 |
PDBsum entry 1fs6

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|

|
|
PDB id:
|
 |
|
 |
| Name: |
 |
Isomerase
|
 |
|
Title:
|
 |
Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase from e.Coli, t conformer, at 2.2a resolution
|
|
Structure:
|
 |
Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase. Chain: a. Synonym: glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase, gnpda, glcn6p deaminase. Engineered: yes
|
|
Source:
|
 |
Escherichia coli. Organism_taxid: 562. Expressed in: escherichia coli. Expression_system_taxid: 562.
|
|
Biol. unit:
|
 |
 Trimer (from PDB file)
Trimer (from PDB file)
|
|
Resolution:
|
 |
|
2.20Å
|
R-factor:
|
0.214
|
R-free:
|
0.235
|
|
|
Authors:
|
 |
E.Rudino-Pinera,S.Morales-Arrieta,S.P.Rojas-Trejo,E.Horjales
|
Key ref:

|
 |
E.Rudiño-Piñera
et al.
(2002).
Structural flexibility, an essential component of the allosteric activation in Escherichia coli glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase.
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr,
58,
10-20.
PubMed id:
|
 |
|
Date:
|
 |
|
08-Sep-00
|
Release date:
|
04-Jan-02
|
|
|

|

|
|
PROCHECK
|

|

|
|
|
Headers
|
 |
|
|
References
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
P0A759
(NAGB_ECOLI) -
Glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase from Escherichia coli (strain K12)
|
|

|

|
Seq:
Struc:
|
 |
 |
 |
266 a.a.
266 a.a.
|

|

|

|

|
|

|

|

|
 |
 |

|
|
Key: |
 |
PfamA domain |
 |
 |
 |
Secondary structure |
 |
 |
CATH domain |
 |
|

|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.3.5.99.6
- glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

Pathway:
|
 |
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine Biosynthesis
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
alpha-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate + H2O = beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate + NH4+
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
alpha-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate
|
+
|
H2O
|
=
|
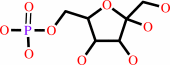 beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
beta-D-fructose 6-phosphate
|
+
|
NH4(+)
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr
58:10-20
(2002)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
Structural flexibility, an essential component of the allosteric activation in Escherichia coli glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase.
|
|
E.Rudiño-Piñera,
S.Morales-Arrieta,
S.P.Rojas-Trejo,
E.Horjales.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
A new crystallographic structure of the free active-site R conformer of the
allosteric enzyme glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase from Escherichia coli,
coupled with previously reported structures of the T and R conformers, generates
a detailed description of the heterotropic allosteric transition in which
structural flexibility plays a central role. The T conformer's external zone
[Horjales et al. (1999), Structure, 7, 527-536] presents higher B values than in
the R conformers. The ligand-free enzyme (T conformer) undergoes an allosteric
transition to the free active-site R conformer upon binding of the allosteric
activator. This structure shows three alternate conformations of the mobile
section of the active-site lid (residues 163-182), in comparison to the high B
values for the unique conformation of the T conformer. One of these alternate R
conformations corresponds to the active-site lid found when the substrate is
bound. The disorder associated with the three alternate conformations can be
related to the biological regulation of the K(m) of the enzyme for the reaction,
which is metabolically required to maintain adequate concentrations of the
activator, which holds the enzyme in its R state. Seven alternate conformations
for the active-site lid and three for the C-terminus were refined for the T
structure using isotropic B factors. Some of these conformers approach that of
the R conformer in geometry. Furthermore, the direction of the atomic vibrations
obtained with anisotropic B refinement supports the hypothesis of an oscillating
rather than a tense T state. The concerted character of the allosteric
transition is also analysed in view of the apparent dynamics of the conformers.

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
R.Alterovitz,
A.Arvey,
S.Sankararaman,
C.Dallett,
Y.Freund,
and
K.Sjölander
(2009).
ResBoost: characterizing and predicting catalytic residues in enzymes.
|
| |
BMC Bioinformatics,
10,
197.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
P.Rezácová,
M.Kozísek,
S.F.Moy,
I.Sieglová,
A.Joachimiak,
M.Machius,
and
Z.Otwinowski
(2008).
Crystal structures of the effector-binding domain of repressor Central glycolytic gene Regulator from Bacillus subtilis reveal ligand-induced structural changes upon binding of several glycolytic intermediates.
|
| |
Mol Microbiol,
69,
895-910.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
S.Zorrilla,
T.Doan,
C.Alfonso,
E.Margeat,
A.Ortega,
G.Rivas,
S.Aymerich,
C.A.Royer,
and
N.Declerck
(2007).
Inducer-modulated cooperative binding of the tetrameric CggR repressor to operator DNA.
|
| |
Biophys J,
92,
3215-3227.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
F.Vincent,
G.J.Davies,
and
J.A.Brannigan
(2005).
Structure and kinetics of a monomeric glucosamine 6-phosphate deaminase: missing link of the NagB superfamily?
|
| |
J Biol Chem,
280,
19649-19655.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
L.I.Alvarez-Añorve,
M.L.Calcagno,
and
J.Plumbridge
(2005).
Why does Escherichia coli grow more slowly on glucosamine than on N-acetylglucosamine? Effects of enzyme levels and allosteric activation of GlcN6P deaminase (NagB) on growth rates.
|
| |
J Bacteriol,
187,
2974-2982.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Linding,
R.B.Russell,
V.Neduva,
and
T.J.Gibson
(2003).
GlobPlot: Exploring protein sequences for globularity and disorder.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
31,
3701-3708.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

