 |
PDBsum entry 1v7x

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of vibrio proteolyticus chitobiose phosphorylase in complex with glcnac and sulfate
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Chitobiose phosphorylase. Chain: a. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Vibrio proteolyticus. Organism_taxid: 671. Gene: chbp. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from PDB file)
Dimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.00Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.163
|
R-free:
|
0.195
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
M.Hidaka,Y.Honda,S.Nirasawa,M.Kitaoka,K.Hayashi,T.Wakagi,H.Shoun, S.Fushinobu
|
Key ref:

|
 |
M.Hidaka
et al.
(2004).
Chitobiose phosphorylase from Vibrio proteolyticus, a member of glycosyl transferase family 36, has a clan GH-L-like (alpha/alpha)(6) barrel fold.
Structure,
12,
937-947.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
24-Dec-03
|
Release date:
|
22-Jun-04
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q76IQ9
(CHBP_VIBPR) -
N,N'-diacetylchitobiose phosphorylase from Vibrio proteolyticus
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
801 a.a.
779 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.4.1.280
- N,N'-diacetylchitobiose phosphorylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
N,N'-diacetylchitobiose + phosphate = N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate + N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
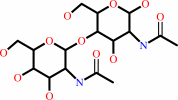 N,N'-diacetylchitobiose
N,N'-diacetylchitobiose
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
=
|
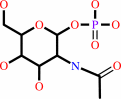 N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate
N-acetyl-alpha-D-glucosamine 1-phosphate
|
+
|
N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Structure
12:937-947
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Chitobiose phosphorylase from Vibrio proteolyticus, a member of glycosyl transferase family 36, has a clan GH-L-like (alpha/alpha)(6) barrel fold.
|
|
M.Hidaka,
Y.Honda,
M.Kitaoka,
S.Nirasawa,
K.Hayashi,
T.Wakagi,
H.Shoun,
S.Fushinobu.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Vibrio proteolyticus chitobiose phosphorylase (ChBP) belongs to glycosyl
transferase family 36 (GT-36), and catalyzes the reversible phosphorolysis of
chitobiose into alpha-GlcNAc-1-phosphate and GlcNAc with inversion of the
anomeric configuration. As the first known structures of a GT-36 enzyme, we
determined the crystal structure of ChBP in a ternary complex with GlcNAc and
SO(4). It is also the first structures of an inverting phosphorolytic enzyme in
a complex with a sugar and a sulfate ion, and reveals a pseudo-ternary complex
structure of enzyme-sugar-phosphate. ChBP comprises a beta sandwich domain and
an (alpha/alpha)(6) barrel domain, constituting a distinctive structure among GT
families. Instead, it shows significant structural similarity with glycoside
hydrolase (GH) enzymes, glucoamylases (GH-15), and maltose phosphorylase (GH-65)
in clan GH-L. The structural similarity reported here, together with distant
sequence similarities between ChBP and GHs, led to the reclassification of
family GT-36 into a novel GH family, namely GH-94.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. Ribbon Diagrams of ChBP and Related Structures(A)
Overall structure of the ChBP monomer (GlcNAc complex) shown as
a ribbon model (N-terminal domain, blue; linker helices, green;
a-helical barrel domain, yellow; C-terminal domain, red). The
bound GlcNAc molecules (red), P394, and I417 (yellow) are shown
as a ball-and-stick model, and the chloride (green) and calcium
(black) ions are shown as a sphere. Residues between P394 and
I417 are not included in the final model structure.(B) Ribbon
diagram presentation of the ChBP dimer. The subunits are located
around the crystallographic 2-fold axis. One subunit is colored
as in (A), and the other one is colored white.(C) A ribbon
diagram of bGA (1LF9; GH-15). Bacterial and archaeal
glucoamylases comprise an N-terminal b sandwich domain (blue),
linker helices (green), and an a-helical barrel domain (yellow),
whereas fungal glucoamylases comprise only an a-helical barrel
domain. The bound acarbose molecule (red) is shown as a
ball-and-stick model.(D) A ribbon diagram of MalP (1H54; GH-65).
The bound phosphate ion is shown as a ball-and-stick model. The
domain constitution is identical with that of ChBP and each
domain is colored as in (A).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figure is
reprinted
by permission from Cell Press:
Structure
(2004,
12,
937-947)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figure was
selected
by the author.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
G.Hai Tran,
T.Desmet,
M.R.De Groeve,
and
W.Soetaert
(2011).
Probing the active site of cellodextrin phosphorylase from Clostridium stercorarium: Kinetic characterization, ligand docking, and site-directed mutagenesis.
|
| |
Biotechnol Prog,
27,
326-332.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Luley-Goedl,
and
B.Nidetzky
(2010).
Carbohydrate synthesis by disaccharide phosphorylases: reactions, catalytic mechanisms and application in the glycosciences.
|
| |
Biotechnol J,
5,
1324-1338.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Fushinobu
(2010).
Unique sugar metabolic pathways of bifidobacteria.
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
74,
2374-2384.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hidaka,
M.Nishimoto,
M.Kitaoka,
T.Wakagi,
H.Shoun,
and
S.Fushinobu
(2009).
The Crystal Structure of Galacto-N-biose/Lacto-N-biose I Phosphorylase: A LARGE DEFORMATION OF A TIM BARREL SCAFFOLD.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
7273-7283.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Henrissat,
G.Sulzenbacher,
and
Y.Bourne
(2008).
Glycosyltransferases, glycoside hydrolases: surprise, surprise!
|
| |
Curr Opin Struct Biol,
18,
527-533.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.L.Lairson,
B.Henrissat,
G.J.Davies,
and
S.G.Withers
(2008).
Glycosyltransferases: structures, functions, and mechanisms.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
77,
521-555.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ravaud,
G.Stjepanovic,
K.Wild,
and
I.Sinning
(2008).
The crystal structure of the periplasmic domain of the Escherichia coli membrane protein insertase YidC contains a substrate binding cleft.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
9350-9358.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Honda,
H.Taniguchi,
and
M.Kitaoka
(2008).
A reducing-end-acting chitinase from Vibrio proteolyticus belonging to glycoside hydrolase family 19.
|
| |
Appl Microbiol Biotechnol,
78,
627-634.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nagae,
A.Tsuchiya,
T.Katayama,
K.Yamamoto,
S.Wakatsuki,
and
R.Kato
(2007).
Structural basis of the catalytic reaction mechanism of novel 1,2-alpha-L-fucosidase from Bifidobacterium bifidum.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
282,
18497-18509.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Nishimoto,
and
M.Kitaoka
(2007).
Identification of the putative proton donor residue of lacto-N-biose phosphorylase (EC 2.4.1.211).
|
| |
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem,
71,
1587-1591.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Kitaoka,
J.Tian,
and
M.Nishimoto
(2005).
Novel putative galactose operon involving lacto-N-biose phosphorylase in Bifidobacterium longum.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
71,
3158-3162.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hidaka,
M.Kitaoka,
K.Hayashi,
T.Wakagi,
H.Shoun,
and
S.Fushinobu
(2004).
Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of cellobiose phosphorylase from Cellvibrio gilvus.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
60,
1877-1878.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

