 |
PDBsum entry 1m32

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Transferase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of 2-aminoethylphosphonate transaminase
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
2-aminoethylphosphonate-pyruvate aminotransferase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: aep-transaminase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Salmonella typhimurium. Organism_taxid: 602. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dimer (from
)
Dimer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.166
|
R-free:
|
0.200
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
C.C.H.Chen,H.Zhang,A.D.Kim,A.Howard,G.M.Sheldrick,D.Mariano-Dunnaway, O.Herzberg
|
Key ref:

|
 |
C.C.Chen
et al.
(2002).
Degradation pathway of the phosphonate ciliatine: crystal structure of 2-aminoethylphosphonate transaminase.
Biochemistry,
41,
13162-13169.
PubMed id:
DOI:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
26-Jun-02
|
Release date:
|
20-Nov-02
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P96060
(PHNW_SALTY) -
2-aminoethylphosphonate--pyruvate transaminase from Salmonella typhimurium (strain LT2 / SGSC1412 / ATCC 700720)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
367 a.a.
361 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.6.1.37
- 2-aminoethylphosphonate--pyruvate transaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
(2-aminoethyl)phosphonate + pyruvate = phosphonoacetaldehyde + L-alanine
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 (2-aminoethyl)phosphonate
(2-aminoethyl)phosphonate
|
+
|
 pyruvate
pyruvate
|
=
|
phosphonoacetaldehyde
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
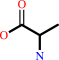 L-alanine
L-alanine
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
Bound ligand (Het Group name =
PLP)
matches with 87.50% similarity
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Biochemistry
41:13162-13169
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Degradation pathway of the phosphonate ciliatine: crystal structure of 2-aminoethylphosphonate transaminase.
|
|
C.C.Chen,
H.Zhang,
A.D.Kim,
A.Howard,
G.M.Sheldrick,
D.Mariano-Dunaway,
O.Herzberg.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Phosphonates allow certain organisms to thrive in otherwise hostile
environments, and 2-aminoethylphosphonate (AEP) is a precursor of many cellular
phosphonates. AEP transaminase (AEPT) is an enzyme essential to phosphonate
synthesis and degradation pathways. The crystal structure of AEP transaminase
was determined by multiwavelength anomalous diffraction of 66 selenium atoms.
The refined structure at 2.2 A resolution revealed an overall fold and active
site location similar to those of the dimeric, two-domain structure of type I
aminotransferases. The active site contains a cofactor, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
(PLP), and the product phosphonoacetaldehyde. Comparison with other type I
aminotransferase structures shows that the PLP-protein interactions are
conserved. Modeling of bound substrates and products reveals the structural
basis for AEP recognition and the stereospecificity of proton elimination at the
alpha-carbon and indicates conformational changes along the reaction pathway.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
N.S.Pannu,
W.J.Waterreus,
P.Skubák,
I.Sikharulidze,
J.P.Abrahams,
and
R.A.de Graaff
(2011).
Recent advances in the CRANK software suite for experimental phasing.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
67,
331-337.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Xu
(2010).
Enhancing MAD F(A) data for substructure determination.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
945-949.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Skubák,
W.J.Waterreus,
and
N.S.Pannu
(2010).
Multivariate phase combination improves automated crystallographic model building.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
783-788.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Terwilliger
(2010).
Rapid model building of alpha-helices in electron-density maps.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
268-275.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Terwilliger
(2010).
Rapid model building of beta-sheets in electron-density maps.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
276-284.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Terwilliger
(2010).
Rapid chain tracing of polypeptide backbones in electron-density maps.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
66,
285-294.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.I.Martínez-Gómez,
S.Martínez-Rodríguez,
J.Pozo-Dengra,
D.Tessaro,
S.Servi,
J.M.Clemente-Jiménez,
F.Rodríguez-Vico,
and
F.J.Las Heras-Vázquez
(2009).
Potential application of N-carbamoyl-beta-alanine amidohydrolase from Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 for beta-amino acid production.
|
| |
Appl Environ Microbiol,
75,
514-520.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Terwilliger,
P.D.Adams,
R.J.Read,
A.J.McCoy,
N.W.Moriarty,
R.W.Grosse-Kunstleve,
P.V.Afonine,
P.H.Zwart,
and
L.W.Hung
(2009).
Decision-making in structure solution using Bayesian estimates of map quality: the PHENIX AutoSol wizard.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
65,
582-601.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
W.W.Metcalf,
and
W.A.van der Donk
(2009).
Biosynthesis of phosphonic and phosphinic acid natural products.
|
| |
Annu Rev Biochem,
78,
65-94.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Xu,
and
C.M.Weeks
(2008).
Rapid and automated substructure solution by Shake-and-Bake.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
64,
172-177.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
Y.Yoshikane,
N.Yokochi,
M.Yamasaki,
K.Mizutani,
K.Ohnishi,
B.Mikami,
H.Hayashi,
and
T.Yagi
(2008).
Crystal structure of pyridoxamine-pyruvate aminotransferase from Mesorhizobium loti MAFF303099.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
283,
1120-1127.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Lima,
R.Khristoforov,
C.Momany,
and
R.S.Phillips
(2007).
Crystal structure of Homo sapiens kynureninase.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
2735-2744.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.S.Rizk,
M.J.Cuneo,
and
H.W.Hellinga
(2006).
Identification of cognate ligands for the Escherichia coli phnD protein product and engineering of a reagentless fluorescent biosensor for phosphonates.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
15,
1745-1751.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
H.Xu,
C.M.Weeks,
and
H.A.Hauptman
(2005).
Optimizing statistical Shake-and-Bake for Se-atom substructure determination.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
976-981.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Skubák,
S.Ness,
and
N.S.Pannu
(2005).
Extending the resolution and phase-quality limits in automated model building with iterative refinement.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1626-1635.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
T.C.Terwilliger
(2003).
Improving macromolecular atomic models at moderate resolution by automated iterative model building, statistical density modification and refinement.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
59,
1174-1182.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

