 |
PDBsum entry 1ibv

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Lyase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Structure of the d53,54n mutant of histidine decarboxylase bound with histidine methyl ester at-170 c
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Histidine decarboxylase beta chain. Chain: a, c, e. Fragment: beta chain (residues 1-81). Engineered: yes. Mutation: yes. Histidine decarboxylase alpha chain. Chain: b, d, f. Fragment: alpha chain (residues 82-310). Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Lactobacillus sp. 30a. Organism_taxid: 1593. Strain: 30a. Gene: hdca. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Dodecamer (from PDB file)
Dodecamer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.50Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.243
|
R-free:
|
0.279
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Worley,E.Schelp,A.F.Monzingo,S.Ernst,J.D.Robertus
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Worley
et al.
(2002).
Structure and cooperativity of a T-state mutant of histidine decarboxylase from Lactobacillus 30a.
Proteins,
46,
321-329.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
29-Mar-01
|
Release date:
|
13-Mar-02
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
Chains A, B, C, D, E, F:
E.C.4.1.1.22
- histidine decarboxylase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
L-histidine + H+ = histamine + CO2
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
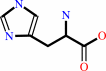 L-histidine
L-histidine
|
+
|
H(+)
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
matches with 91.67% similarity
|
=
|
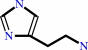 histamine
histamine
|
+
|
 CO2
CO2
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Cofactor:
|
 |
Pyruvate or pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 Pyruvate
Pyruvate
|
or
|
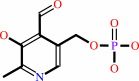 pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
pyridoxal 5'-phosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
Proteins
46:321-329
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structure and cooperativity of a T-state mutant of histidine decarboxylase from Lactobacillus 30a.
|
|
S.Worley,
E.Schelp,
A.F.Monzingo,
S.Ernst,
J.D.Robertus.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Histidine decarboxylase (HDC) from Lactobacillus 30a converts histidine to
histamine, a process that enables the bacteria to maintain the optimum pH range
for cell growth. HDC is regulated by pH; it is active at low pH and inactive at
neutral to alkaline pH. The X-ray structure of HDC at pH 8 revealed that a helix
was disordered, resulting in the disruption of the substrate-binding site. The
HDC trimer has also been shown to exhibit cooperative kinetics at neutral pH,
that is, histidine can trigger a T-state to R-state transition. The D53,54N
mutant of HDC has an elevated Km, even at low pH, indicating that the enzyme
assumes the low activity T-state. We have solved the structures of the D53,54N
mutant at low pH, with and without the substrate analog histidine methyl ester
(HME) bound. Structural analysis shows that the apo-D53,54N mutant is in the
inactive or T-state and that binding of the substrate analog induces the enzyme
to adopt the active or R-state. A mechanism for the cooperative transition is
proposed.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Binding of HME in the active site of the D53,54N
mutant of HDC. Residues from the right-hand monomer of the
molecular interface are labeled with (  ).
The pyruvoyl moiety (PVL) is part of the left-hand monomer and
is shown bonded to HME. Hydrogen bonds are drawn with dashed
lines. ).
The pyruvoyl moiety (PVL) is part of the left-hand monomer and
is shown bonded to HME. Hydrogen bonds are drawn with dashed
lines.
|
 |
Figure 4.
Figure 4. Superposition of the wild-type pH 8 (T-state) and pH
4.8 (R-state) models at the molecular interface shows how the
change in the position of residue E227 affects its interaction
with R64  .
The pH 8 model is shown with light bonds and pH 4.8 model with
dark bonds. In the R-state model, E227 forms ion pair
interactions across the molecular interface with R48 .
The pH 8 model is shown with light bonds and pH 4.8 model with
dark bonds. In the R-state model, E227 forms ion pair
interactions across the molecular interface with R48  and
R64 and
R64  .
R64 .
R64  also
forms an interaction with D231. In the T state, interactions
with E227 are not observed. R64 also
forms an interaction with D231. In the T state, interactions
with E227 are not observed. R64  only
interacts with D231, and R48 only
interacts with D231, and R48  is
disordered. is
disordered.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from John Wiley & Sons, Inc.:
Proteins
(2002,
46,
321-329)
copyright 2002.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
D.E.Graham,
H.Xu,
and
R.H.White
(2002).
Methanococcus jannaschii uses a pyruvoyl-dependent arginine decarboxylase in polyamine biosynthesis.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
277,
23500-23507.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
|
 |
|

