,
A.Ebihara,
N.Shimizu,
N.Nakagawa,
A.Shinkai,
M.Yamamoto,
S.Kuramitsu,
Y.Shiro,
K.Sekar,
and
S.Yokoyama
(2007).
Preliminary X-ray crystallographic study of glucose dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus HB8.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
63,
446-448.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Blagova,
V.Levdikov,
N.Milioti,
M.J.Fogg,
A.K.Kalliomaa,
J.A.Brannigan,
K.S.Wilson,
and
A.J.Wilkinson
(2006).
Crystal structure of dihydrodipicolinate synthase (BA3935) from Bacillus anthracis at 1.94 A resolution.
|
| |
Proteins,
62,
297-301.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
A.Theodossis,
C.C.Milburn,
N.I.Heyer,
H.J.Lamble,
D.W.Hough,
M.J.Danson,
and
G.L.Taylor
(2005).
Preliminary crystallographic studies of glucose dehydrogenase from the promiscuous Entner-Doudoroff pathway in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
61,
112-115.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Siebers,
and
P.Schönheit
(2005).
Unusual pathways and enzymes of central carbohydrate metabolism in Archaea.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
8,
695-705.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

