 |
PDBsum entry 1f4l

|

|

|
|
 |
Contents |
 |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Residue conservation analysis
|
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Enzyme class:
|
 |
E.C.6.1.1.10
- methionine--tRNA ligase.
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Reaction:
|
 |
tRNA(Met) + L-methionine + ATP = L-methionyl-tRNA(Met) + AMP + diphosphate
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
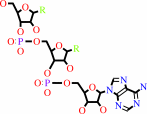 tRNA(Met)
tRNA(Met)
|
+
|
L-methionine
Bound ligand (Het Group name = )
corresponds exactly
|
+
|
 ATP
ATP
|
=
|
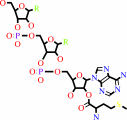 L-methionyl-tRNA(Met)
L-methionyl-tRNA(Met)
|
+
|
 AMP
AMP
|
+
|
 diphosphate
diphosphate
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Molecule diagrams generated from .mol files obtained from the
KEGG ftp site
|
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |

|

|

|
| |
|
|
| |
|
DOI no:
|
J Mol Biol
306:863-876
(2001)
|
|
PubMed id:
|
|
|
|

|
| |
|
How methionyl-tRNA synthetase creates its amino acid recognition pocket upon L-methionine binding.
|
|
L.Serre,
G.Verdon,
T.Choinowski,
N.Hervouet,
J.L.Risler,
C.Zelwer.
|
|
|

|
| |
ABSTRACT
|
|

|
| |

|
Amino acid selection by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases requires efficient mechanisms
to avoid incorrect charging of the cognate tRNAs. A proofreading mechanism
prevents Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA synthetase (EcMet-RS) from activating
in vivo L-homocysteine, a natural competitor of L-methionine recognised by the
enzyme. The crystal structure of the complex between EcMet-RS and L-methionine
solved at 1.8 A resolution exhibits some conspicuous differences with the
recently published free enzyme structure. Thus, the methionine delta-sulphur
atom replaces a water molecule H-bonded to Leu13N and Tyr260O(eta) in the free
enzyme. Rearrangements of aromatic residues enable the protein to form a
hydrophobic pocket around the ligand side-chain. The subsequent formation of an
extended water molecule network contributes to relative displacements, up to 3
A, of several domains of the protein. The structure of this complex supports a
plausible mechanism for the selection of L-methionine versus L-homocysteine and
suggests the possibility of information transfer between the different
functional domains of the enzyme.

|

|
|
|

|
| |
Selected figure(s)
|
|

|
| |
 |
 |

|
 |

|
 |
Figure 6.
Figure 6. Conformational changes in the area of helix aE
and strand b5 with ball-and-stick representation for the
complexed and free protein. The native protein is shown green
and the complex is red.
|
 |
Figure 8.
Figure 8. Superimposition of the a-carbon backbones of the
anticodon recognition domain for the free and the complexed
Met-RS. The colour code is the same as that used in Figure 7.
|
 |
|
|

|
| |
The above figures are
reprinted
by permission from Elsevier:
J Mol Biol
(2001,
306,
863-876)
copyright 2001.
|
|
| |
Figures were
selected
by an automated process.
|
|

|

|
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Literature references that cite this PDB file's key reference
|
|
 |
| |
PubMed id
|
 |
Reference
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
H.Ingvarsson,
and
T.Unge
(2010).
Flexibility and communication within the structure of the Mycobacterium smegmatis methionyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
FEBS J,
277,
3947-3962.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
E.Schmitt,
I.C.Tanrikulu,
T.H.Yoo,
M.Panvert,
D.A.Tirrell,
and
Y.Mechulam
(2009).
Switching from an induced-fit to a lock-and-key mechanism in an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase with modified specificity.
|
| |
J Mol Biol,
394,
843-851.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
I.C.Tanrikulu,
E.Schmitt,
Y.Mechulam,
W.A.Goddard,
and
D.A.Tirrell
(2009).
Discovery of Escherichia coli methionyl-tRNA synthetase mutants for efficient labeling of proteins with azidonorleucine in vivo.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
106,
15285-15290.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
N.Shen,
M.Zhou,
B.Yang,
Y.Yu,
X.Dong,
and
J.Ding
(2008).
Catalytic mechanism of the tryptophan activation reaction revealed by crystal structures of human tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase in different enzymatic states.
|
| |
Nucleic Acids Res,
36,
1288-1299.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
M.E.Budiman,
M.H.Knaggs,
J.S.Fetrow,
and
R.W.Alexander
(2007).
Using molecular dynamics to map interaction networks in an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Proteins,
68,
670-689.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
R.Sathyapriya,
and
S.Vishveshwara
(2007).
Structure networks of E. coli glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase: effects of ligand binding.
|
| |
Proteins,
68,
541-550.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
S.W.Lue,
and
S.O.Kelley
(2007).
A single residue in leucyl-tRNA synthetase affecting amino acid specificity and tRNA aminoacylation.
|
| |
Biochemistry,
46,
4466-4472.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
A.J.Link,
M.K.Vink,
N.J.Agard,
J.A.Prescher,
C.R.Bertozzi,
and
D.A.Tirrell
(2006).
Discovery of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase activity through cell-surface display of noncanonical amino acids.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
103,
10180-10185.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
J.Roach,
S.Sharma,
M.Kapustina,
and
C.W.Carter
(2005).
Structure alignment via Delaunay tetrahedralization.
|
| |
Proteins,
60,
66-81.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
U.A.Ochsner,
C.L.Young,
K.C.Stone,
F.B.Dean,
N.Janjic,
and
I.A.Critchley
(2005).
Mode of action and biochemical characterization of REP8839, a novel inhibitor of methionyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Antimicrob Agents Chemother,
49,
4253-4262.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
D.Datta,
N.Vaidehi,
D.Zhang,
and
W.A.Goddard
(2004).
Selectivity and specificity of substrate binding in methionyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Protein Sci,
13,
2693-2705.
|
 |
|
|
|
|
 |
L.D.Sherlin,
and
J.J.Perona
(2003).
tRNA-dependent active site assembly in a class I aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
Structure,
11,
591-603.
|
 |
|
PDB code:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.J.Newberry,
Y.M.Hou,
and
J.J.Perona
(2002).
Structural origins of amino acid selection without editing by cysteinyl-tRNA synthetase.
|
| |
EMBO J,
21,
2778-2787.
|
 |
|
PDB codes:
|
 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
K.L.Kiick,
E.Saxon,
D.A.Tirrell,
and
C.R.Bertozzi
(2002).
Incorporation of azides into recombinant proteins for chemoselective modification by the Staudinger ligation.
|
| |
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,
99,
19-24.
|
 |
|
 |
 |
|
The most recent references are shown first.
Citation data come partly from CiteXplore and partly
from an automated harvesting procedure. Note that this is likely to be
only a partial list as not all journals are covered by
either method. However, we are continually building up the citation data
so more and more references will be included with time.
Where a reference describes a PDB structure, the PDB
codes are
shown on the right.
|
 |

