 |
PDBsum entry 1i32

|
|
|

|
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
 |

|

|

|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
Oxidoreductase
|
PDB id
|
|

|

|
1i32
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Oxidoreductase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Leishmania mexicana glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase in complex with inhibitors
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase. Chain: a, b, c, d, e, f. Synonym: gapdh. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Leishmania mexicana. Organism_taxid: 5665. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Tetramer (from PDB file)
Tetramer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.60Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.205
|
R-free:
|
0.256
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
S.Suresh,J.C.Bressi,K.J.Kennedy,C.L.M.J.Verlinde,M.H.Gelb,W.G.J.Hol
|
Key ref:

|
 |
S.Suresh
et al.
(2001).
Conformational changes in Leishmania mexicana glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase induced by designed inhibitors.
J Mol Biol,
309,
423-435.
PubMed id:
DOI:

|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
12-Feb-01
|
Release date:
|
03-Oct-01
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
Q27890
(G3PG_LEIME) -
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, glycosomal from Leishmania mexicana
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
361 a.a.
358 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.1.2.1.12
- glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (phosphorylating).
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase (phosphorylating)
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate + phosphate + NAD+ = (2R)-3-phospho- glyceroyl phosphate + NADH + H+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
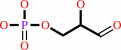 D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
|
+
|
 phosphate
phosphate
|
+
|
 NAD(+)
NAD(+)
|
=
|
(2R)-3-phospho- glyceroyl phosphate
|
+
|
 NADH
NADH
|
+
|
H(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
309:423-435
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Conformational changes in Leishmania mexicana glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase induced by designed inhibitors.
|
|
S.Suresh,
J.C.Bressi,
K.J.Kennedy,
C.L.Verlinde,
M.H.Gelb,
W.G.Hol.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
The glycolytic enzymes of trypanosomes are attractive drug targets, since the
blood-stream form of Trypanosoma brucei lacks a functional citric acid cycle and
is dependent solely on glycolysis for its energy requirements.
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases (GAPDH) from the pathogenic
trypanosomatids T. brucei, Trypanosoma cruzi and Leishmania mexicana are quite
similar to each other, and yet have sufficient structural differences compared
to the human enzyme to enable the structure-based design of compounds that
selectively inhibit all three trypanosomatid enzymes but not the human
homologue.Adenosine analogs with substitutions on N-6 of the adenine ring and on
the 2' position of the ribose moiety were designed, synthesized and tested for
inhibition. Two crystal structures of L. mexicana glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
dehydrogenase in complex with high-affinity inhibitors that also block parasite
growth were solved at a resolution of 2.6 A and 3.0 A. The complexes
crystallized in the same crystal form, with one and a half tetramers in the
crystallographic asymmetric unit. There is clear electron density for the
inhibitor in all six copies of the binding site in each of the two structures.
The L. mexicana GAPDH subunit exhibits substantial structural plasticity upon
binding the inhibitor. Movements of the protein backbone, in response to
inhibitor binding, enlarge a cavity at the binding site to accommodate the
inhibitor in a classic example of induced fit. The extensive hydrophobic
interactions between the protein and the two substituents on the adenine
scaffold of the inhibitor provide a plausible explanation for the high affinity
of these inhibitors for trypanosomatid GAPDHs.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 2.
Figure 2.
(a) Model-unbiased 6-fold averaged 2F
o
-
F
c
map of NMDBA bound to L. mexicana GAPDH at 2.6 A
Ê
con-
toured at 0.82s to within 2.0 A
Ê
of NMDBA atoms. The map was calculated after refining the six protein monomers
in the asymmetric unit and prior to modeling in the bound inhibitor (NMDBA, gold C atoms). In (a)-(d) residues in
green and violet are from adjacent monomers of the biological tetramer. (b) Model-unbiased sixfold averaged 2F
o
-
F
c
map of TNDBA bound to L. mexicana GAPDH at 3.0 A
Ê
, contoured at 0.82s to within 2.0 A
Ê
of TNDBA atoms.
(a) and (b) were made with Bobscript.
41
(c) Superposition of the six copies of the bound inhibitor NMDBA (gold C
atoms), in the crystal structure in complex with L. mexicana GAPDH. The 358 C
a
atoms of each monomer were used
in the superposition. (d) Superposition of the crystal structures of L. mexicana GAPDH in complex with NMDBA
(gold) and the structure in complex with TNDBA (grey). (c) and (d) Created with MOLSCRIPT
38
and Raster3D.
39,40
|
 |
Figure 3.
Figure 3. (a) Schematic drawn by LIGPLOT
42
showing interactions of NMDBA with L. mexicana GAPDH. (b) Sche-
matic drawn by LIGPLOT
42
showing interactions of TNDBA with L. mexicana GAPDH.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2001,
309,
423-435)
copyright 2001.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
J.Frayne,
A.Taylor,
G.Cameron,
and
A.T.Hadfield
(2009).
Structure of insoluble rat sperm glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) via heterotetramer formation with Escherichia coli GAPDH reveals target for contraceptive design.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
284,
22703-22712.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
W.J.Cook,
O.Senkovich,
and
D.Chattopadhyay
(2009).
An unexpected phosphate binding site in glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase: crystal structures of apo, holo and ternary complex of Cryptosporidium parvum enzyme.
|
| |
BMC Struct Biol,
9,
9.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.Goyal,
and
S.C.Mande
(2008).
Exploiting 3D structural templates for detection of metal-binding sites in protein structures.
|
| |
Proteins,
70,
1206-1218.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Ferreira-da-Silva,
P.J.Pereira,
L.Gales,
M.Roessle,
D.I.Svergun,
P.Moradas-Ferreira,
and
A.M.Damas
(2006).
The crystal and solution structures of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase reveal different quaternary structures.
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
281,
33433-33440.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.L.Jenkins,
and
J.J.Tanner
(2006).
High-resolution structure of human D-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
62,
290-301.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.A.Robien,
J.Bosch,
F.S.Buckner,
W.C.Van Voorhis,
E.A.Worthey,
P.Myler,
C.Mehlin,
E.E.Boni,
O.Kalyuzhniy,
L.Anderson,
A.Lauricella,
S.Gulde,
J.R.Luft,
G.DeTitta,
J.M.Caruthers,
K.O.Hodgson,
M.Soltis,
F.Zucker,
C.L.Verlinde,
E.A.Merritt,
L.W.Schoenfeld,
and
W.G.Hol
(2006).
Crystal structure of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Plasmodium falciparum at 2.25 A resolution reveals intriguing extra electron density in the active site.
|
| |
Proteins,
62,
570-577.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
J.F.Satchell,
R.L.Malby,
C.S.Luo,
A.Adisa,
A.E.Alpyurek,
N.Klonis,
B.J.Smith,
L.Tilley,
and
P.M.Colman
(2005).
Structure of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Plasmodium falciparum.
|
| |
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
61,
1213-1221.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Ladame,
R.Fauré,
C.Denier,
F.Lakhdar-Ghazal,
and
M.Willson
(2005).
Selective inhibition of Trypanosoma cruzi GAPDH by "bi-substrate" analogues.
|
| |
Org Biomol Chem,
3,
2070-2072.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.J.Teague
(2003).
Implications of protein flexibility for drug discovery.
|
| |
Nat Rev Drug Discov,
2,
527-541.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Choe,
S.Suresh,
G.Wisedchaisri,
K.J.Kennedy,
M.H.Gelb,
and
W.G.Hol
(2002).
Anomalous differences of light elements in determining precise binding modes of ligands to glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
|
| |
Chem Biol,
9,
1189-1197.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

