 |
PDBsum entry 1tzc

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 1:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.8
- mannose-6-phosphate isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
GDP-L-Fucose and GDP-mannose Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-mannose 6-phosphate = D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
D-mannose 6-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 82.35% similarity
|
=
|
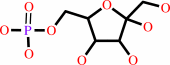 D-fructose 6-phosphate
D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Zn(2+)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class 2:
|
 |
E.C.5.3.1.9
- glucose-6-phosphate isomerase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate = beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-D-glucose 6-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 82.35% similarity
|
=
|
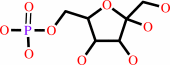 beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Note, where more than one E.C. class is given (as above), each may
correspond to a different protein domain or, in the case of polyprotein
precursors, to a different mature protein.
|
|
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Biol Chem
279:39838-39845
(2004)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
A novel phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI)/phosphomannose isomerase from the crenarchaeon Pyrobaculum aerophilum is a member of the PGI superfamily: structural evidence at 1.16-A resolution.
|
|
M.K.Swan,
T.Hansen,
P.Schönheit,
C.Davies.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The crystal structure of a dual specificity phosphoglucose isomerase
(PGI)/phosphomannose isomerase from Pyrobaculum aerophilum (PaPGI/PMI) has been
determined in native form at 1.16-A resolution and in complex with the enzyme
inhibitor 5-phosphoarabinonate at 1.45-A resolution. The similarity of its fold,
with the inner core structure of PGIs from eubacterial and eukaryotic sources,
confirms this enzyme as a member of the PGI superfamily. The almost total
conservation of amino acids in the active site, including the glutamate base
catalyst, shows that PaPGI/PMI uses the same catalytic mechanisms for both ring
opening and isomerization for the interconversion of glucose 6-phosphate
(Glc-6-P) to fructose 6-phosphate (Fru-6-P). The lack of structural differences
between native and inhibitor-bound enzymes suggests this activity occurs without
any of the conformational changes that are the hallmark of the well
characterized PGI family. The lack of a suitable second base in the active site
of PaPGI/PMI argues against a PMI mechanism involving a trans-enediol
intermediate. Instead, PMI activity may be the result of additional space in the
active site imparted by a threonine, in place of a glutamine in other PGI
enzymes, which could permit rotation of the C-2-C-3 bond of mannose 6-phosphate.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
FIG. 1. Fischer projections of the three substrates for
PGI/PMI from P. aerophilum, Glc-6-P, Fru-6-P, and Man-6-P, as
well as the PGI inhibitor used in this study, PAB.
|
 |
Figure 6.
FIG. 6. The structure of PGI/PMI from P. aerophilum in
complex with PAB at 1.45-Å resolution. a, a stereo view
showing PAB bound to the active site region. Shown is the active
site from subunit B but the contacts are essentially identical
in subunit A. The electron density shown around the inhibitor in
blue is an unbiased (|F[o]| -|F[c]|) difference map, calculated
from the final coordinates refined in the absence of ligand. The
side chains of those residues surrounding the ligand are shown
in bond form in which carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen are yellow,
red, and blue, respectively, except for His-219 which is colored
orange to indicate it is part of subunit A. PAB is colored with
green bonds. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. Important
contacts are shown as dashed lines. The figure was produced
using PYMOL (40). b, a diagram of the distances (in Å)
between atoms of PAB (colored green) and of amino acids in the
active site (colored black).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from the ASBMB:
J Biol Chem
(2004,
279,
39838-39845)
copyright 2004.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
C.Roux,
F.Bhatt,
J.Foret,
B.de Courcy,
N.Gresh,
J.P.Piquemal,
C.J.Jeffery,
and
L.Salmon
(2011).
The reaction mechanism of type I phosphomannose isomerases: new information from inhibition and polarizable molecular mechanics studies.
|
| |
Proteins,
79,
203-220.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
G.Gowda,
S.R.Sagurthi,
H.S.Savithri,
and
M.R.Murthy
(2008).
Cloning, expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of the mannose 6-phosphate isomerase from Salmonella typhimurium.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun,
64,
81-84.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
C.Roux,
N.Gresh,
L.E.Perera,
J.P.Piquemal,
and
L.Salmon
(2007).
Binding of 5-phospho-D-arabinonohydroxamate and 5-phospho-D-arabinonate inhibitors to zinc phosphomannose isomerase from Candida albicans studied by polarizable molecular mechanics and quantum mechanics.
|
| |
J Comput Chem,
28,
938-957.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Reher,
S.Gebhard,
and
P.Schönheit
(2007).
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate ferredoxin oxidoreductase (GAPOR) and nonphosphorylating glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPN), key enzymes of the respective modified Embden-Meyerhof pathways in the hyperthermophilic crenarchaeota Pyrobaculum aerophilum and Aeropyrum pernix.
|
| |
FEMS Microbiol Lett,
273,
196-205.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Seetharaman,
K.R.Rajashankar,
V.Solorzano,
R.Kniewel,
C.D.Lima,
J.B.Bonanno,
S.K.Burley,
and
S.Swaminathan
(2006).
Crystal structures of two putative phosphoheptose isomerases.
|
| |
Proteins,
63,
1092-1096.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
B.Siebers,
and
P.Schönheit
(2005).
Unusual pathways and enzymes of central carbohydrate metabolism in Archaea.
|
| |
Curr Opin Microbiol,
8,
695-705.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.Hansen,
B.Schlichting,
J.Grötzinger,
M.K.Swan,
C.Davies,
and
P.Schönheit
(2005).
Mutagenesis of catalytically important residues of cupin type phosphoglucose isomerase from Archaeoglobus fulgidus.
|
| |
FEBS J,
272,
6266-6275.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

