 |
PDBsum entry 1kfl

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Crystal structure of phenylalanine-regulated 3-deoxy-d-arabino- heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase (dahp synthase) from e.Coli complexed with mn2+, pep, and phe
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
3-deoxy-d-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h. Synonym: phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase, phe-sensitive. Dahp synthetase, phenylalanine repressible. Phospho-2-keto-3- deoxyheptonate aldolase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Gene: arog. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from
)
Tetramer (from
)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.80Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.218
|
R-free:
|
0.246
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
I.A.Shumilin,C.Zhao,R.Bauerle,R.H.Kretsinger
|
Key ref:

|
 |
I.A.Shumilin
et al.
(2002).
Allosteric inhibition of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase alters the coordination of both substrates.
J Mol Biol,
320,
1147-1156.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
21-Nov-01
|
Release date:
|
23-Aug-02
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0AB91
(AROG_ECOLI) -
Phospho-2-dehydro-3-deoxyheptonate aldolase, Phe-sensitive from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
350 a.a.
350 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.2.5.1.54
- 3-deoxy-7-phosphoheptulonate synthase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Shikimate and Chorismate Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-erythrose 4-phosphate + phosphoenolpyruvate + H2O = 7-phospho-2- dehydro-3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptonate + phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
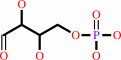 D-erythrose 4-phosphate
D-erythrose 4-phosphate
|
+
|
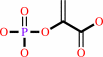 phosphoenolpyruvate
phosphoenolpyruvate
|
+
|
H2O
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
=
|
7-phospho-2- dehydro-3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptonate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
320:1147-1156
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Allosteric inhibition of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase alters the coordination of both substrates.
|
|
I.A.Shumilin,
C.Zhao,
R.Bauerle,
R.H.Kretsinger.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
3-Deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase (DAHPS), the first enzyme
of the aromatic biosynthetic pathway in microorganisms and plants, catalyzes the
aldol-like condensation of phosphoenolpyruvate and D-erythrose-4-phosphate with
the formation of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate. In Escherichia
coli, there are three isoforms of DAHPS, each specifically feedback-regulated by
one of the three aromatic amino acid end products. The crystal structure of the
phenylalanine-regulated DAHPS from E.coli in complex with its inhibitor,
L-phenylalanine, phosphoenolpyruvate, and metal cofactor, Mn(2+), has been
determined to 2.8A resolution. Phe binds in a cavity formed by residues of two
adjacent subunits and is located about 20A from the closest active site. A model
for the mechanism of allosteric inhibition has been derived from conformational
differences between the Phe-bound and previously determined Phe-free structures.
Two interrelated paths of conformational changes transmit the inhibitory signal
from the Phe-binding site to the active site of DAHPS. The first path involves
transmission within a single subunit due to the movement of adjacent segments of
the protein. The second involves alterations in the contacts between subunits.
The combination of these two paths changes the conformation of one of the active
site loops significantly and shifts the other slightly. This alters the
interaction of DAHPS with both of its substrates. Upon binding of Phe, the
enzyme loses the ability to bind D-erythrose-4-phosphate and binds
phosphoenolpyruvate in a flipped orientation.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 1.
Figure 1. The DAHPS*Mn*PEP*Phe tetramer. (a) One of two
nearly identical +Phe tetramers in the asymmetric unit. Each of
the tight dimers forming the tetramer (AB and CD) consists of a
green and a purple subunit. The eight strands of the (b/a)[8]
barrel are blue in all subunits. Mn2+ (cyan) and PEP (gold) are
at the C-end of the barrel. Bound Phe (gold) is near the
inter-subunit b6a/b6b/b0^* sheets. The orange square outlines
the area represented in (b), which shows the superposition of
Leu16 and the Trp215-Gly216-His217 segments of four subunits of
-Phe (gray) and +Phe (same color as in (a)). The 222 symmetry of
the -Phe enzyme is reduced to 2-fold symmetry in the +Phe
enzyme. H-bonds formed in +Phe DAHPS are shown as light blue
dotted lines. All figures were drawn with RIBBONS.[15]
|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. Flipping of PEP in the active site of DAHPS upon
Phe binding. The PEP coordinating sphere shown in the same
orientation in (a) -Phe and (b) +Phe DAHPS. H-bonds, shown as
dotted lines, are in the range of 2.8-3.3 Å. In both
forms, PEP also has p,p interaction with the imidazole ring of
His268. The thin gray trace in (b) represents superimposed PEP
from (a). Non-coordinating Lys97 and Arg165 (two conformers) are
shown in (b).
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2002,
320,
1147-1156)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Wu,
and
R.W.Woodard
(2006).
New insights into the evolutionary links relating to the 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate synthase subfamilies.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
4042-4048.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Helmstaedt,
A.Strittmatter,
W.N.Lipscomb,
and
G.H.Braus
(2005).
Evolution of 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase-encoding genes in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
102,
9784-9789.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Wu,
D.L.Howe,
and
R.W.Woodard
(2003).
Thermotoga maritima 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate 7-phosphate (DAHP) synthase: the ancestral eubacterial DAHP synthase?
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
278,
27525-27531.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
M.Hartmann,
T.R.Schneider,
A.Pfeil,
G.Heinrich,
W.N.Lipscomb,
and
G.H.Braus
(2003).
Evolution of feedback-inhibited beta /alpha barrel isoenzymes by gene duplication and a single mutation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
100,
862-867.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
code is
shown on the right.
|
 |

